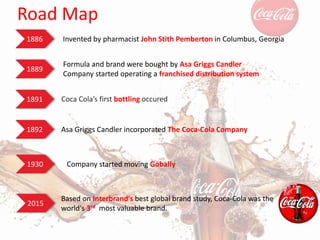
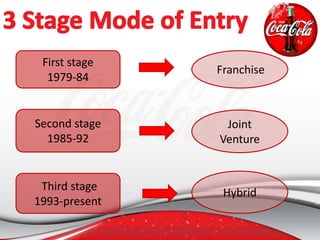
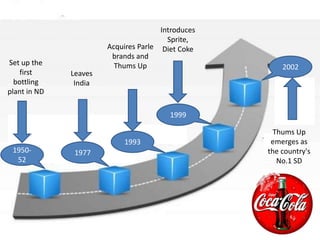
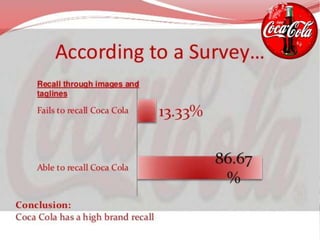
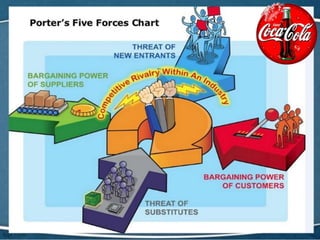
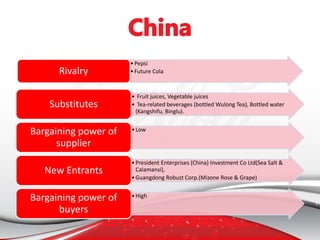
Coca-Cola entered the Chinese market in the 1920s and established several bottling plants before withdrawing in 1949. In 1978, China adopted an open door policy and Coca-Cola re-entered China in 1979, first using a franchise model and later transitioning to joint ventures. Coca-Cola has since grown its operations and market share in China through strategic marketing, product innovation, and adapting to Chinese culture and consumer preferences. However, the company also faces challenges from regulations, competition, and changing consumer trends in China.