Embed presentation
Download to read offline

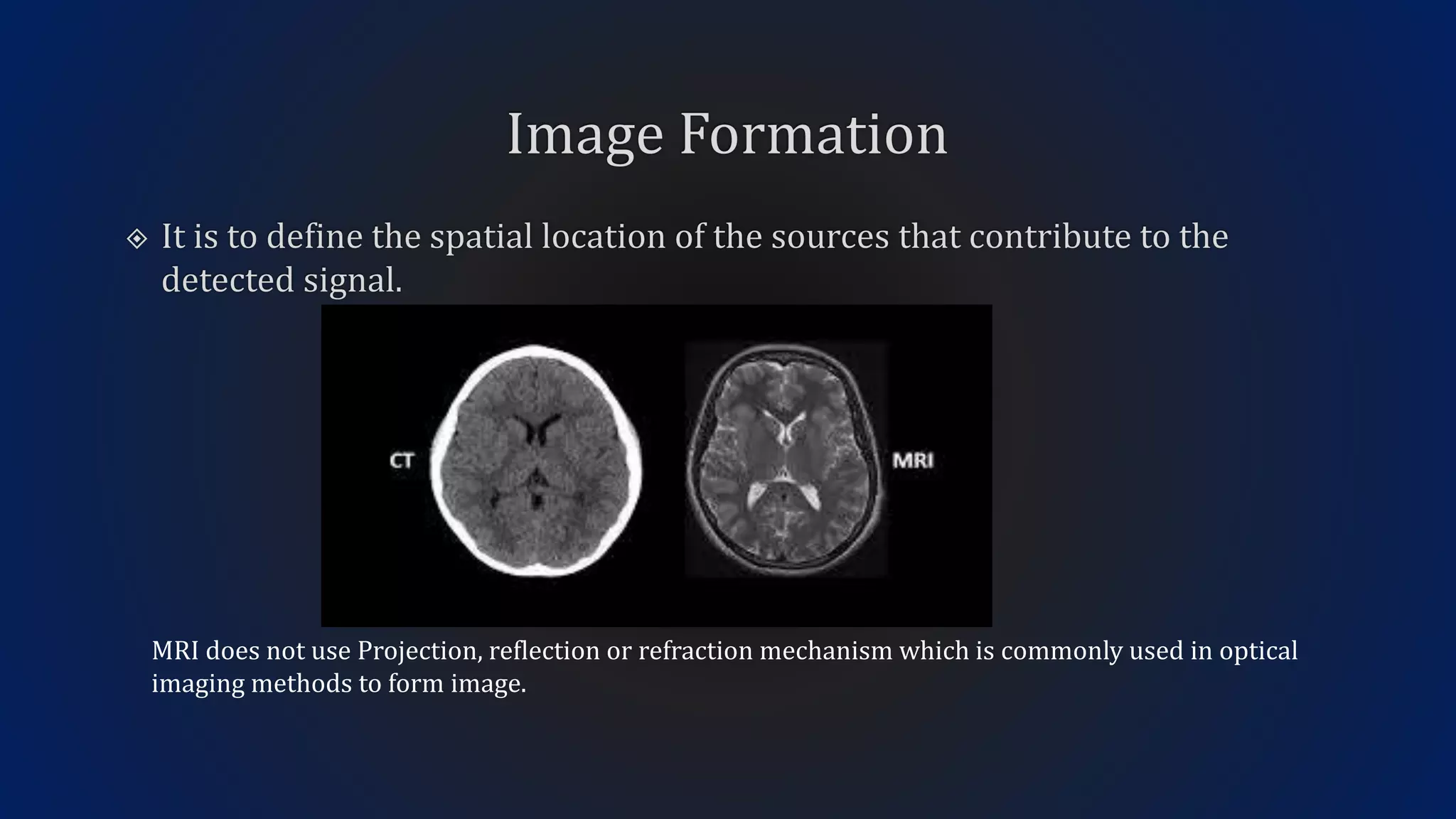
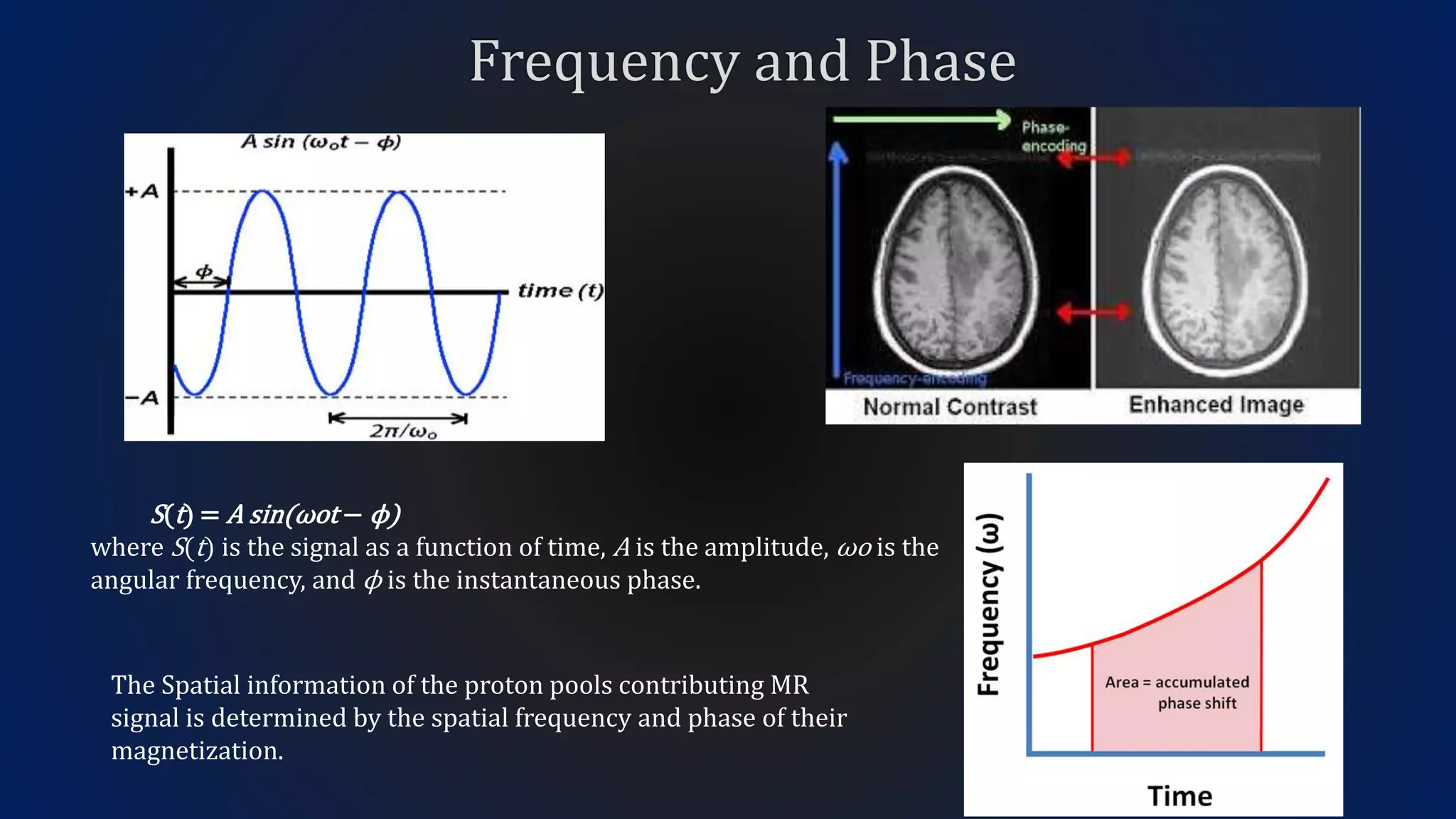
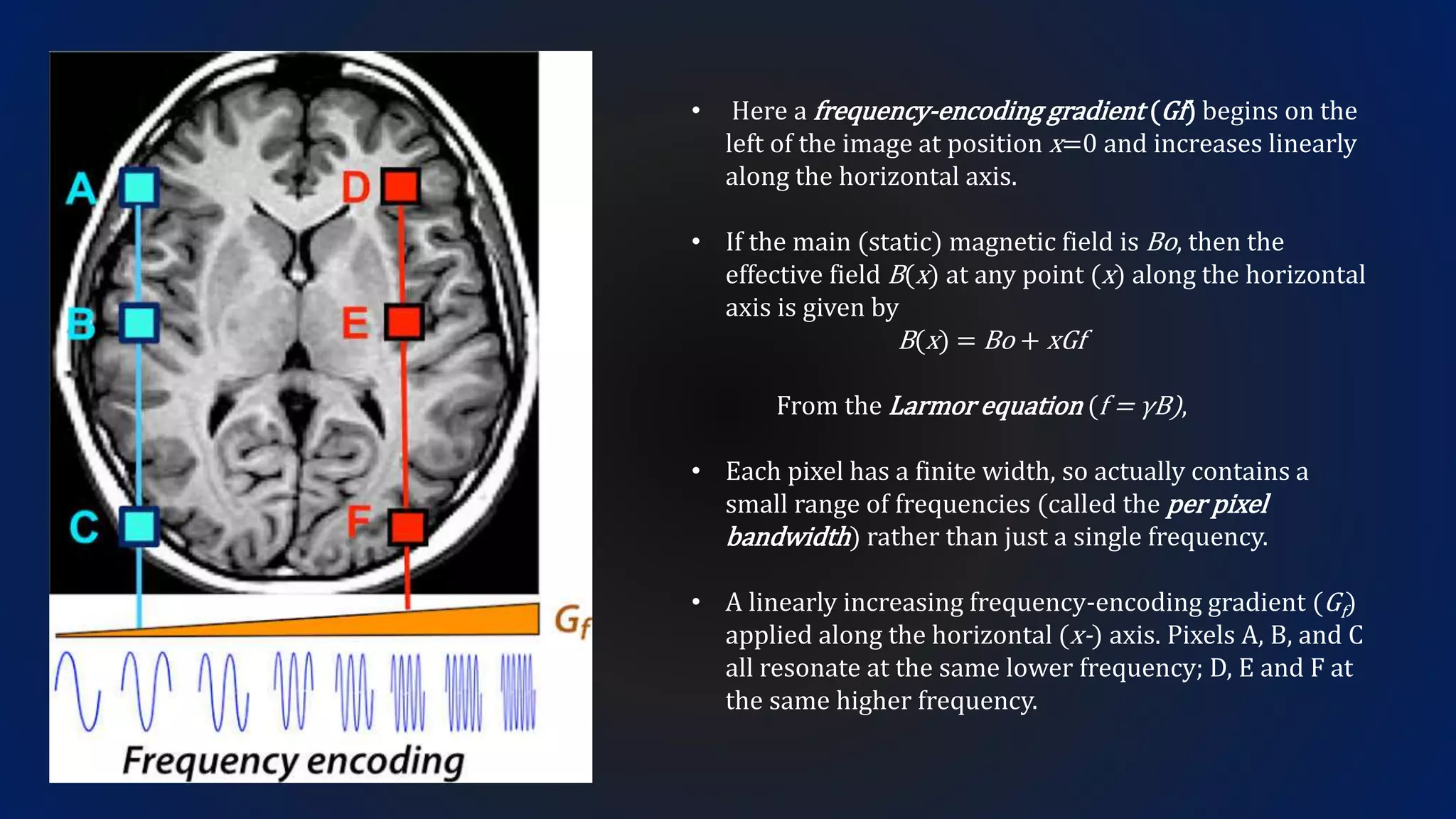
