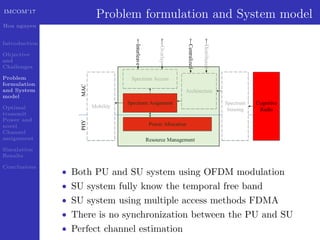
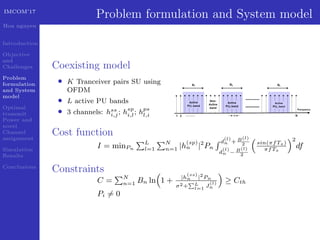
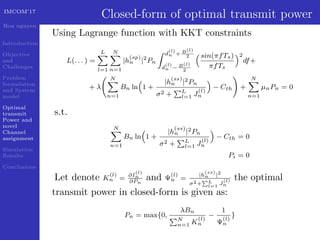
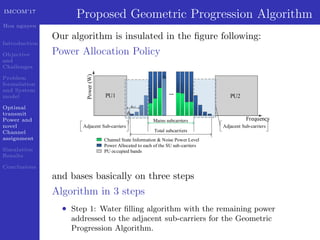
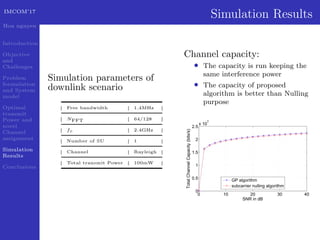
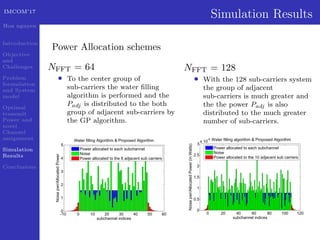
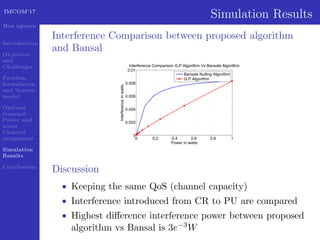
This document presents a geometric progression algorithm for adjacent band power allocation in OFDM-based cognitive radio. The objectives are to minimize interference from secondary users to primary users through optimal transmit power allocation and a novel channel assignment method. The proposed algorithm allocates power to center subcarriers using waterfilling and distributes remaining power to adjacent subcarriers geometrically. Simulation results show the algorithm achieves higher capacity than subcarrier nulling and introduces less interference to primary users compared to an existing method. In conclusion, an analytic closed-form solution is derived for optimal power allocation and the geometric progression algorithm is presented and verified through simulations.