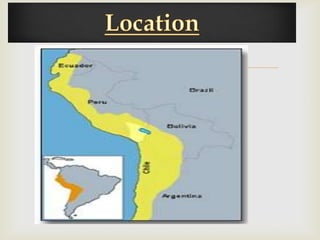
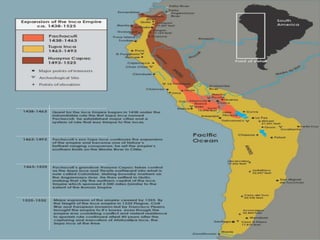
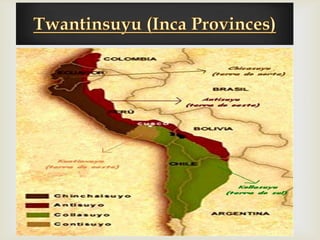
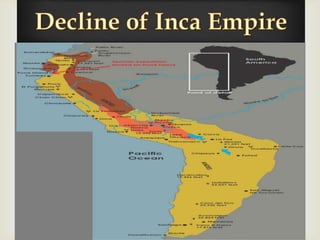
The document discusses the history of the Inca Empire, detailing its founding by Manco Cápac in the 12th century, expansion under leaders like Pachacuti, and the construction of Machu Picchu. It highlights societal structures, agricultural practices, labor systems like mita, and religious beliefs, including human sacrifices. The narrative concludes with the account of the Spanish conquest led by Francisco Pizarro, civil conflicts, and the devastating impact of smallpox on the Inca population.