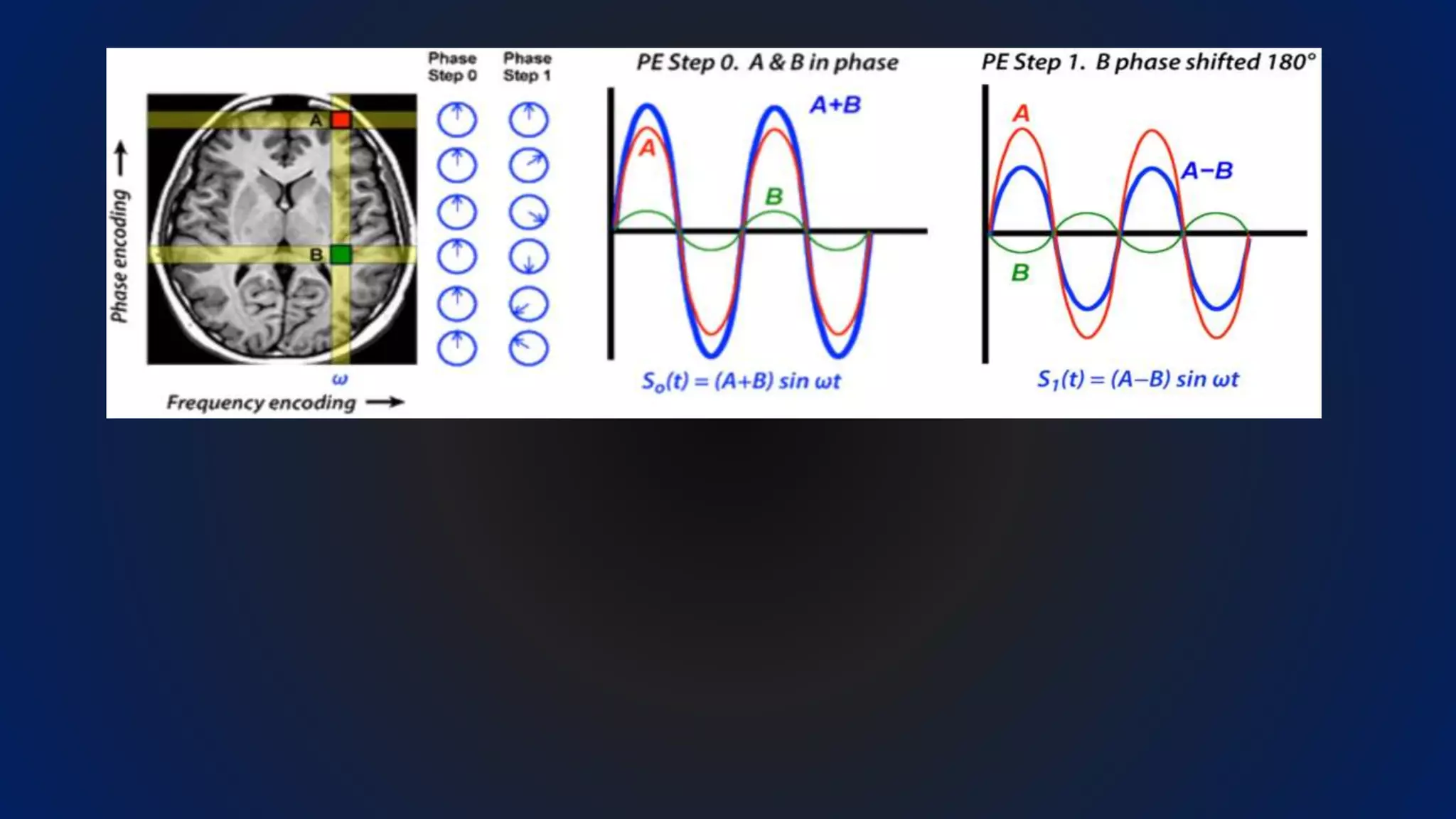
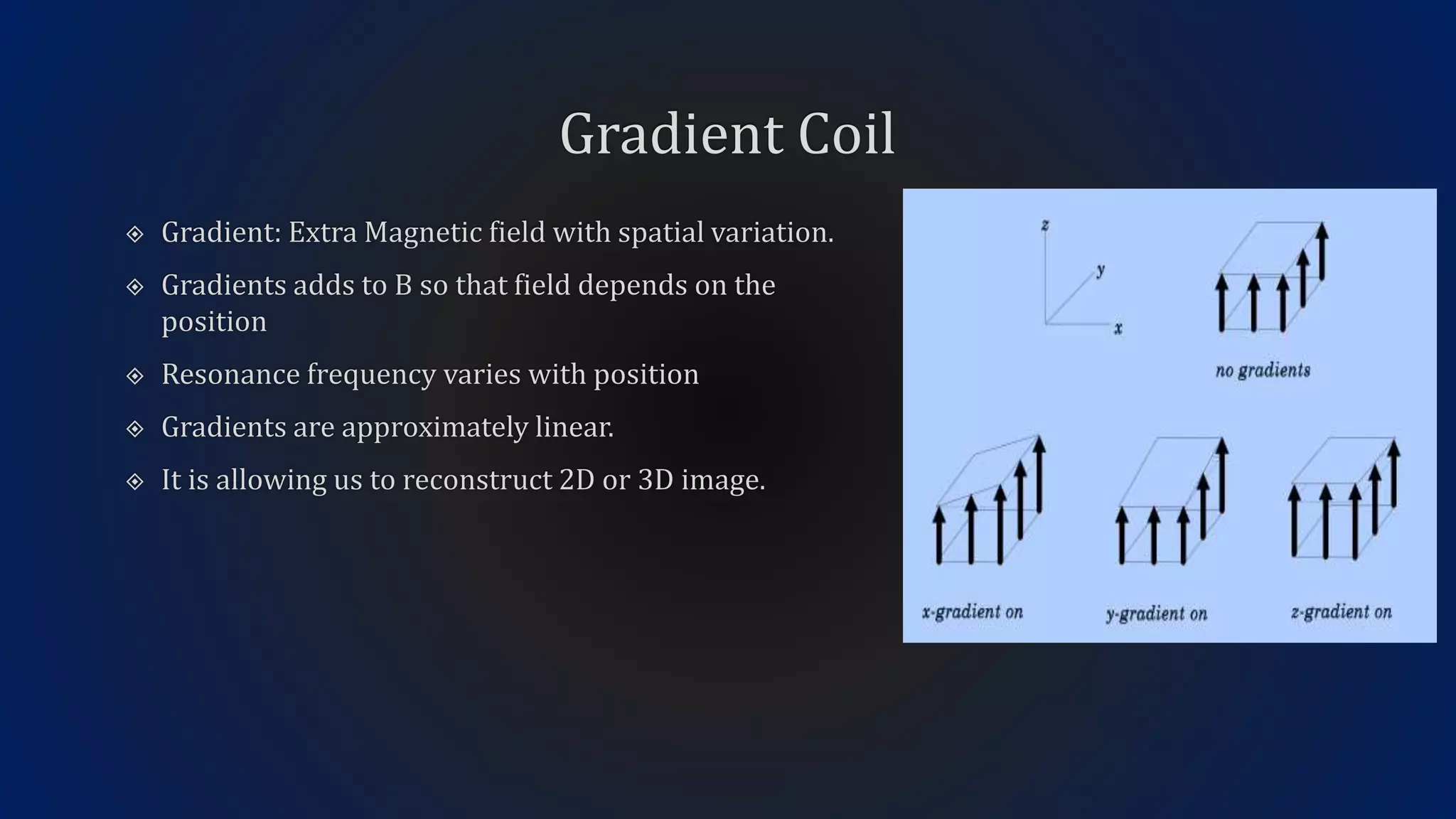
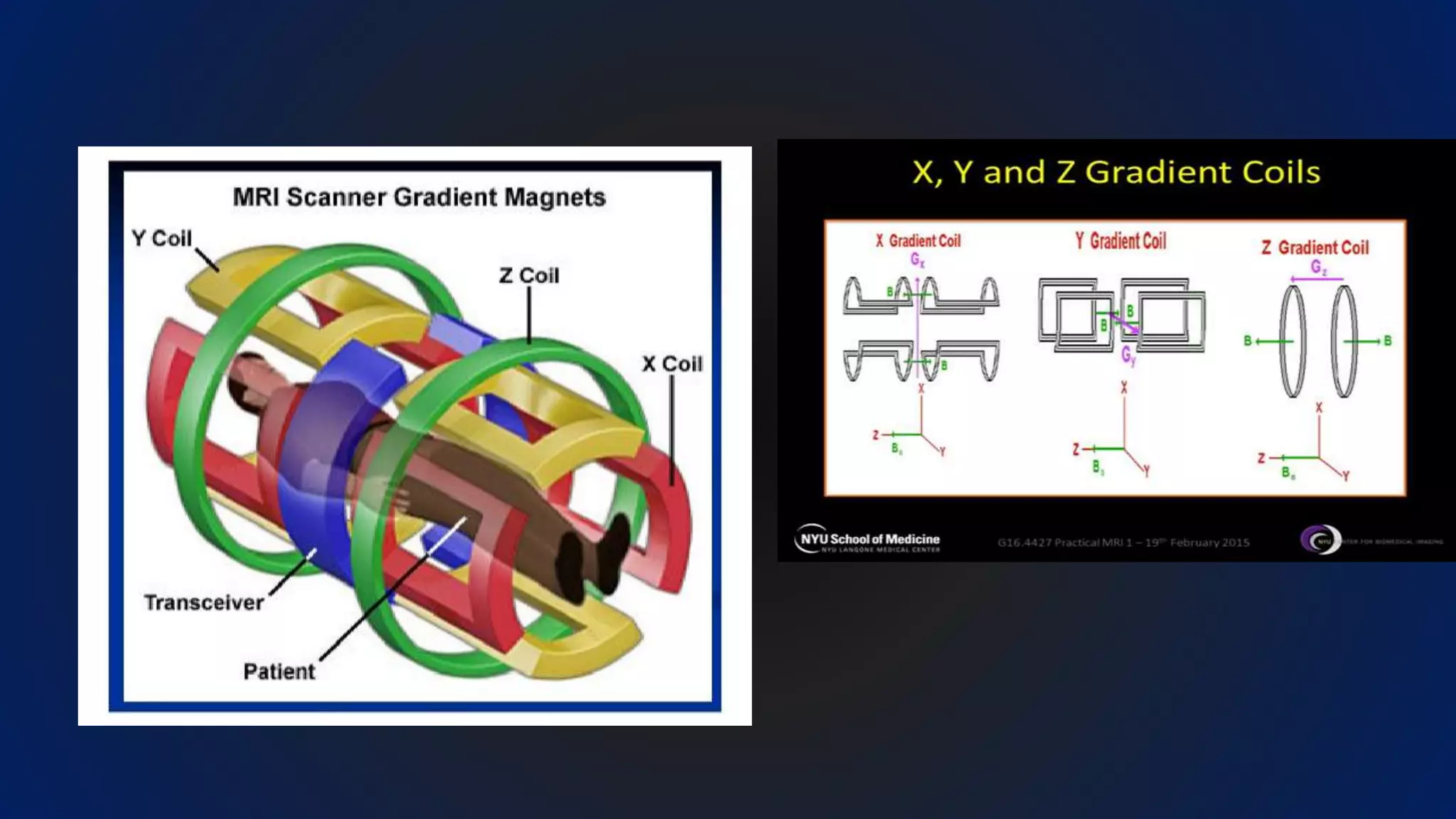

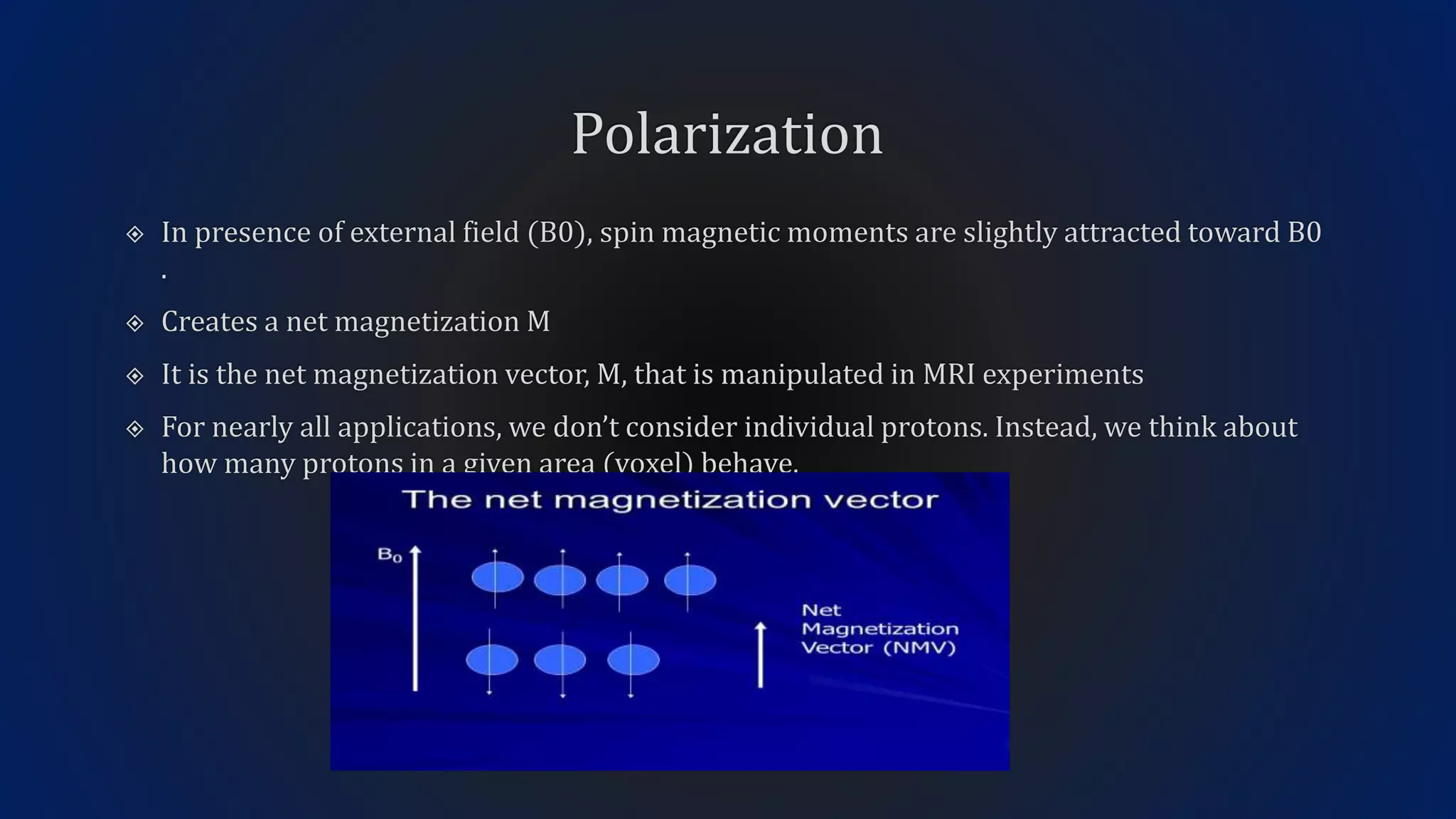
