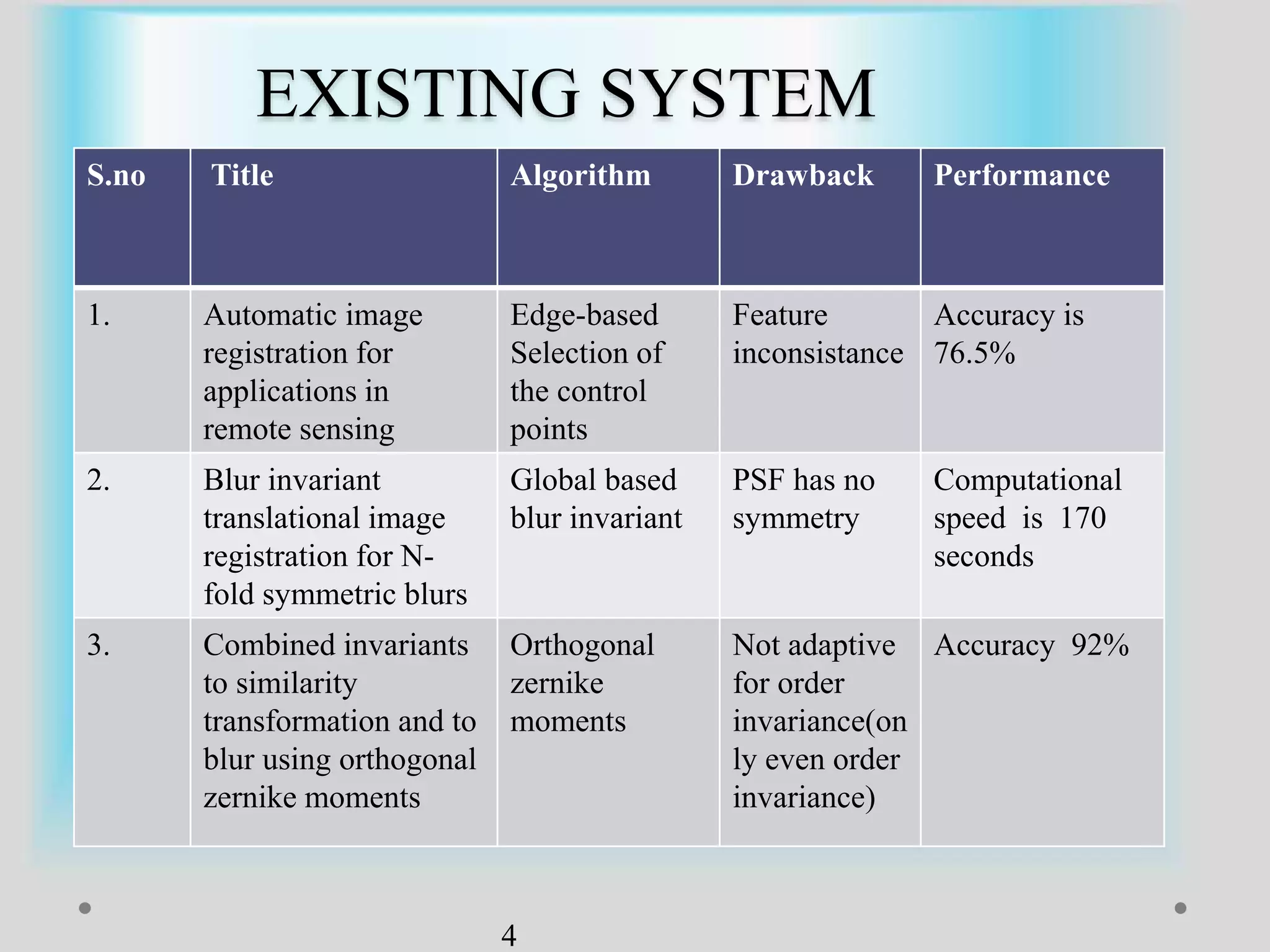
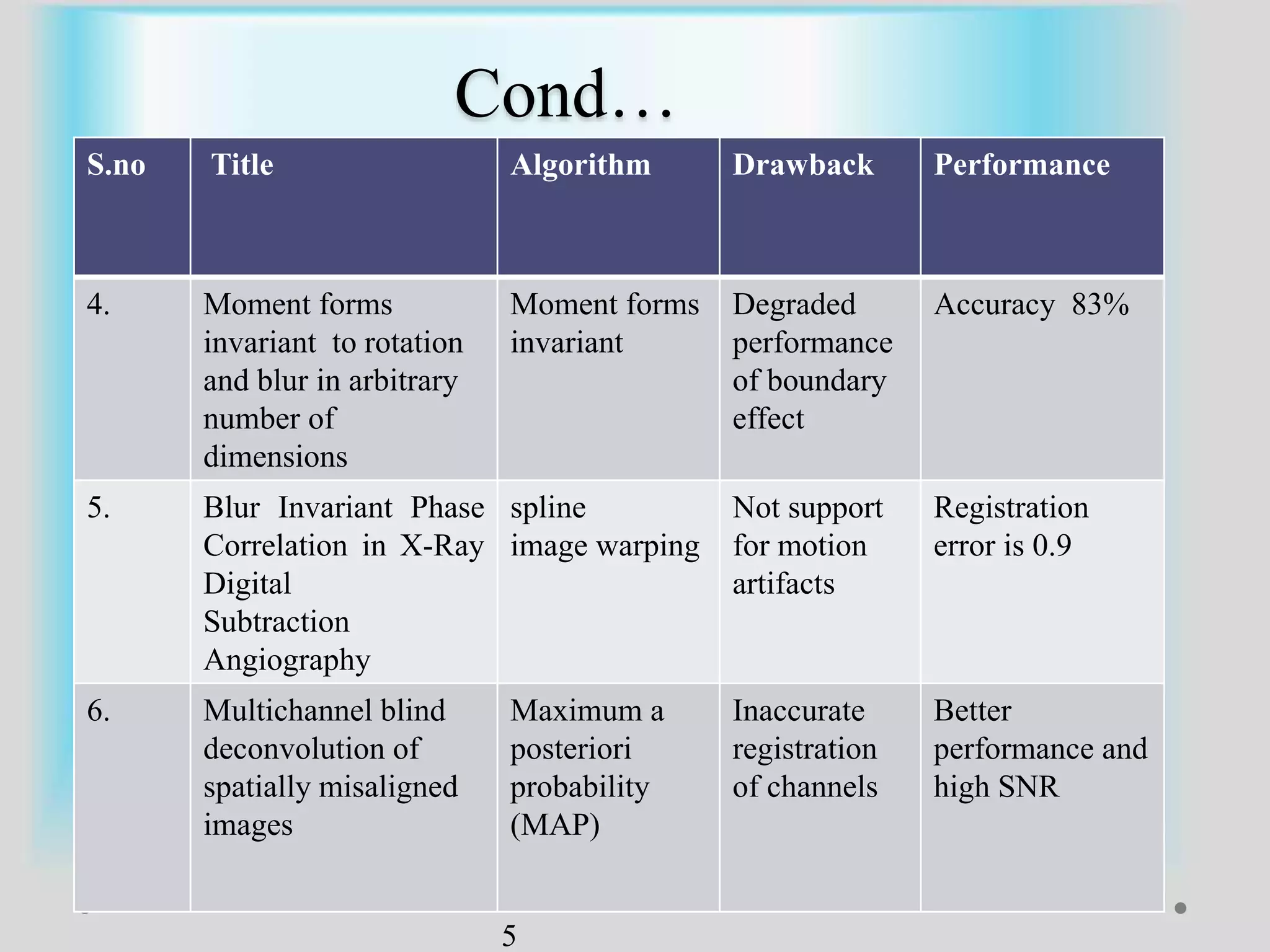
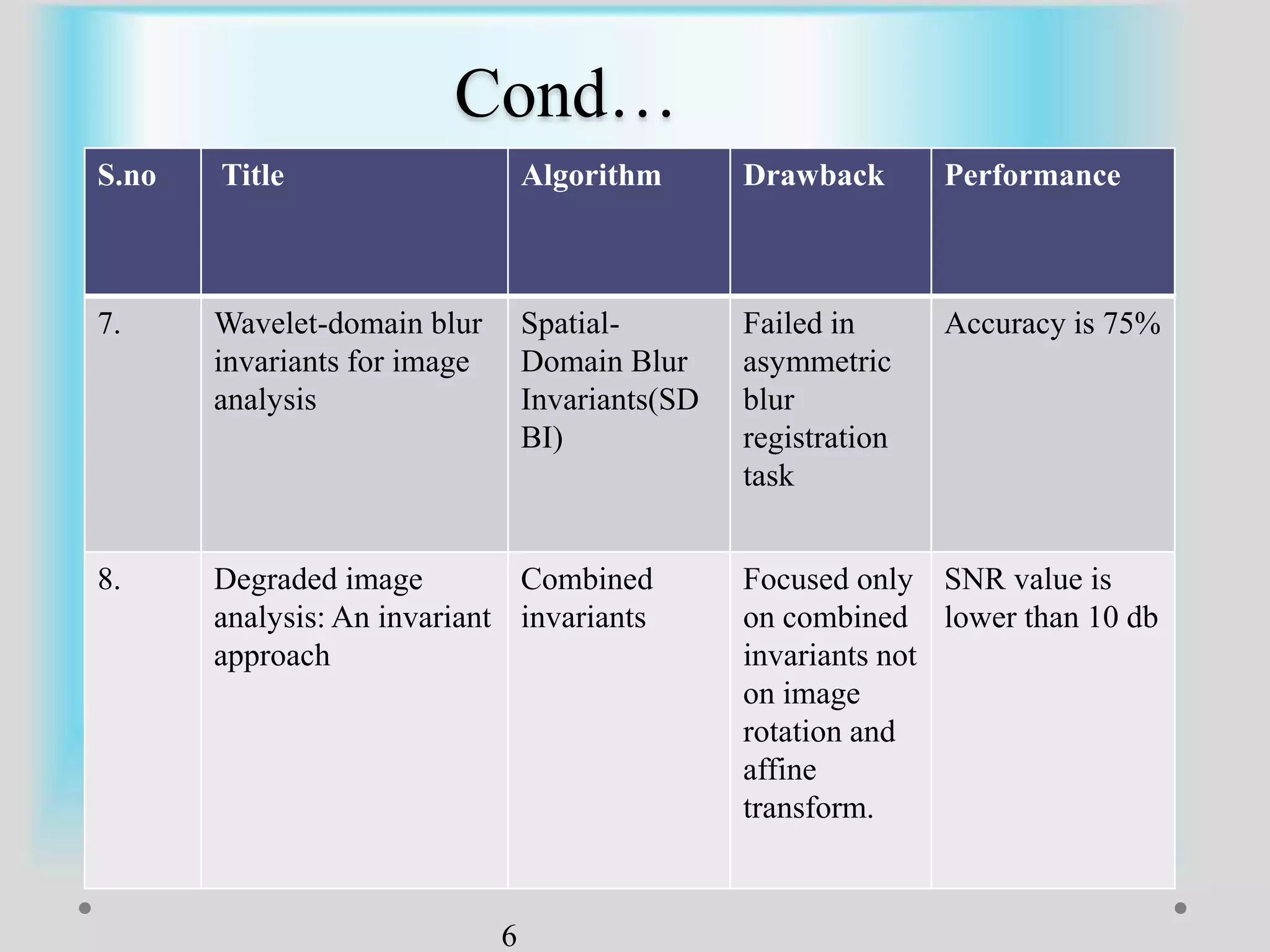
