Textile testing is an important part of the textile production process. It involves determining various properties of fibers, yarns, and fabrics to ensure quality standards are met. The objectives of textile testing include selecting raw materials, controlling manufacturing processes, ensuring quality of finished products, and facilitating research and product development. There are different types of textile testing for fibers, yarns, woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, and nonwoven fabrics. Test methods are established by various standards organizations and influence factors like sampling methods, atmospheric conditions, equipment used, and technician skill.
![1
Introduction:
Textile Testing is an important part for textile production, distribution, and
consumption. We can also define Textile Testing as the process of determining the
properties of different kinds of Textile substances. The primary purpose of textile
testing and analysis is to assess textile product performance and to use test results
to make predictions about product performance. Product performance must be
considered in conjunction with end use; therefore, tests are performed with the
ultimate end use in mind. Examples of testing for end-use performance include
testing draperies for light fastness or tire cords for strength. [1]
What is Testing?
Testing is the way of control or the process to check or verify the nature, kind or
character of fiber, yarn, fabric or any material, hence control the degree of
excellence.
Now, testing may be different type
Fiber- length, strength, fineness, maturity.
Yarn- strength, count, twist
Fabric- EPI, PPI, GSM. [2]
Objects of textile testing:
The objectives of Textile Testing are as follows –
In case of research, the results of testing will help the scientist to decide
which route should be followed.
It helps to select the properraw materials. Raw material is a relative term.
As for example, fibre is the raw material of spinner, yarn is the raw material
of weaver etc.
Textile Testing helps to controlthe different processes. Suchas Spinning,
Weaving, Dyeing, Finishing etc. End breakage is controlled by controlling
weight per lap length, sliver length and roving length. Weaving process is
controlled by controlling the excessive breakage of warp and weft yarn.
Dyeing process is controlled by M : L, temperature and pressure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importantoftextiletesting-171221124123/75/Important-of-textile-testing-1-2048.jpg)


![4
Fabric Testing (Woven, Knitted & Nonwoven)
Our ultimate aim is to achieve optimum quality fabric. So to check whether the
quality is achieved or not testing of fabric is done.
Tensile strength.
GSM.
Pilling tendency.
Abrasion.
Drapeability or hanging property.
Moisture%.
Cover factor.
Creaserecovery and creaseresistance.
Stiffness.
Air permeability.
Shrinkage, etc.
All these testing is done after conditioning of material and in standard
atmospheric conditions.[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importantoftextiletesting-171221124123/75/Important-of-textile-testing-4-2048.jpg)
![5
Importance of Textile Testing:
1. Research Work: Test of the textiles helps the authority to decide the next
route.
2. Selection of Raw Materials: During textiles testing the variation of a fibre or
fabric i.e. length, color, fineness (in case of textile fibre), threads per inch, cover
factor (in case of textile fabric), is detected properly. Thus proper raw materials
are selected properly.
3. Process Control: Certain standard level should be maintained to control
increase of waste, rise of costetc. By textile testing we can easily detect the faults
of machinery and materials during test of textiles.
4. Process Development: Research Institute, pilot plants can achieve process
development through testing or exact investigation into better, cheaper and
quicker methods.
5. Search for effective productivity: Continuous test of the textiles results a
enhanced and efficient output of the production.
6. Specification Test: To meet up the customer requirement, specification is very
useful. In this concept, testing plays a vital role.[5]
Factors affecting testresults:
-The sampling
-Atmospheric condition during testing
-Methods of testing
-Instruments used
-Efficiency of the technician[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importantoftextiletesting-171221124123/75/Important-of-textile-testing-5-2048.jpg)
![6
Some important testing standards:
AATCC: American Association of Textile Chemists & Colorists
ASTM: American Society for Testing & Materials
ISO: International Organization for Standardization
BSTI: Bangladesh Standards & Testing Institution
WIRA: The Wool Industries Research Association
AS: Australian Standard
BSI: British Standards Institution [2]
Moisture in case oftesting
Most textile fibers are hygroscopic, i.e. they have the ability to absorb or give up
moisture. This moisture is picked up or absorbed bythe hygroscopic material from
the atmosphere if the relative amount of moisture in the air is greater than that in
the material. Conversely, the moisture will be given up by the material if the
relative amount of moisture in the air is less than that in the material.