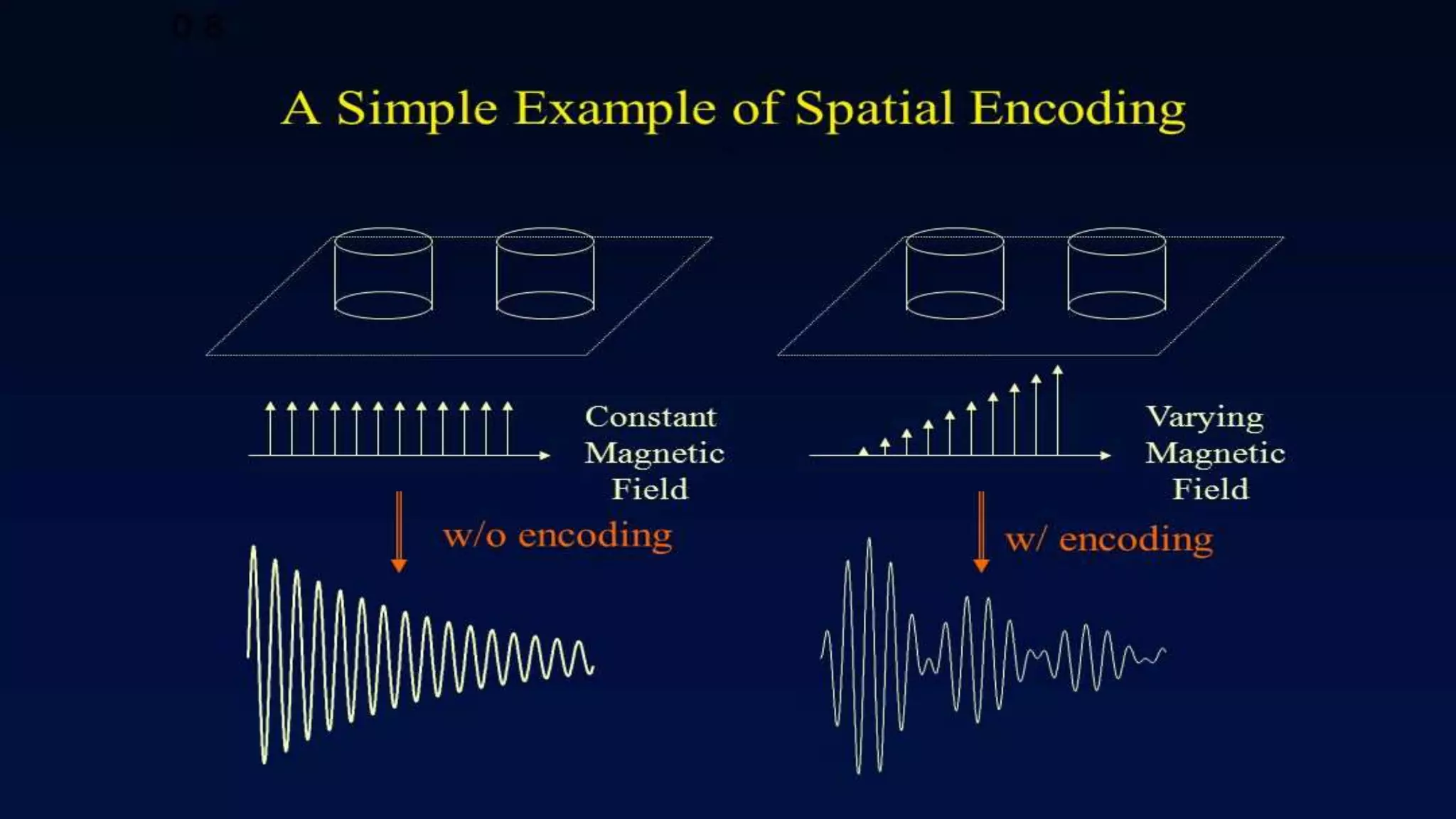
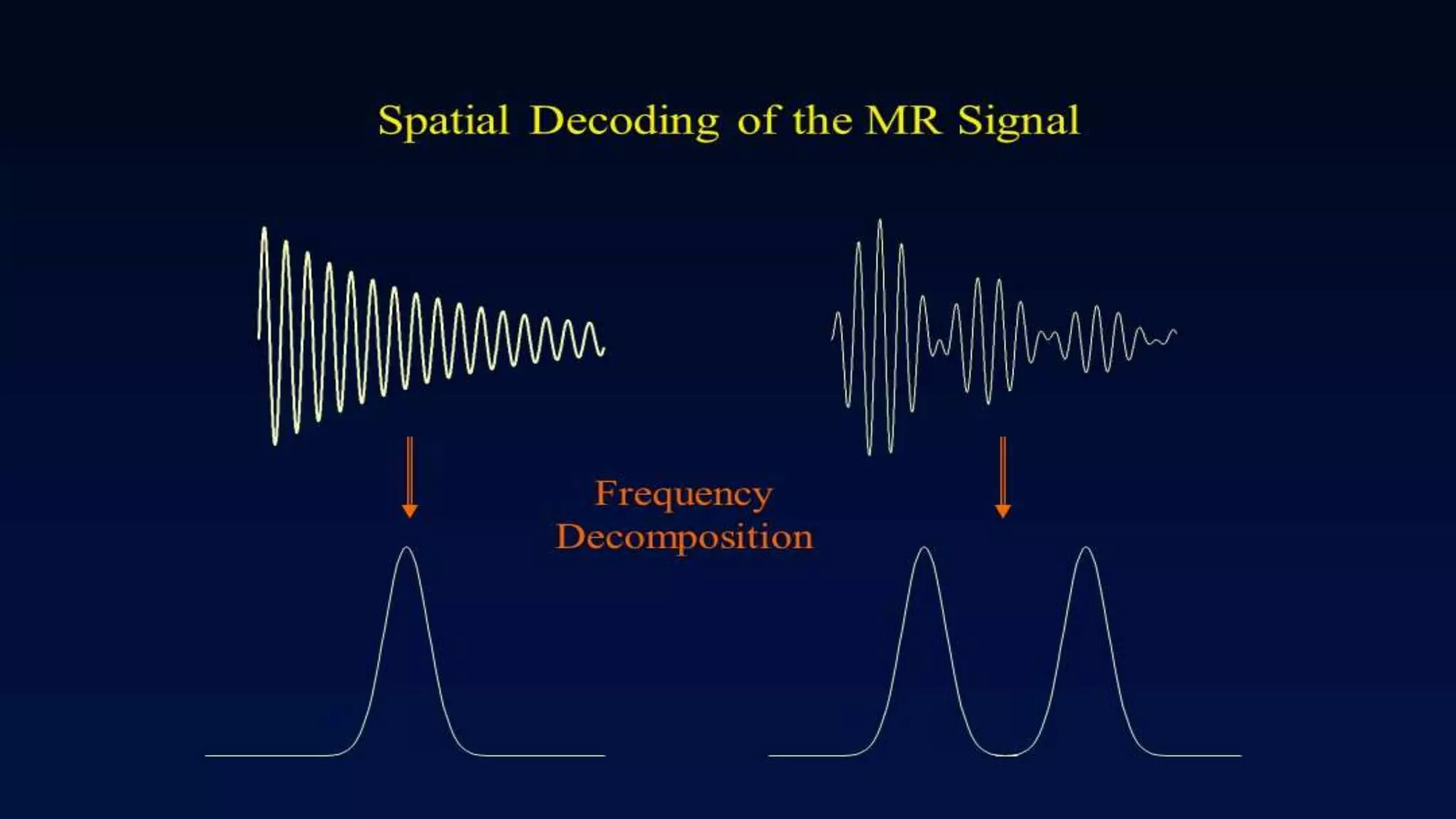

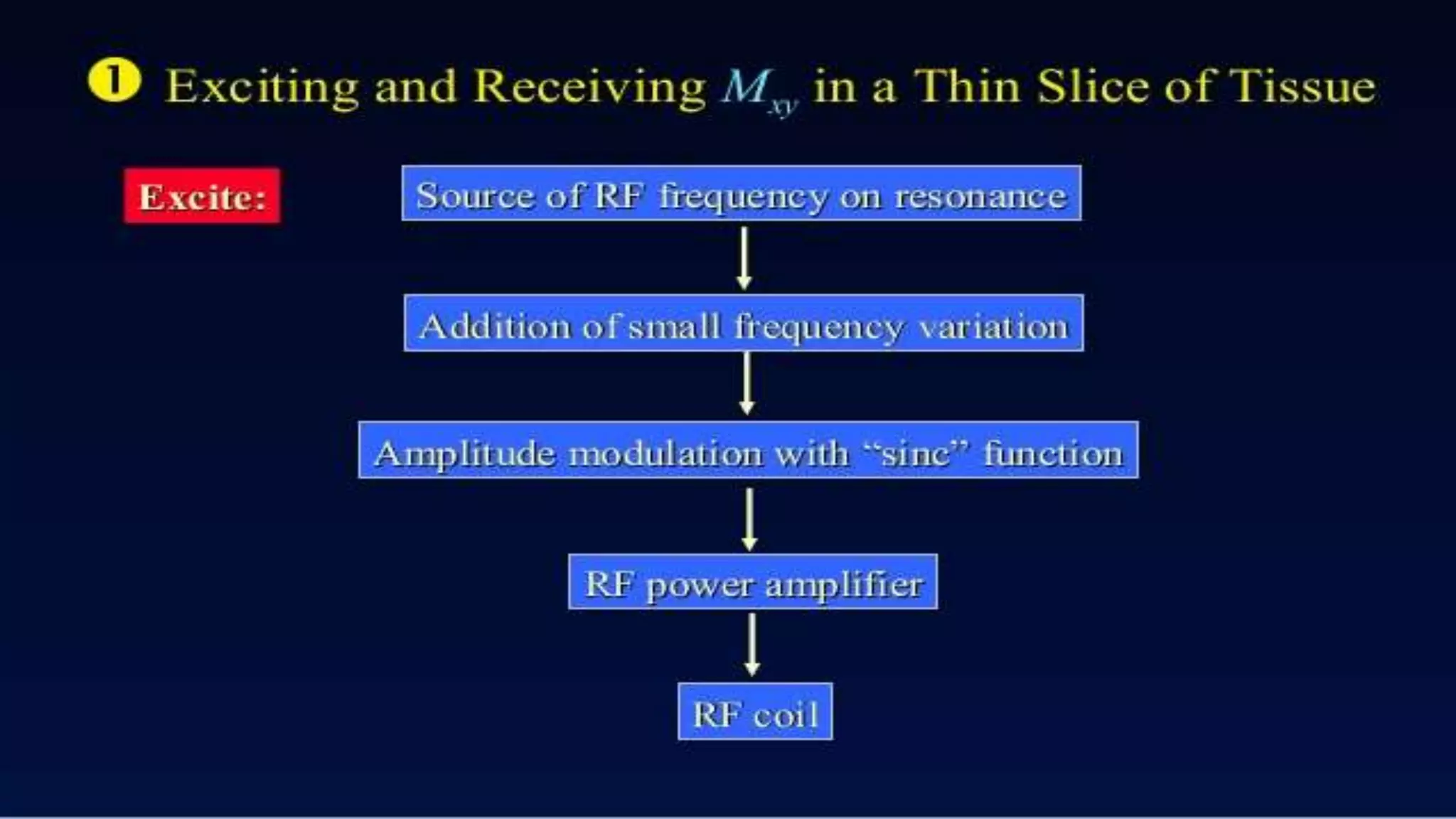