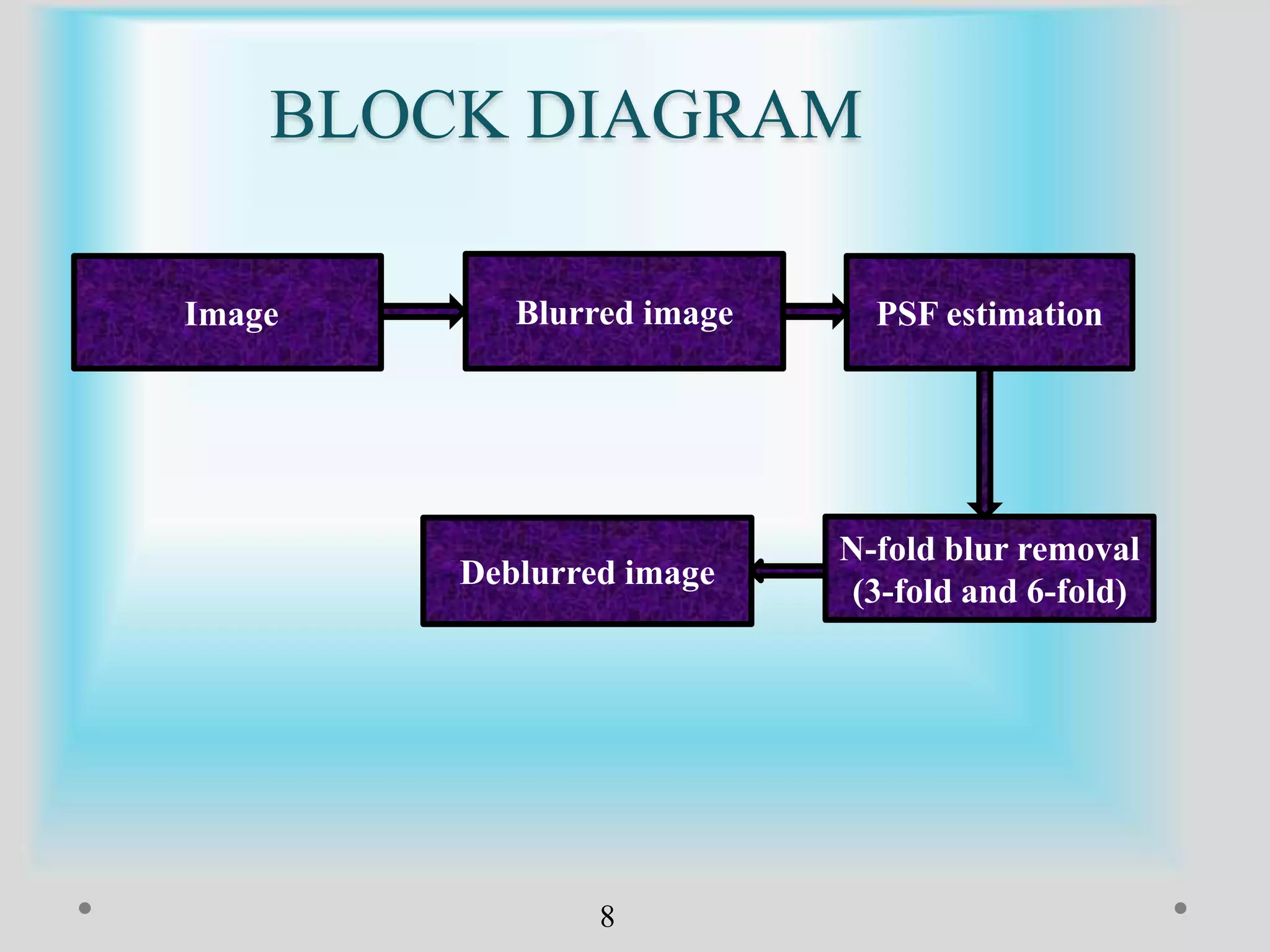
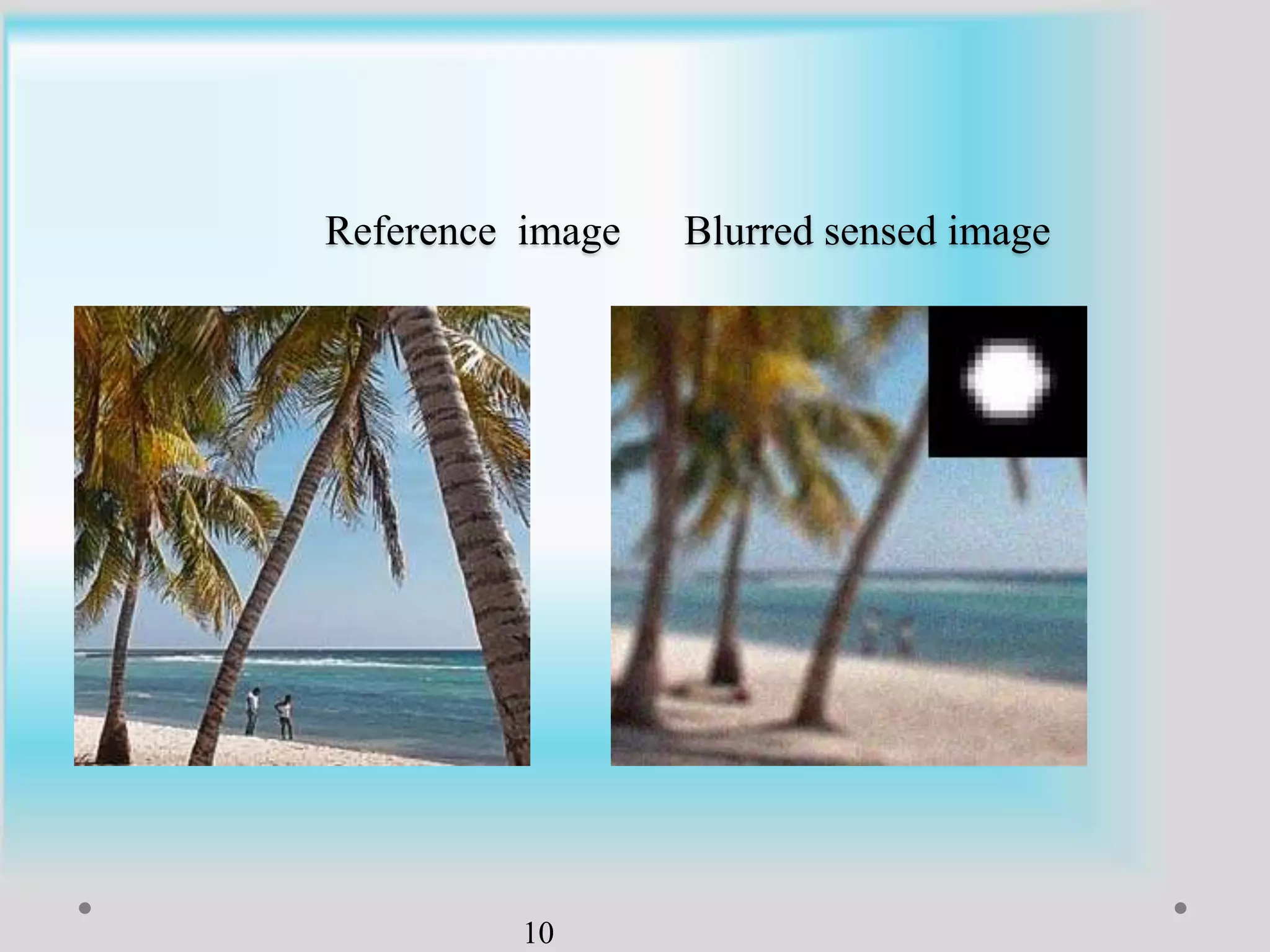
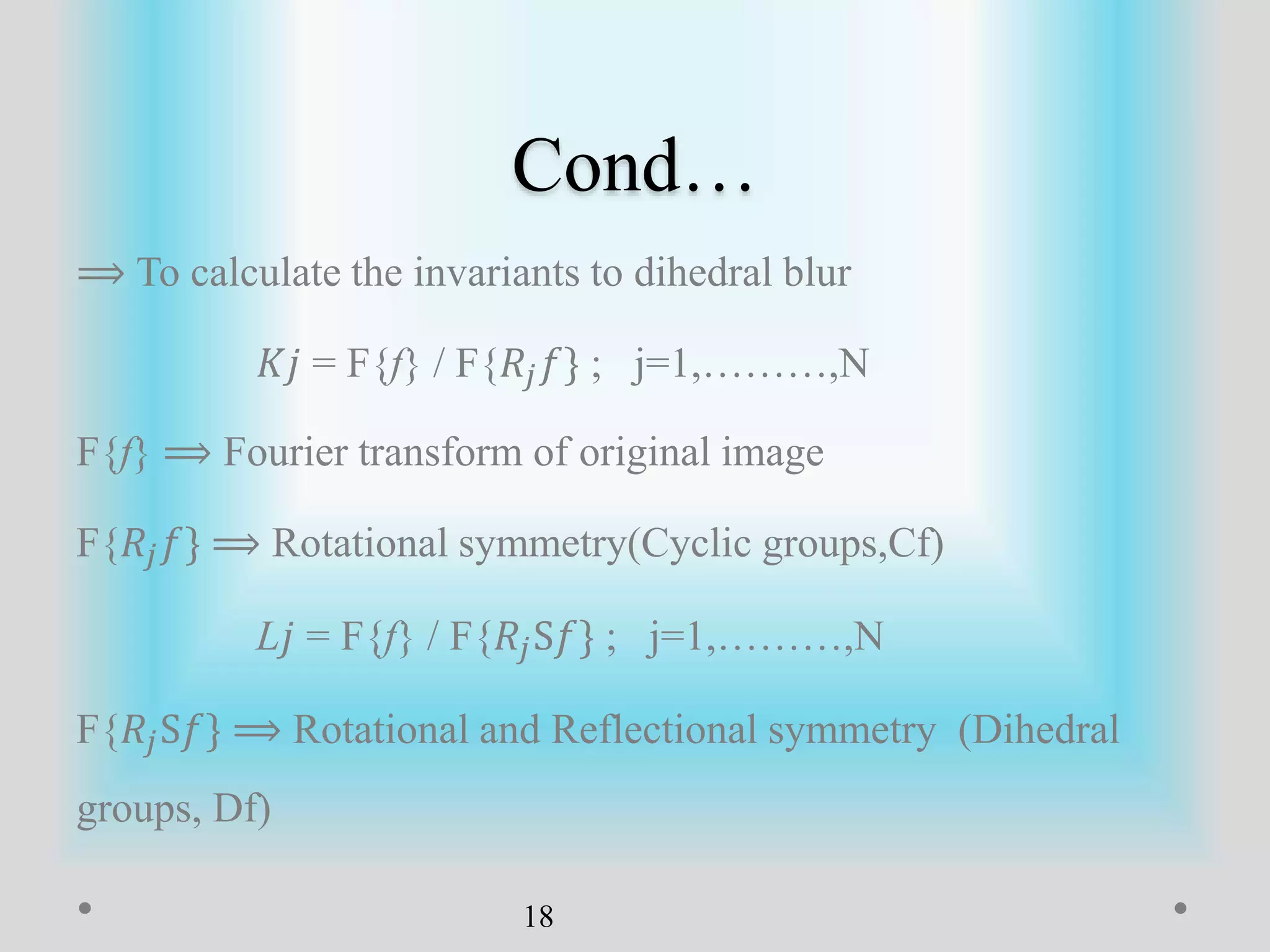
