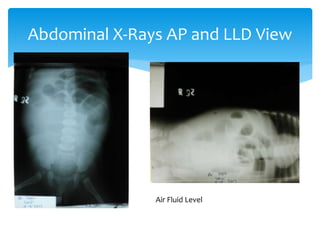
This document discusses ileus obstruction, which occurs when the bowels cannot move food and waste normally due to a blockage. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the blockage but can include abdominal pain, vomiting, distension, and lack of bowel movements. Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging tests like abdominal x-rays and ultrasound, and lab tests. Treatment focuses on rehydration, decompression of the bowels by inserting tubes, and consultation with surgeons who may perform exploratory laparotomy if needed.