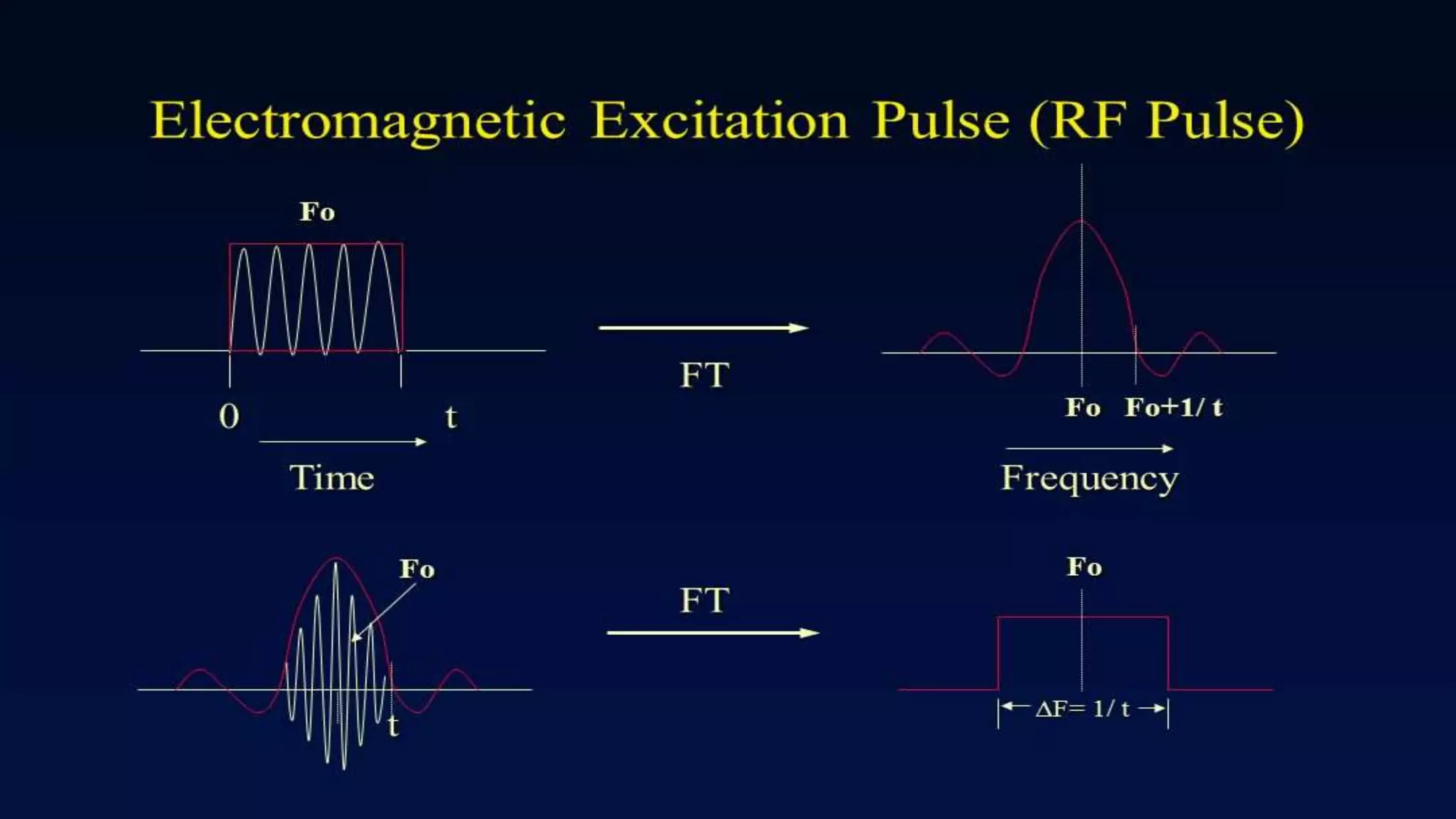
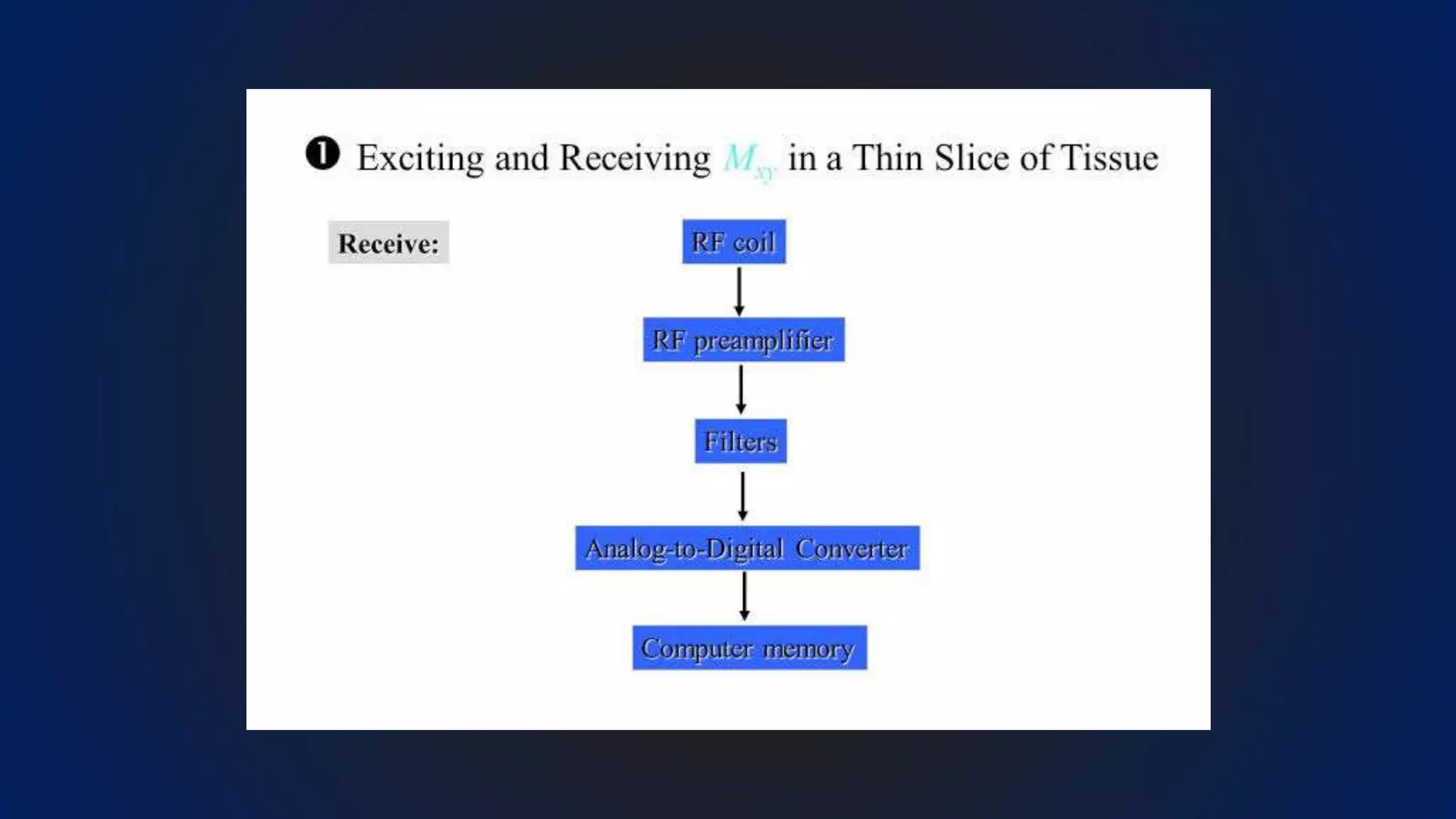
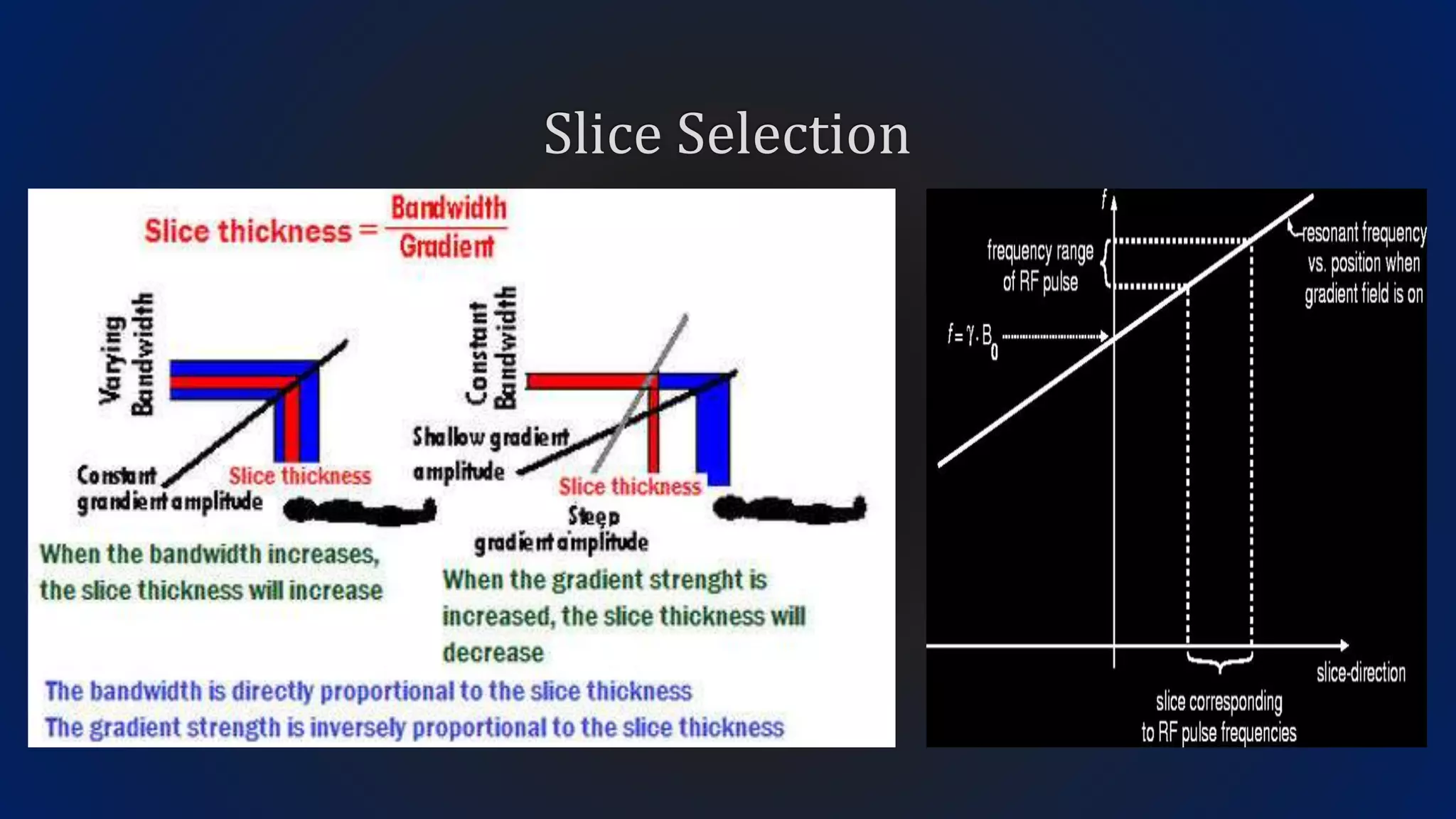

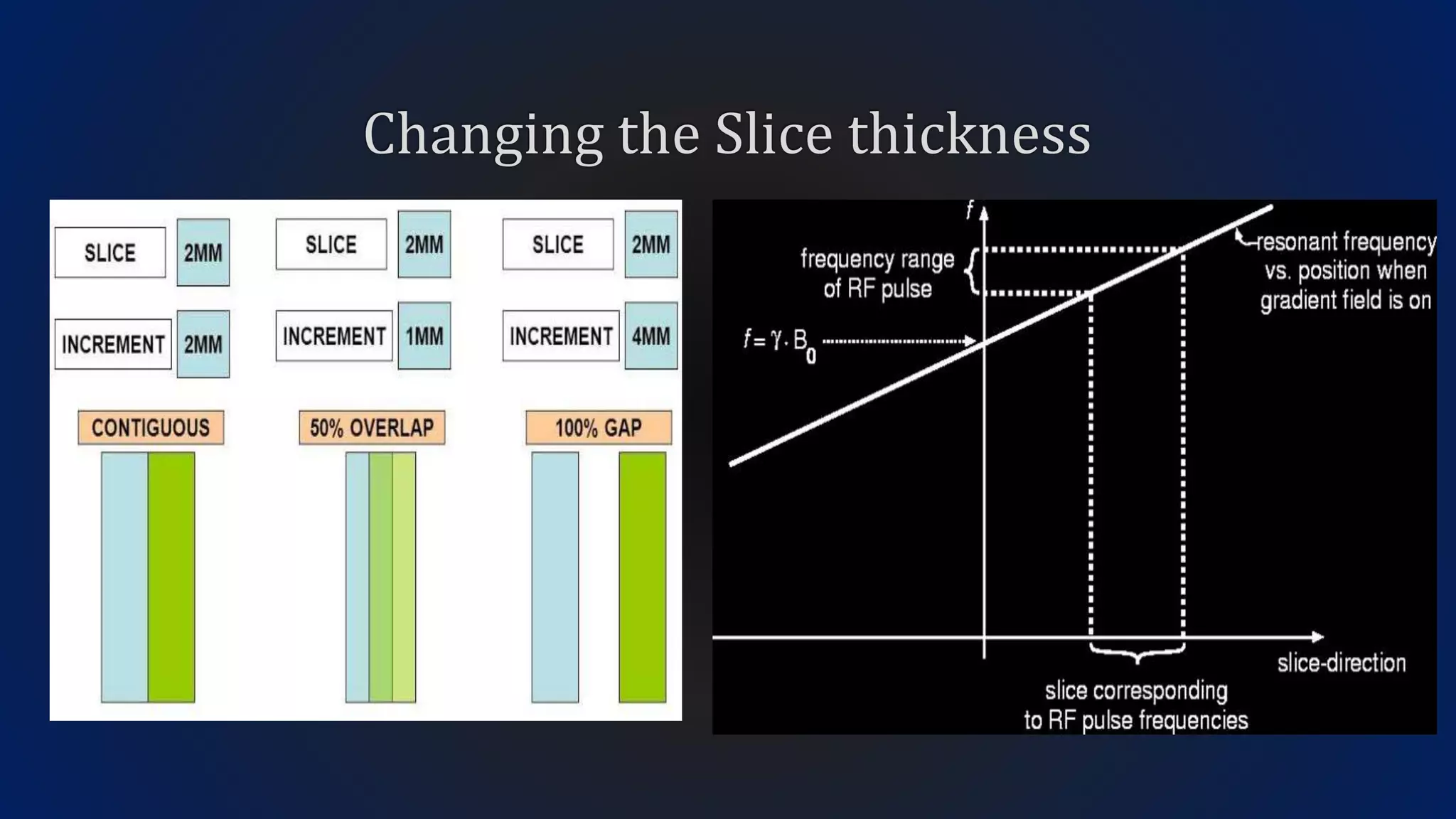

