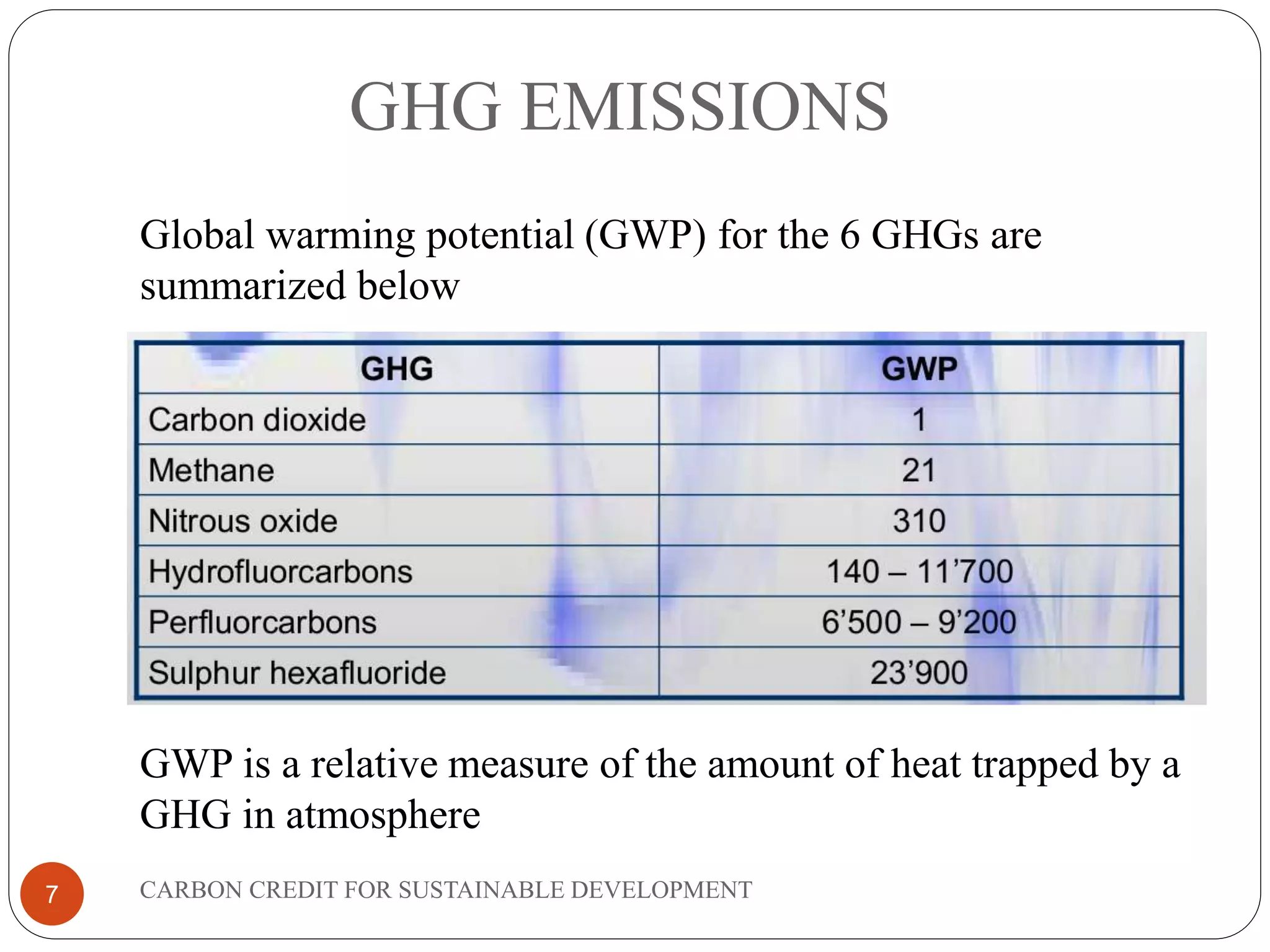
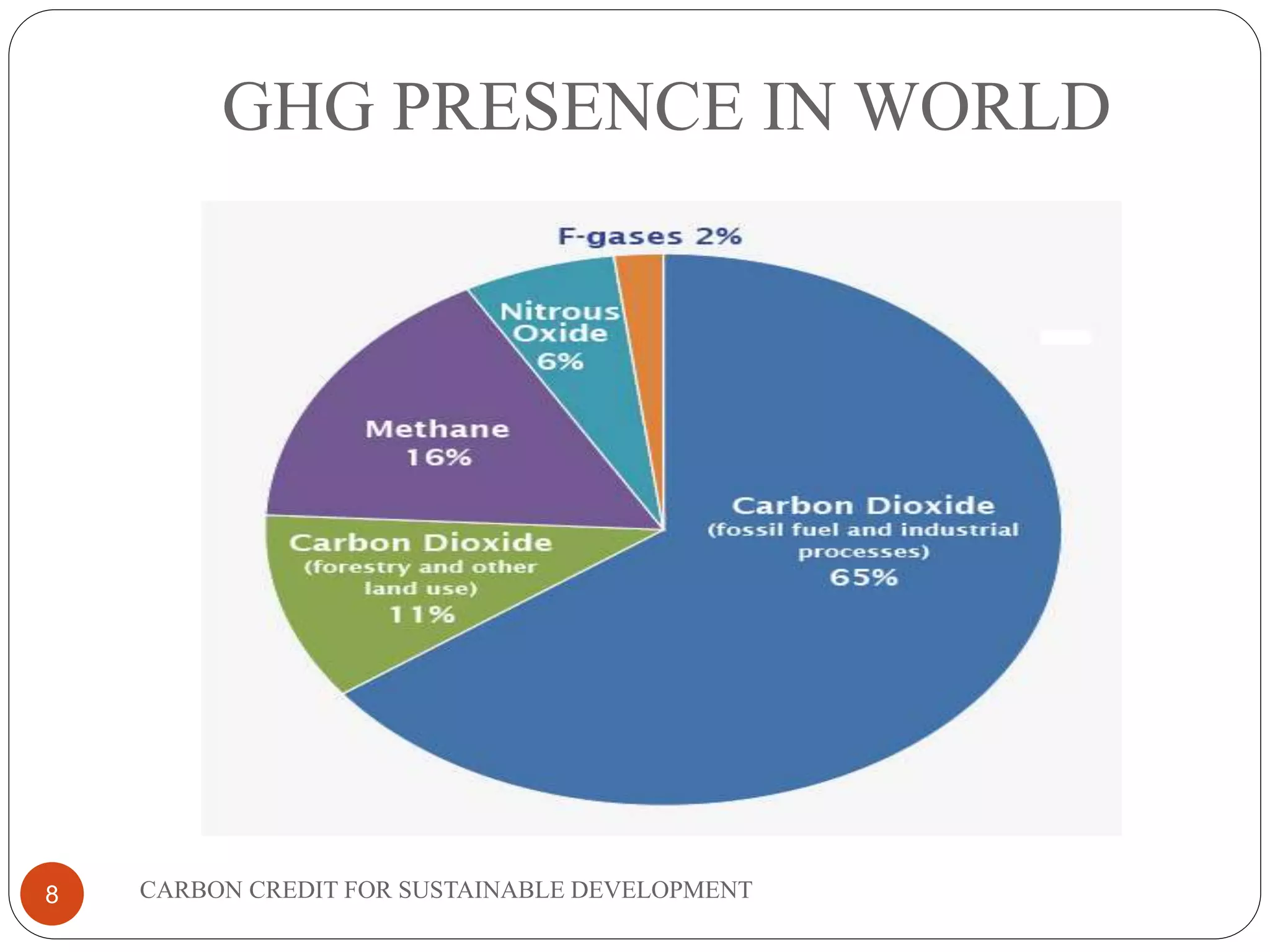
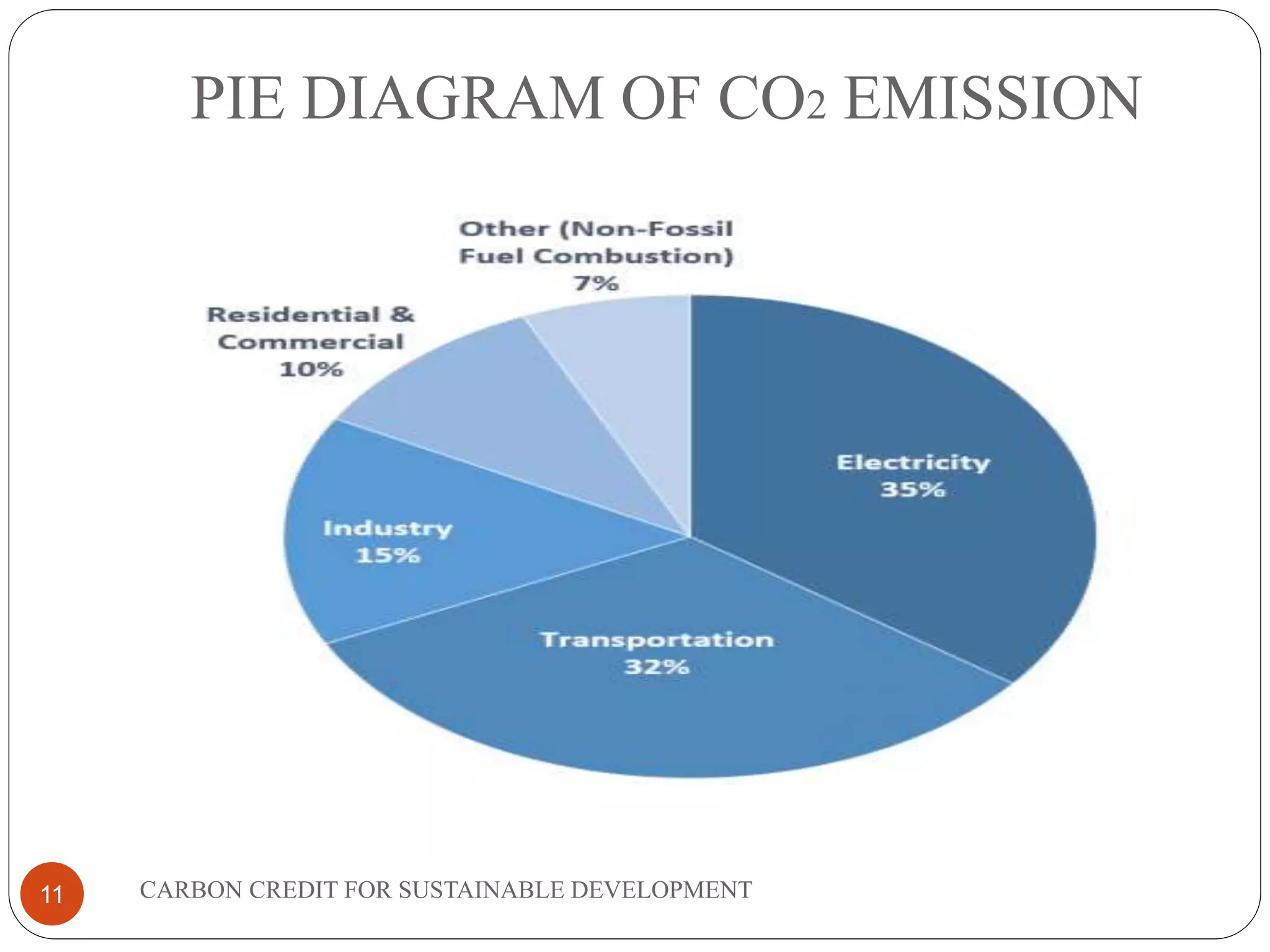
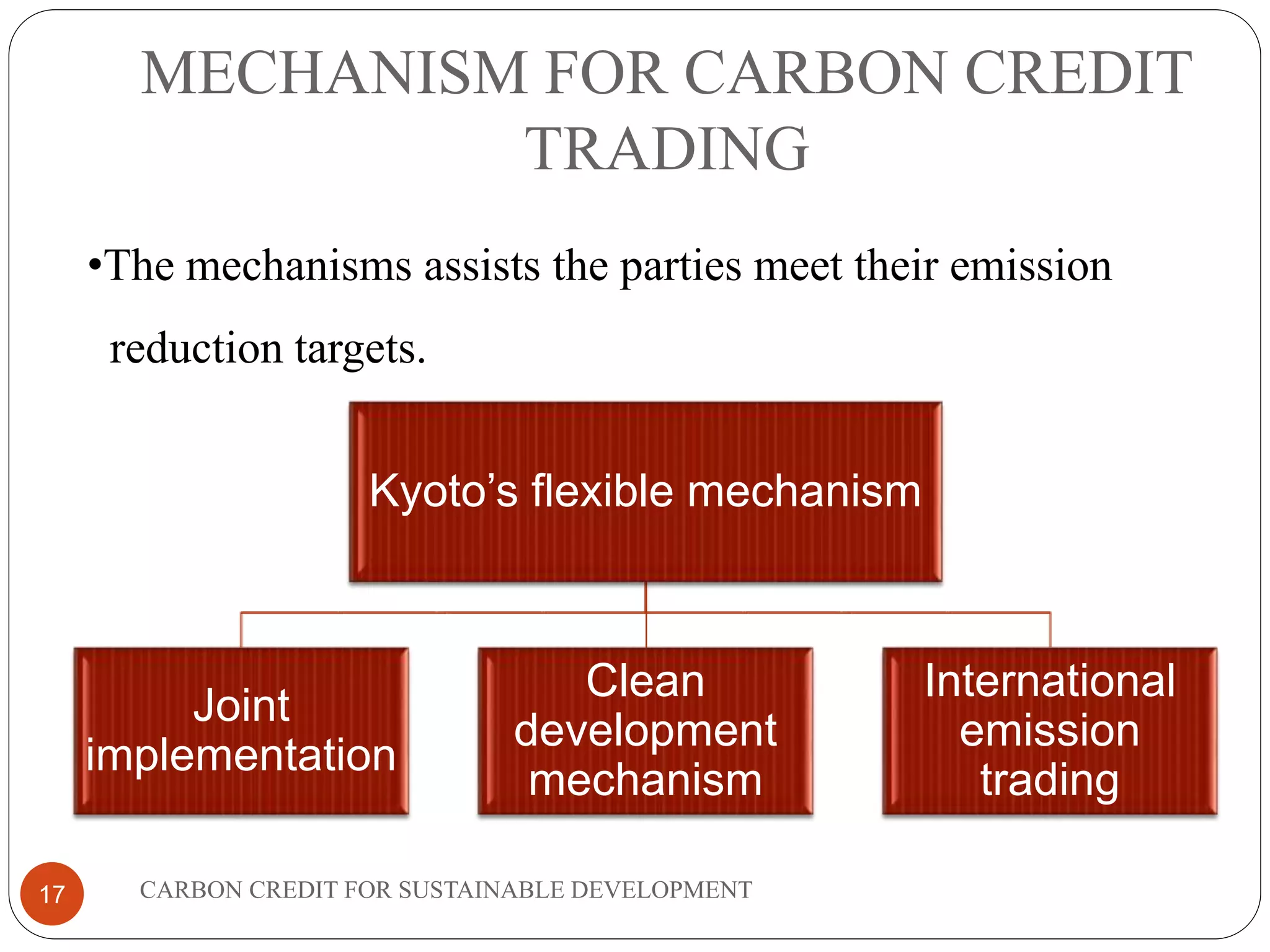
