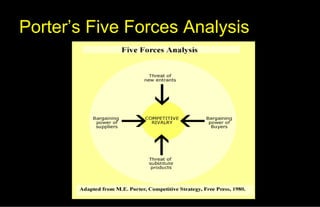
The CSD (carbonated soft drink) industry is dominated by two major players, Coca-Cola and Pepsi, which have high brand identity and reputation. The industry has high barriers to entry due to large capital requirements and faces strong competition between the major brands. Threats of substitution are moderate as customers have many beverage options but low inclination to switch brands. Supplier power is weak due to many ingredient providers, while some large buyers have bargaining power over the brands. The bottling industry serving CSD brands also has high barriers to entry, concentration among a few major players, and threats of substitution from alternative packaging types. Both industries have potential challenges from market saturation and competitive strategies of the major brands.