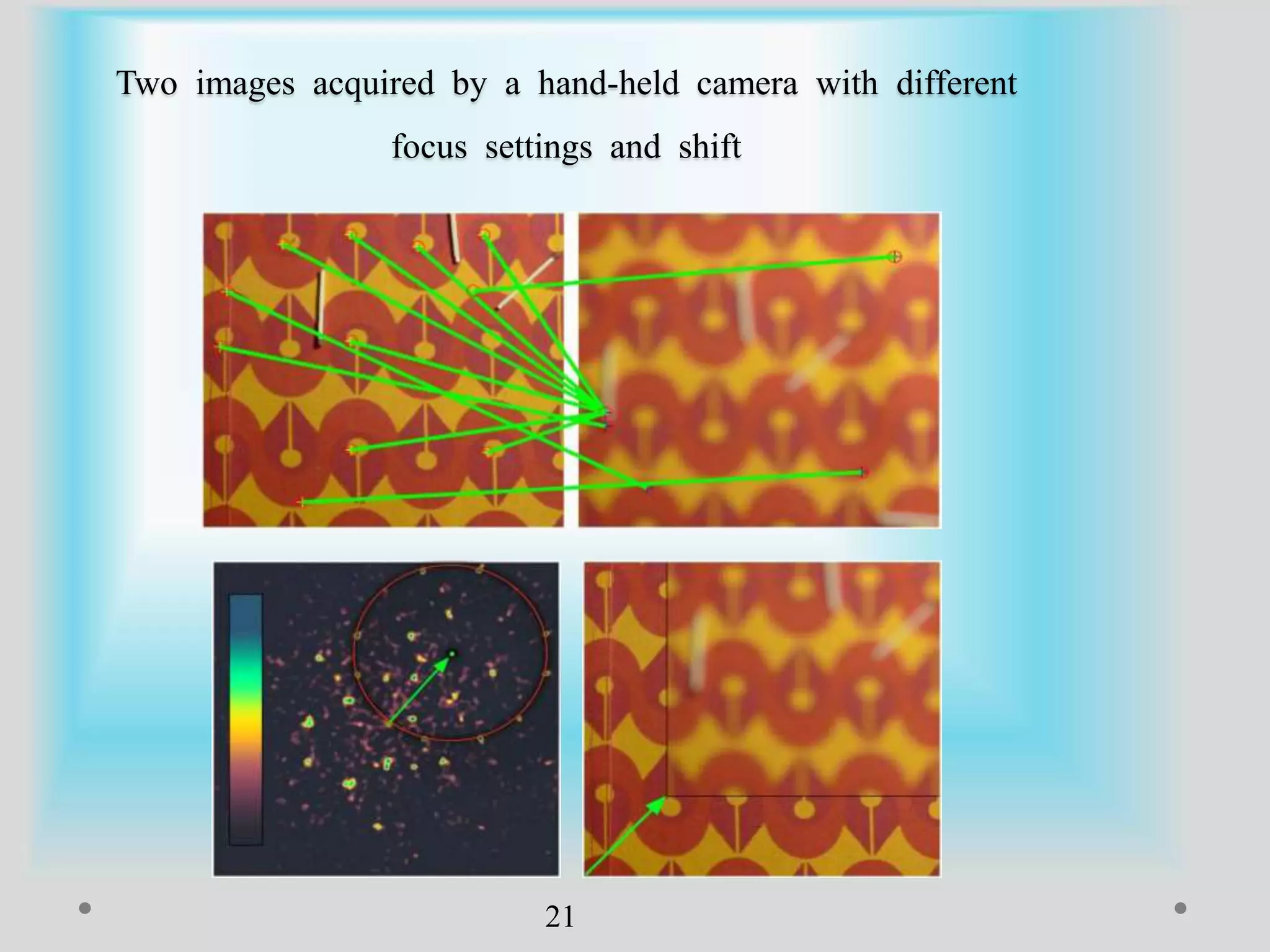
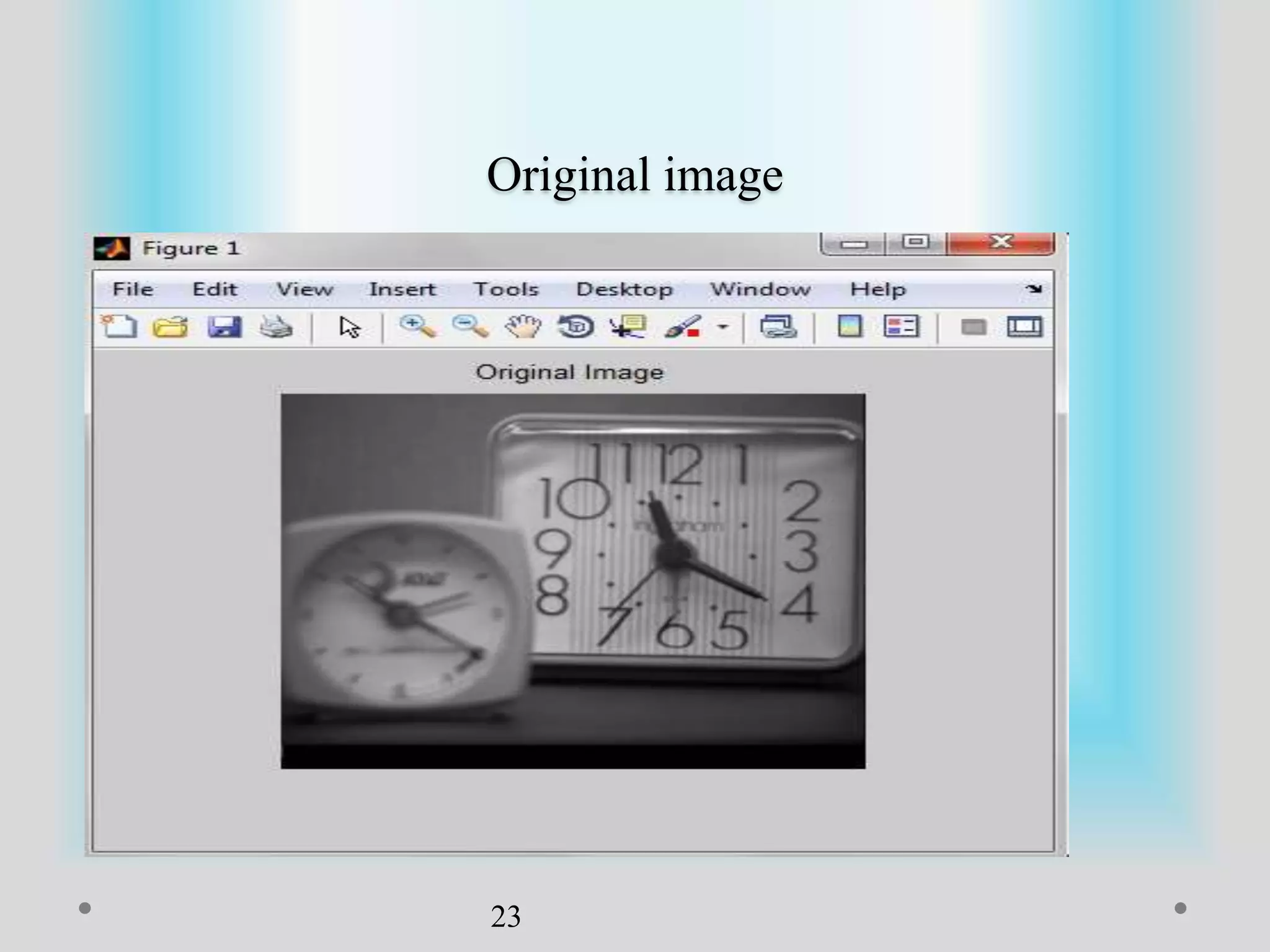
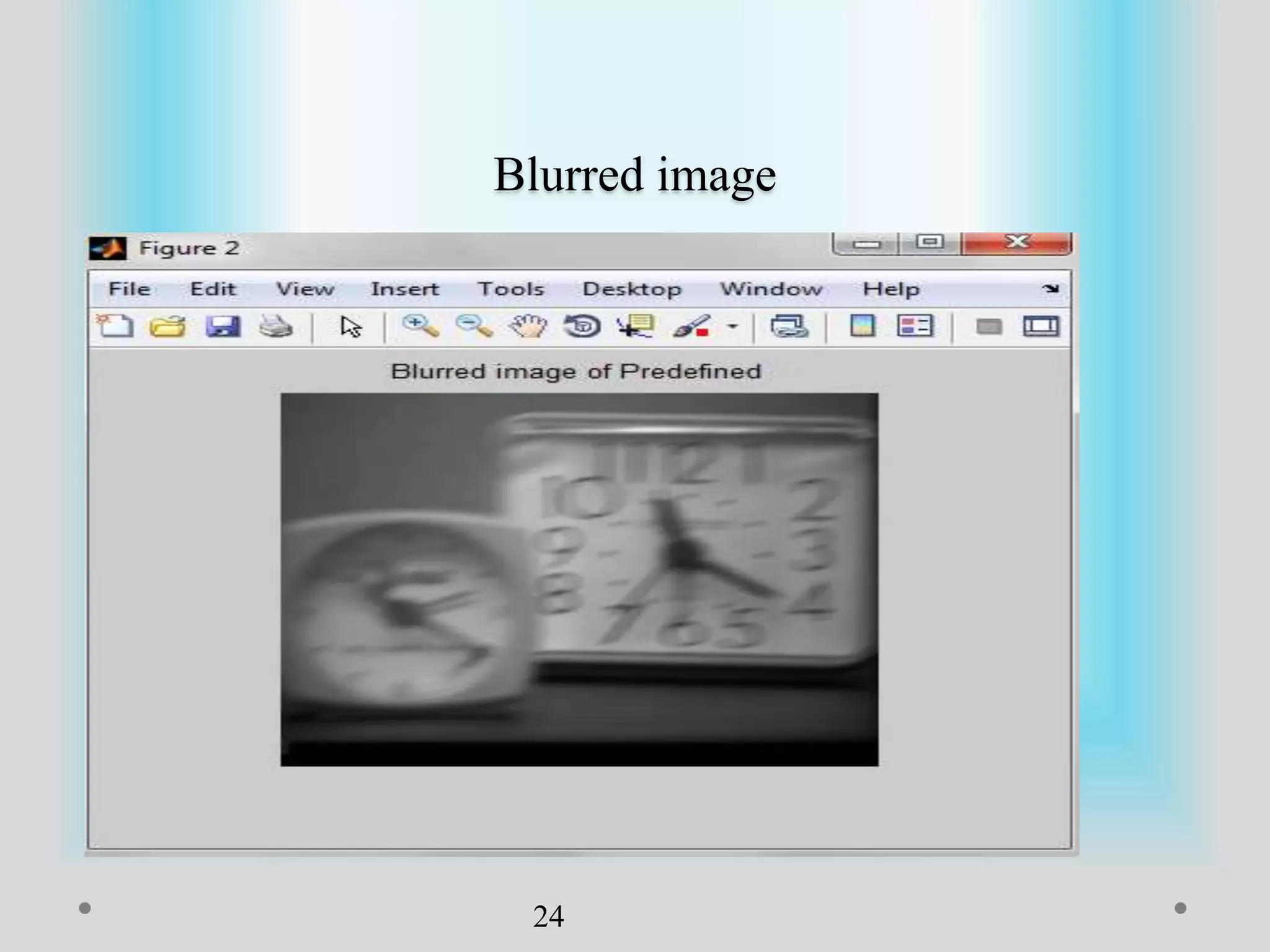
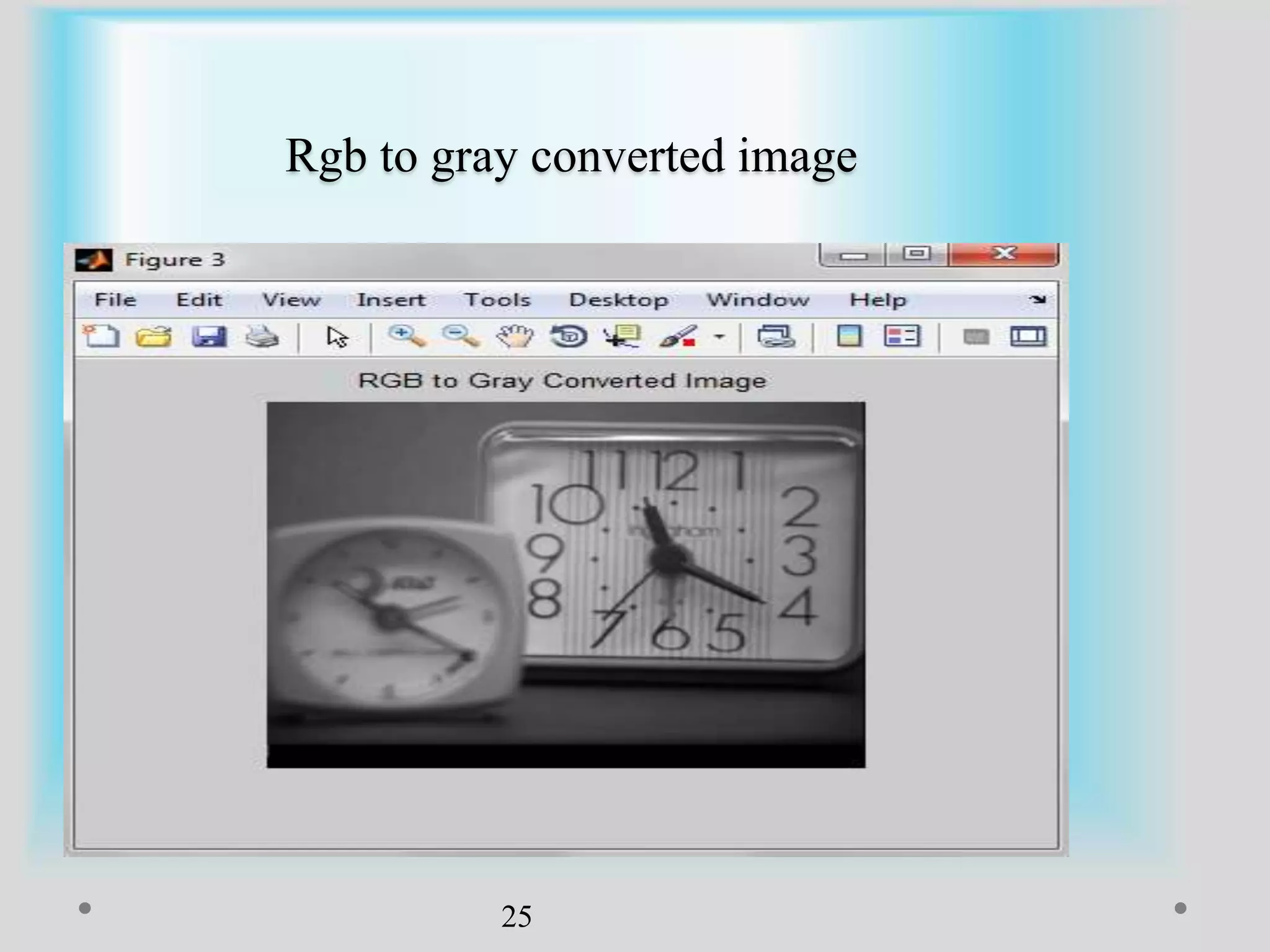