Many physical properties of a fiber are affected by the amount of water absorbed,
such as dimensions, tensile strength, elastic recovery, electrical resistance and so
on. [2]
Different Types OfTextile Testing Methods
Different buyers usedifferent Textile testing methods. There are different types of
Textile and Garments Testing methods such as –
American Society of Testing &Materials (ASTM)
American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC)
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
European Norms (EN)
British Standards (BS)
British Standards for European Nations (BS EN)
DeutschesInstitut fur Normung (DIN)
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importantoftextiletesting-171221124123/75/Important-of-textile-testing-6-2048.jpg)
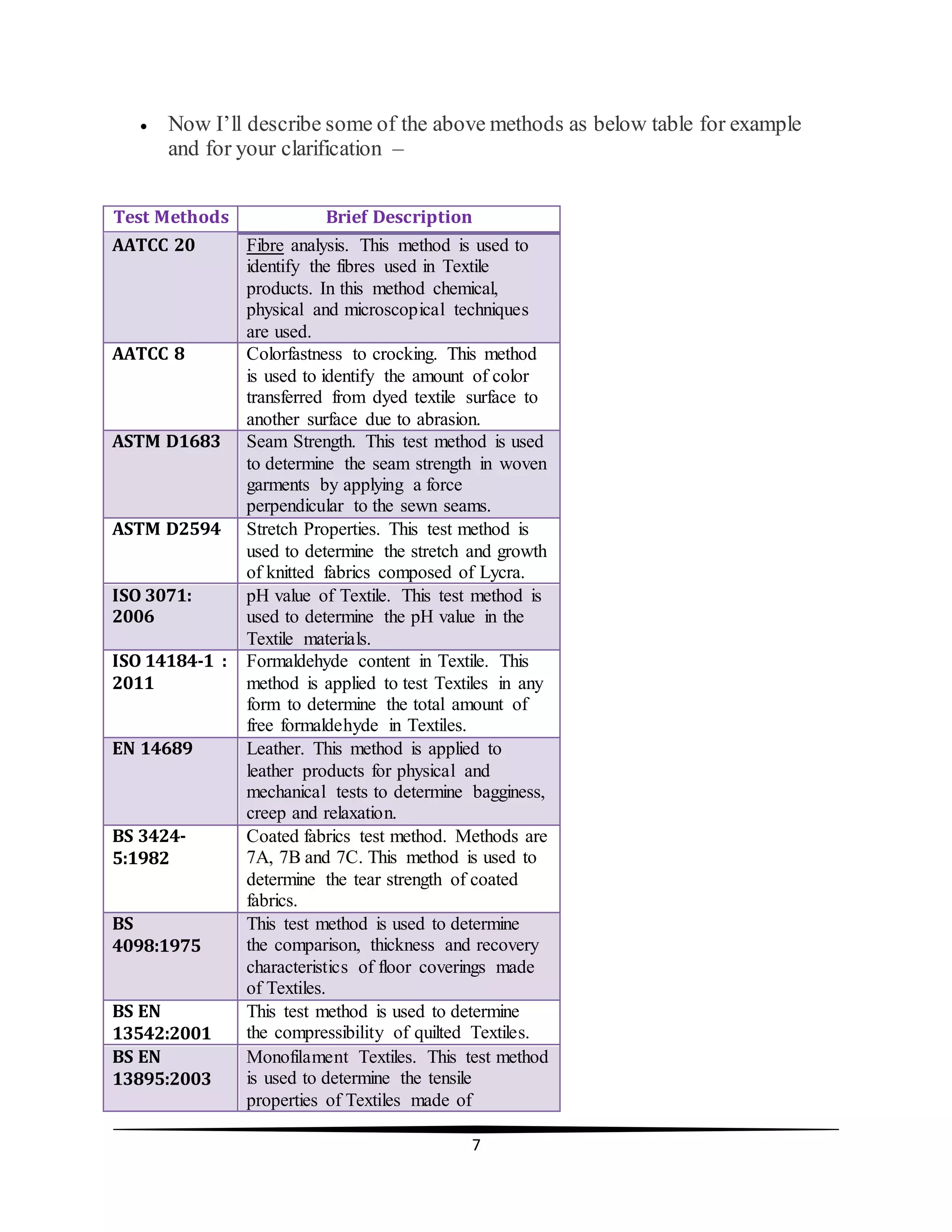
![8
[10]
Conclusion:
Testing means checking, examine and verification of some items. On the other
way we can define testing as; it is the process or procedureto determines the
quality of a product.
Reference:
1: https://textileapex.blogspot.com/2015/10/what-is-textile-testing-definition.html
2/7/8/9: http://textilequalitytest.blogspot.com/
4: http://textilelearner.blogspot.com/2012/02/textile-testing-objects-of-textile.html
5 :http://www.testextextile.com/textile-testing-importance-of-testing-in-textiles/
10: https://textileapex.blogspot.com/2016/06/textile-testing-methods.html
monofilament yarns.
BS EN ISO
9073-4:1997
Non-woven Textiles. This test method is
used to determine the tear resistance of
Non-Woven Textiles.
BS EN ISO
105-
E01:2013
Colorfastness to water. This test method
is used to define the amount of color
transferred from dyed textiles in
presence of water.
JIS L
1041:2011
Formaldehyde content in Textiles. This
test method is used to determine the
amount of formaldehyde content in
Textiles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importantoftextiletesting-171221124123/75/Important-of-textile-testing-8-2048.jpg)