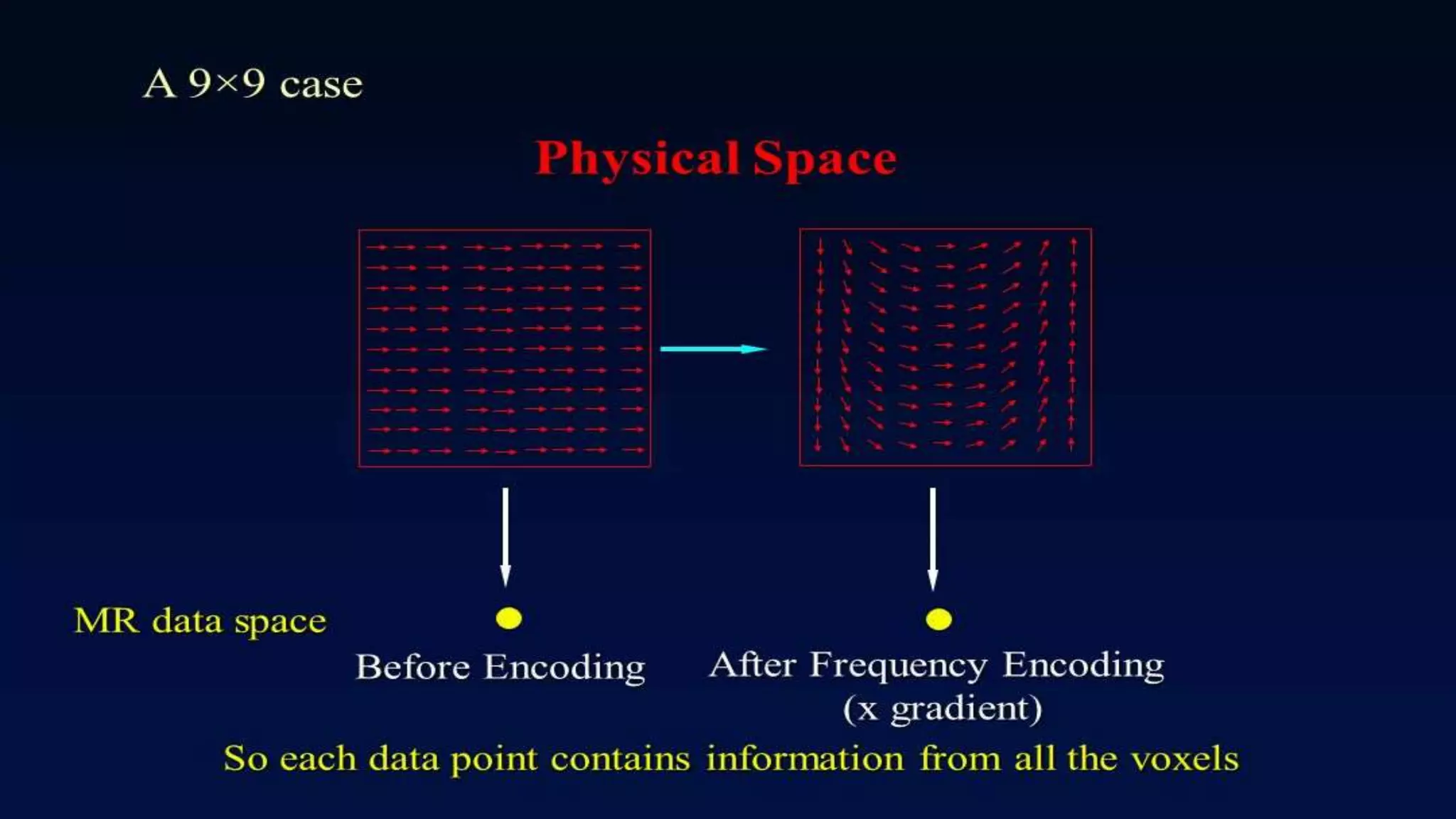
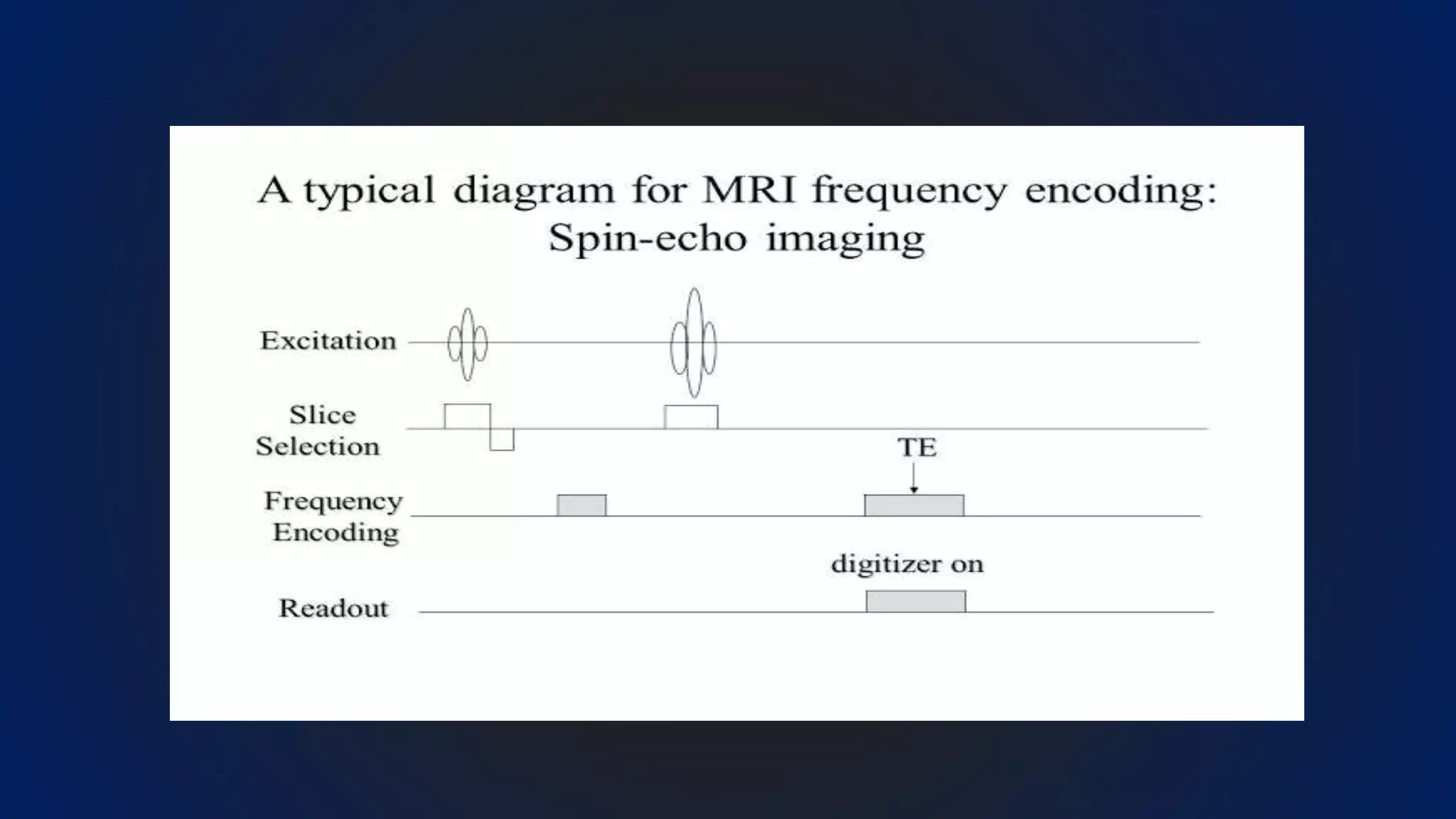
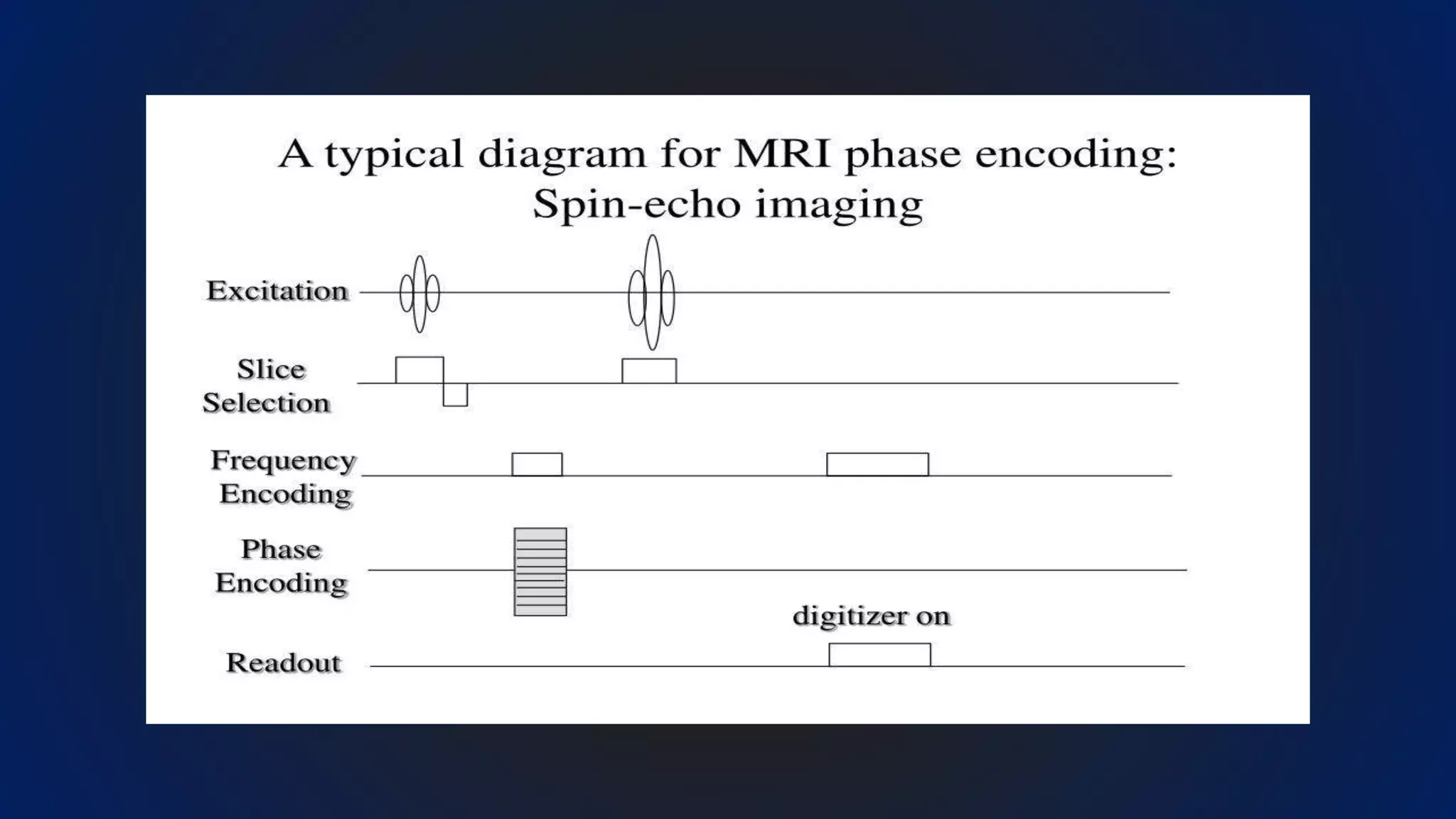

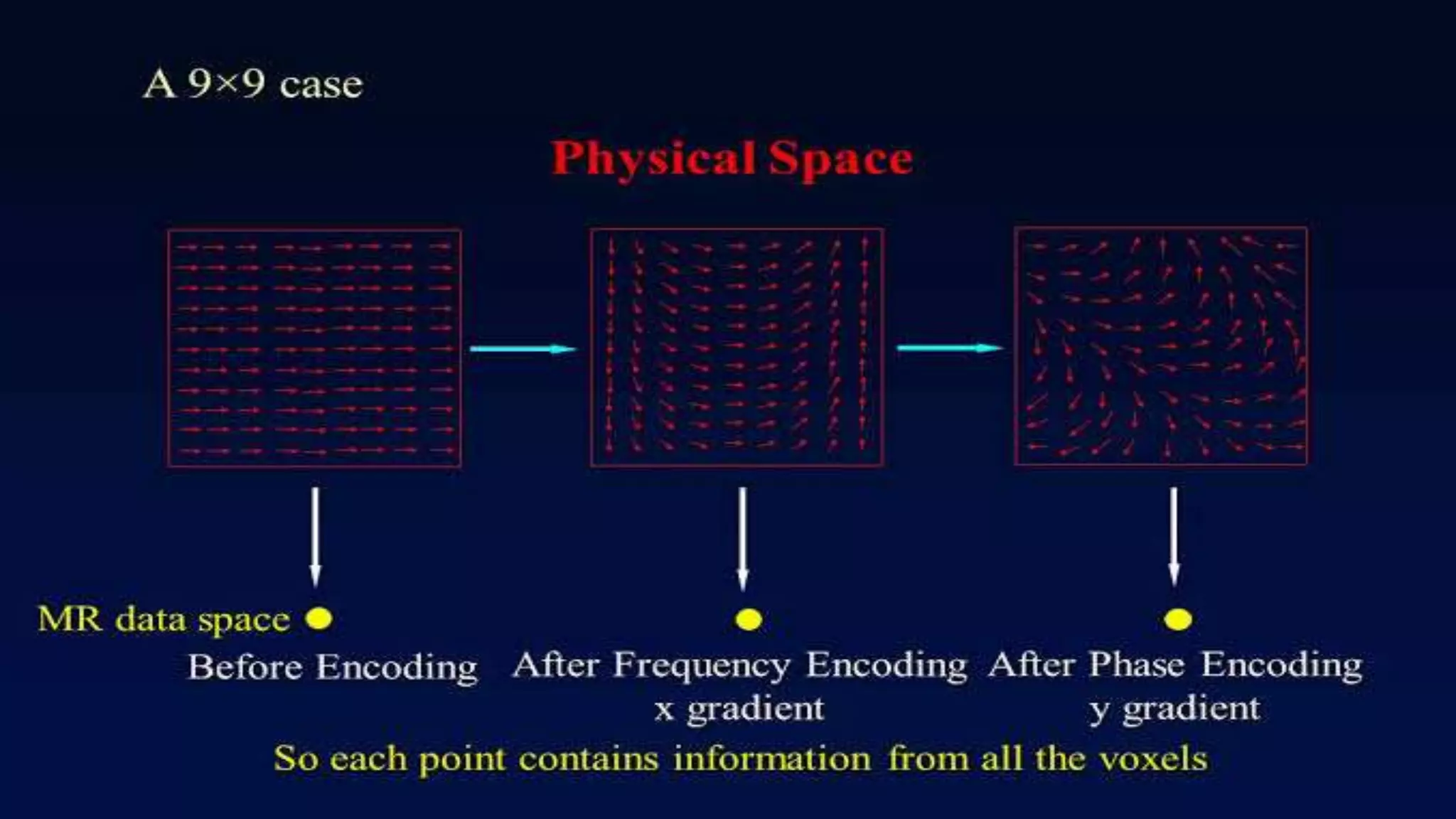
