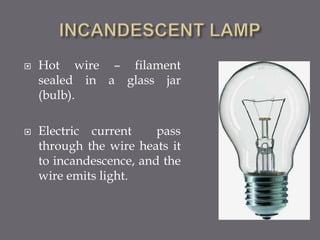
This document discusses different types of lamps used for illumination. It describes incandescent lamps which use a heated filament to produce light and have benefits of being inexpensive and having a warm color but are inefficient. It also describes discharge lamps which produce light through passing electric current through vapor or gas rather than a heated filament. The document also discusses different lighting schemes classified by location and purpose including direct, indirect, semi-direct, and general lighting.