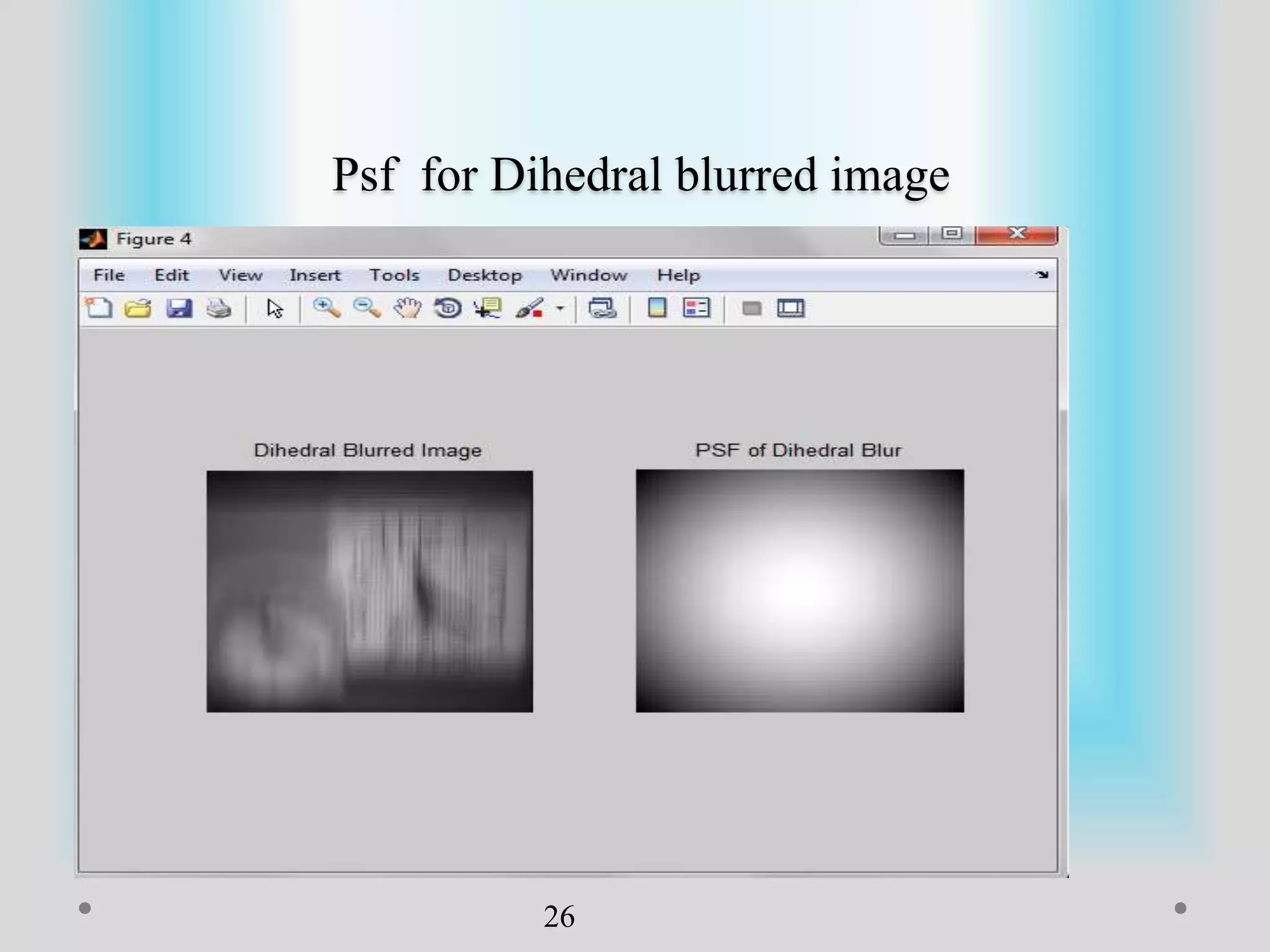
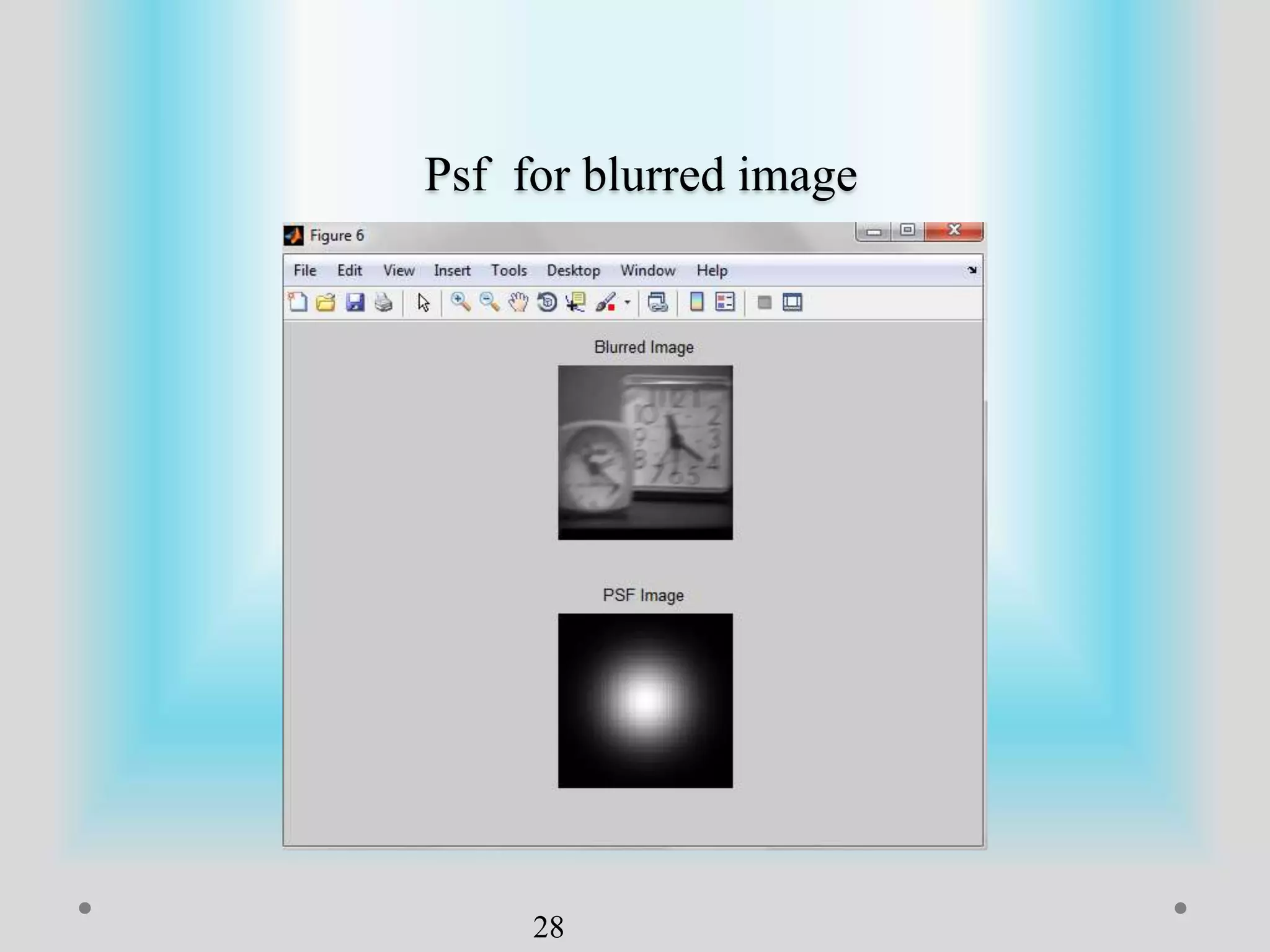
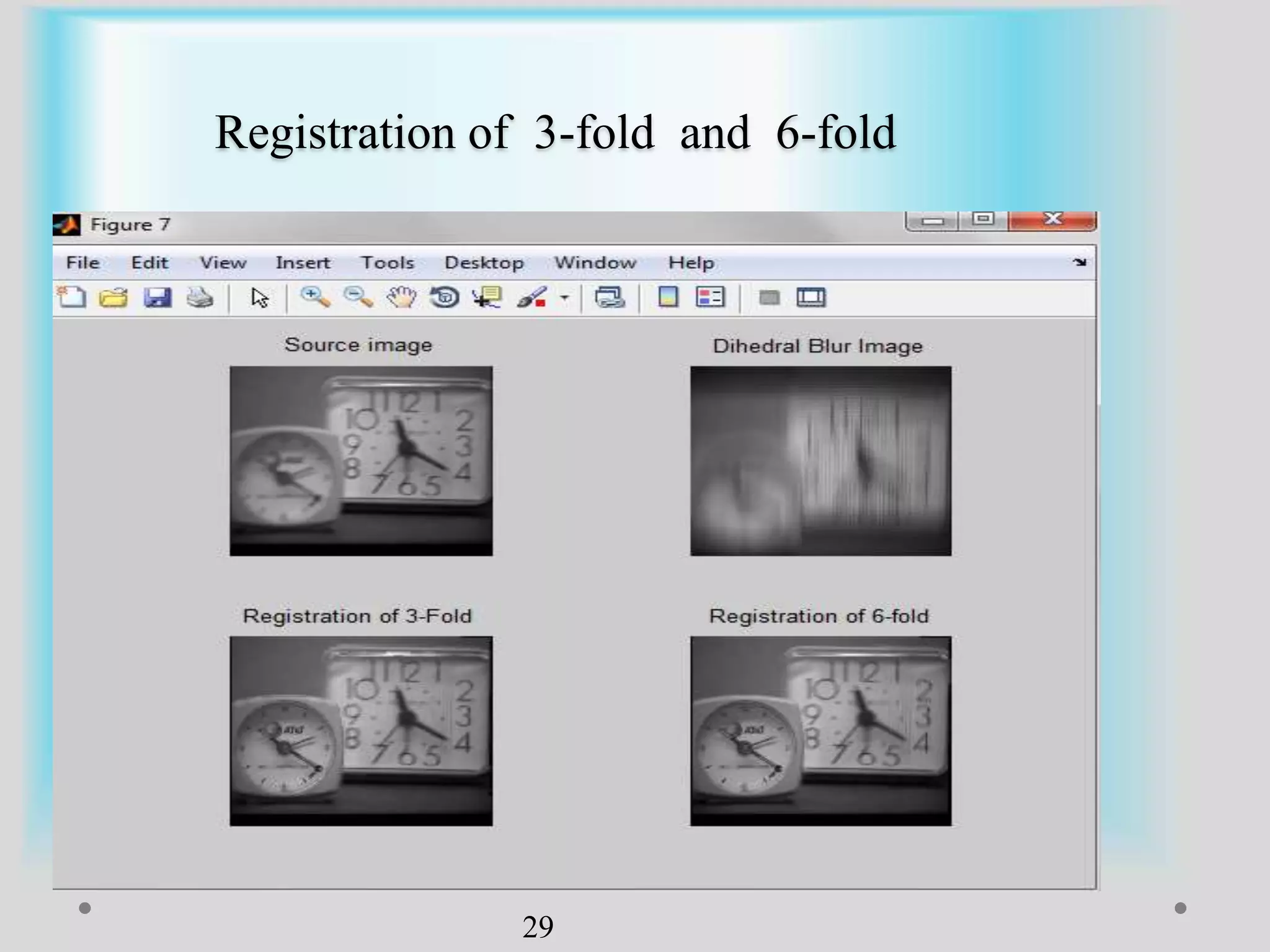
