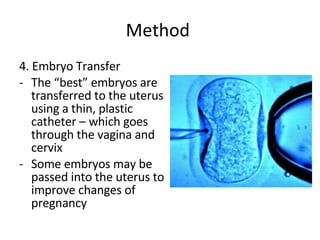
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a process where eggs are fertilized by sperm outside of the body. It involves hormonally controlling a woman's ovulation, removing her eggs and letting sperm fertilize them in a fluid medium. The fertilized egg is then transferred to the woman's uterus. The major steps are ovarian stimulation through injections, egg retrieval using a transvaginal technique, fertilizing the eggs with sperm in a growth medium, and embryo transfer through the vagina and cervix. For IVF to be successful, healthy eggs, sperm, and a uterus capable of maintaining a pregnancy are needed. While IVF can help women who have gone through menopause get pregnant, success rates average