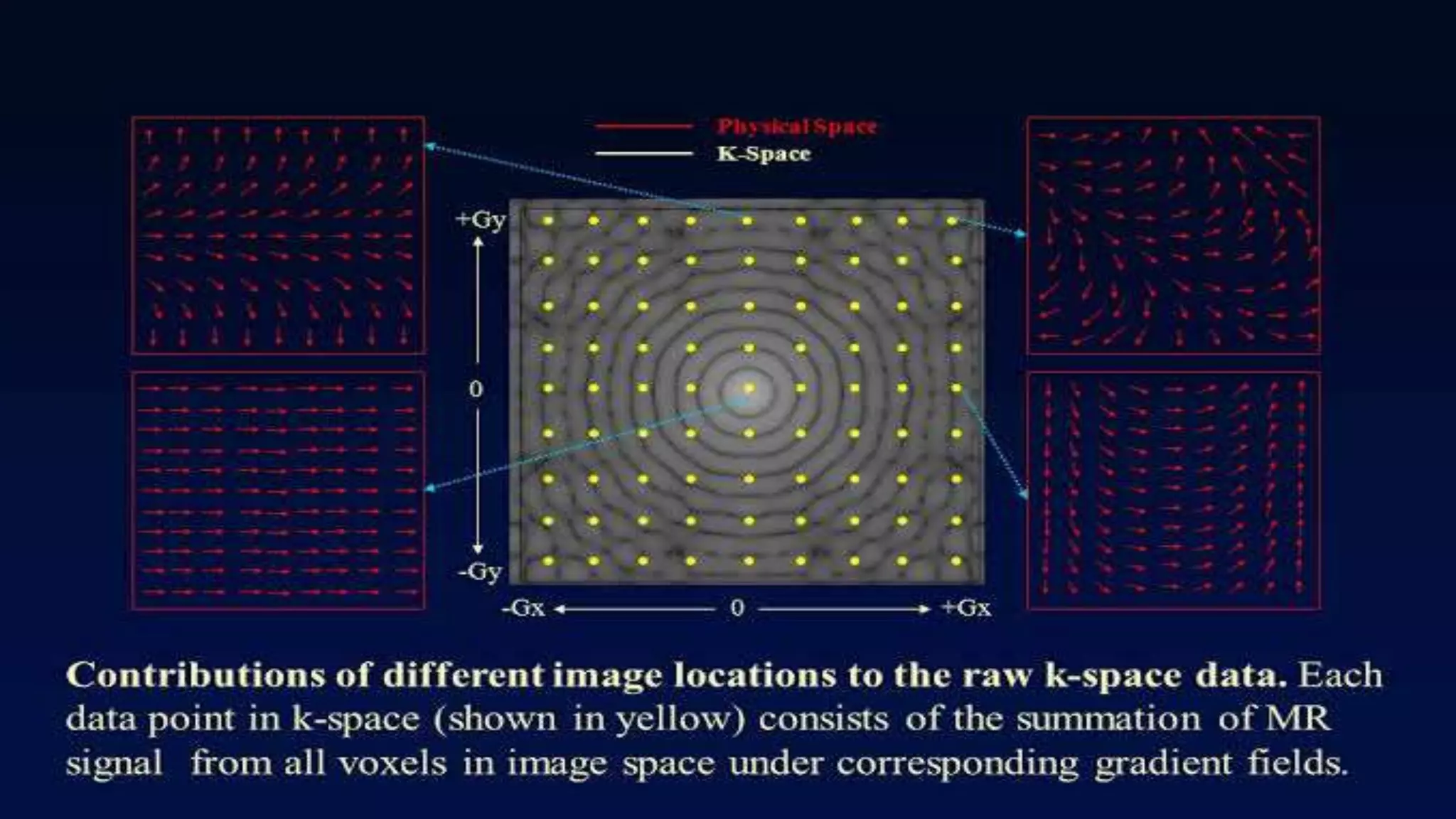
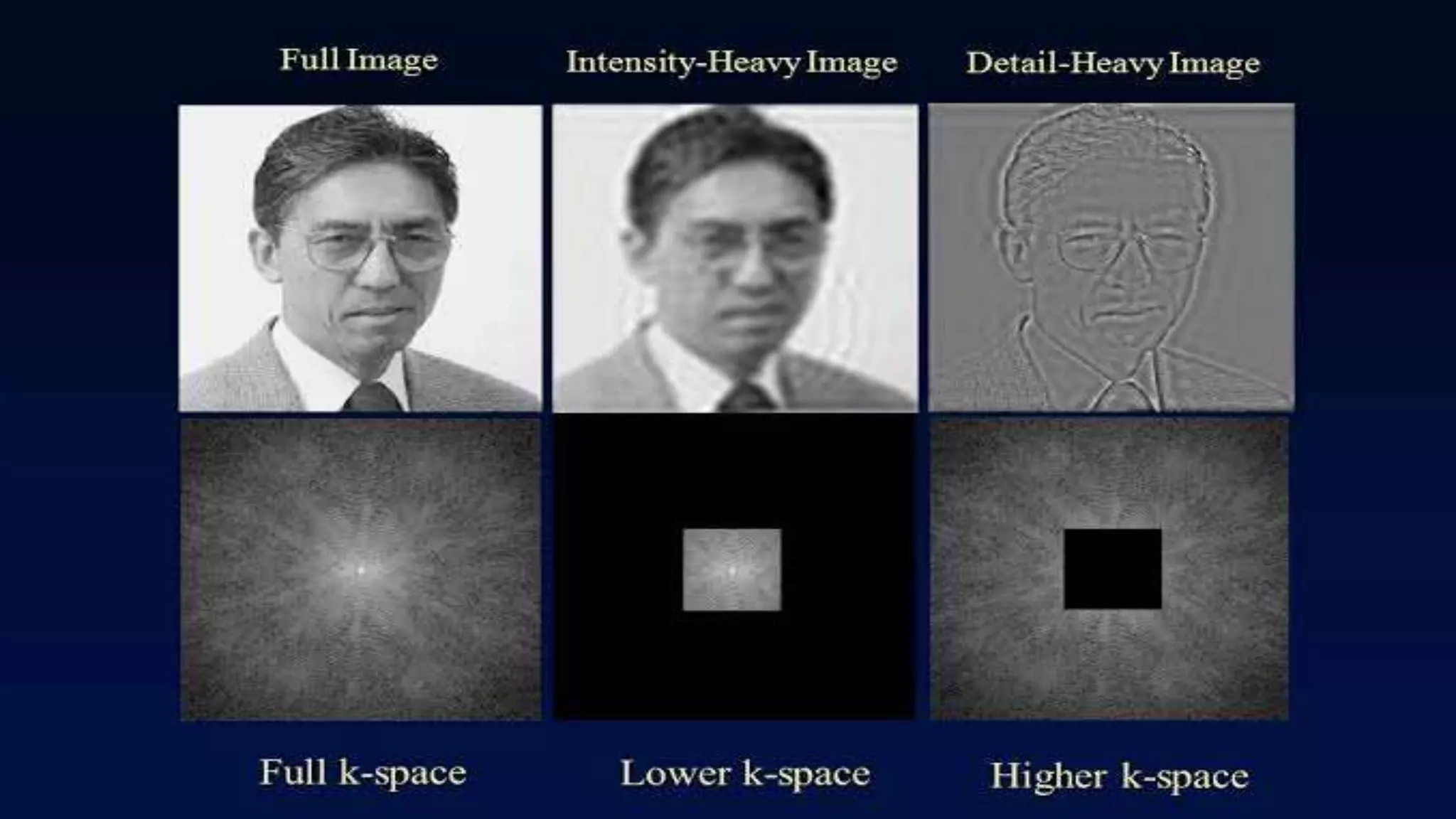
MRI uses the spatial frequency and phase of proton magnetization to form images, rather than projection or reflection methods. The signal is influenced by a frequency-encoding gradient that varies along the horizontal axis, impacting the effective magnetic field at each pixel. Additionally, each pixel encompasses a range of frequencies due to its finite width.

























