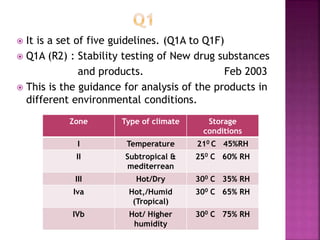
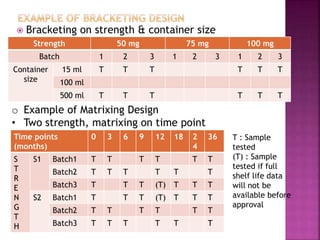
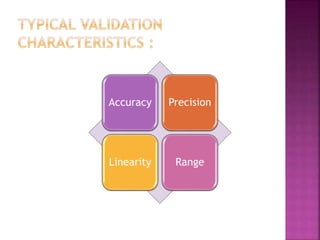
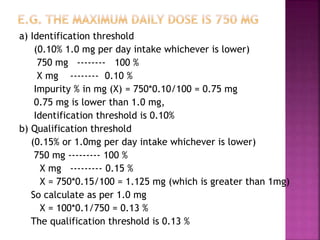
This document provides an overview of ICH guidelines related to quality (Q series). It describes the composition and objectives of ICH, which aims to harmonize technical requirements for pharmaceutical registration among regulators and industry in the EU, Japan, and US. The key points are that ICH guidelines are divided into four categories, including the Q series which relates to chemical and pharmaceutical quality. The Q series guidelines cover topics like stability testing, analytical validation, impurities, and residual solvents. The goal is to establish common standards for assessing safety, quality and efficacy of medicines.