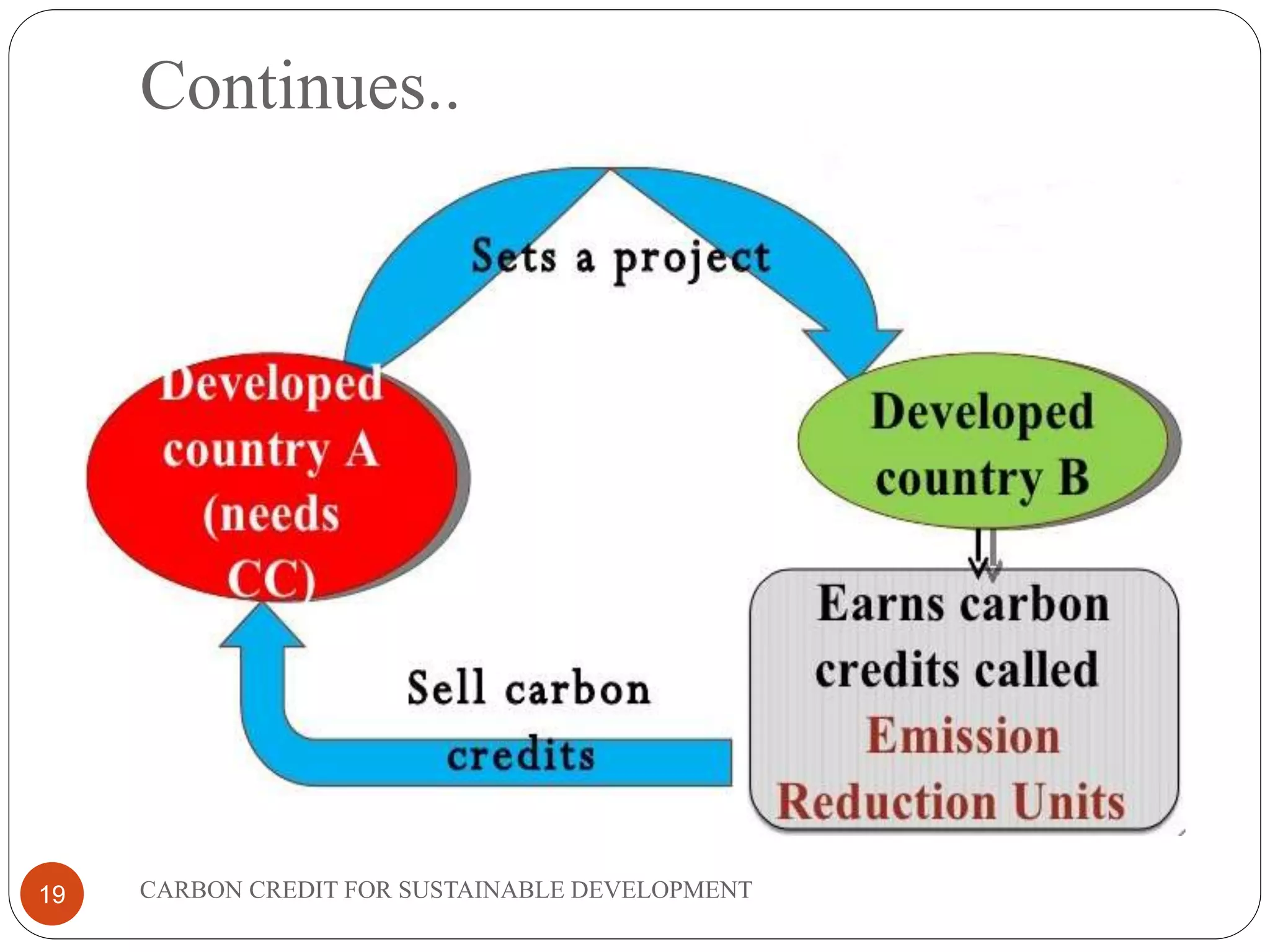
The document discusses carbon credits for sustainable development. It introduces carbon credits as permits that allow the holder to emit 1 tonne of CO2. Carbon credits are generated through projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and can be traded on international markets. The Kyoto Protocol established a framework for carbon trading between developed and developing countries through mechanisms like clean development. The document provides examples of how projects in India have generated carbon credits and the overall benefits of carbon credits for sustainable development and reducing global warming.