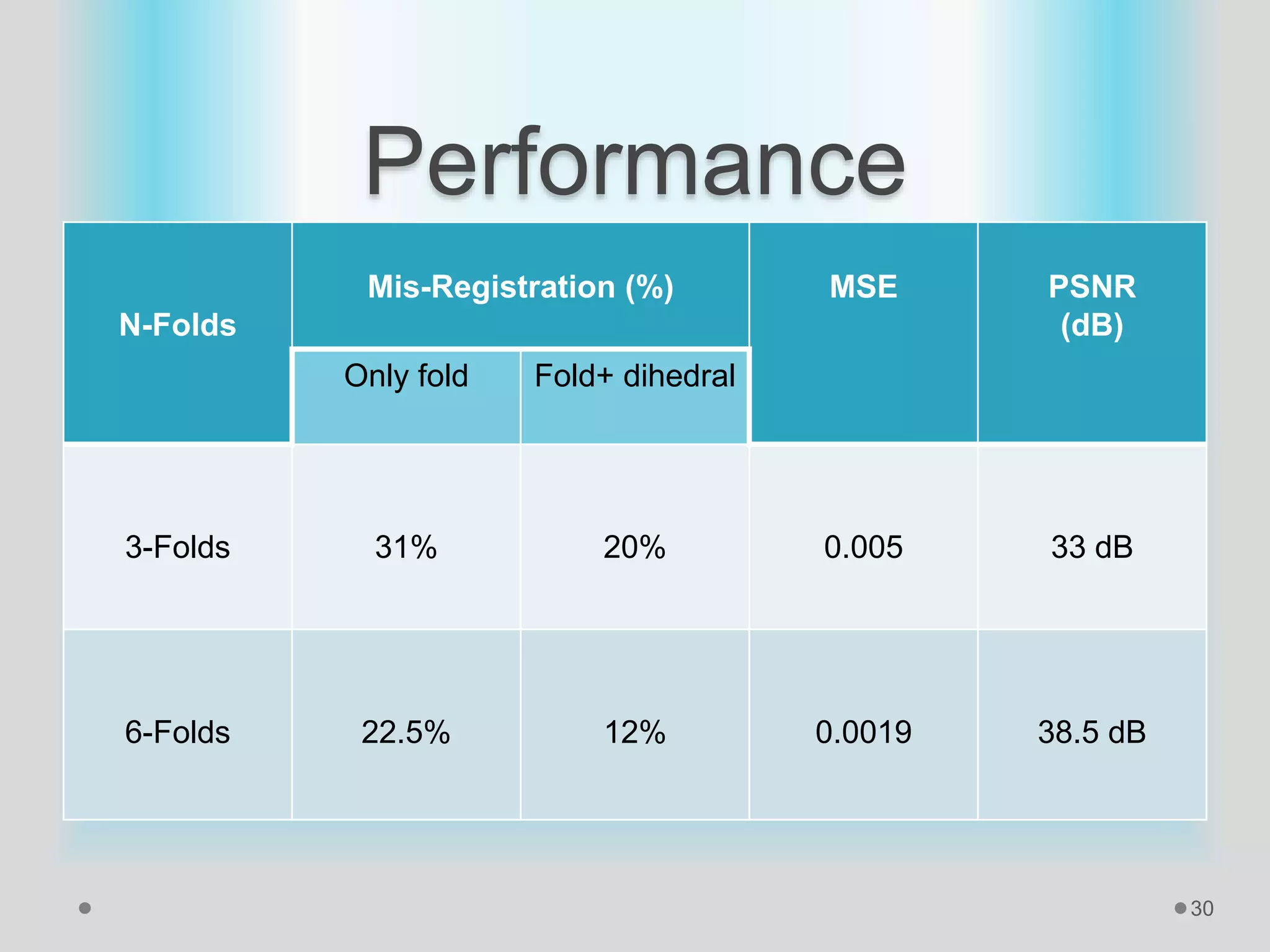
The document presents a method for image registration using n-fold blur removal, aimed at improving the accuracy and performance of registering blurred images. It discusses existing systems and their drawbacks, showcasing the proposed registration method designed specifically for blurred images with n-fold rotational symmetry. The proposed system utilizes a global-based blur invariant approach and provides detailed algorithms and performance metrics for different blur configurations.