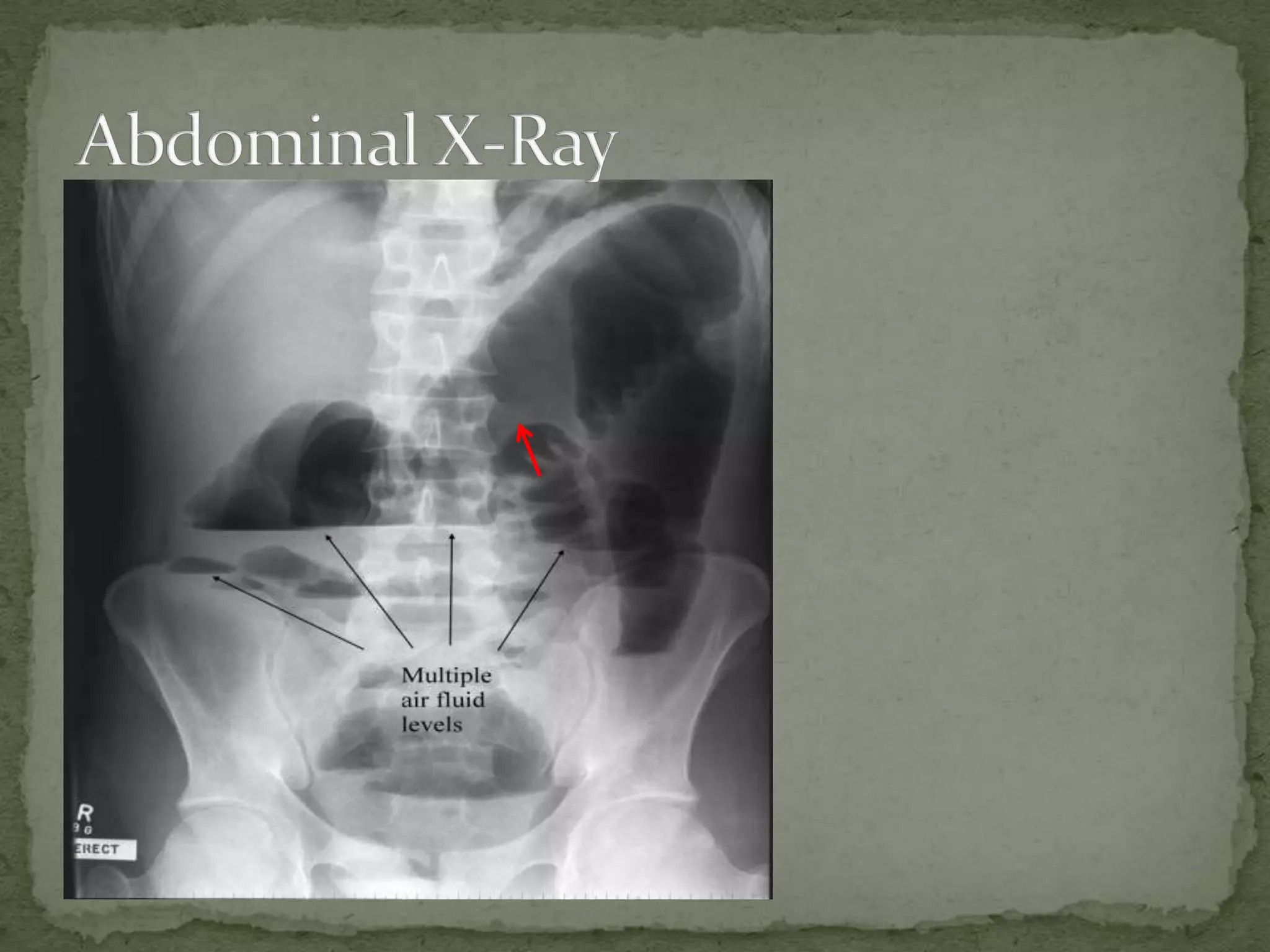
(1) 78 year old white female presents with increasing abdominal distention, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain, and 3 days of constipation. She has a history of chronic constipation.
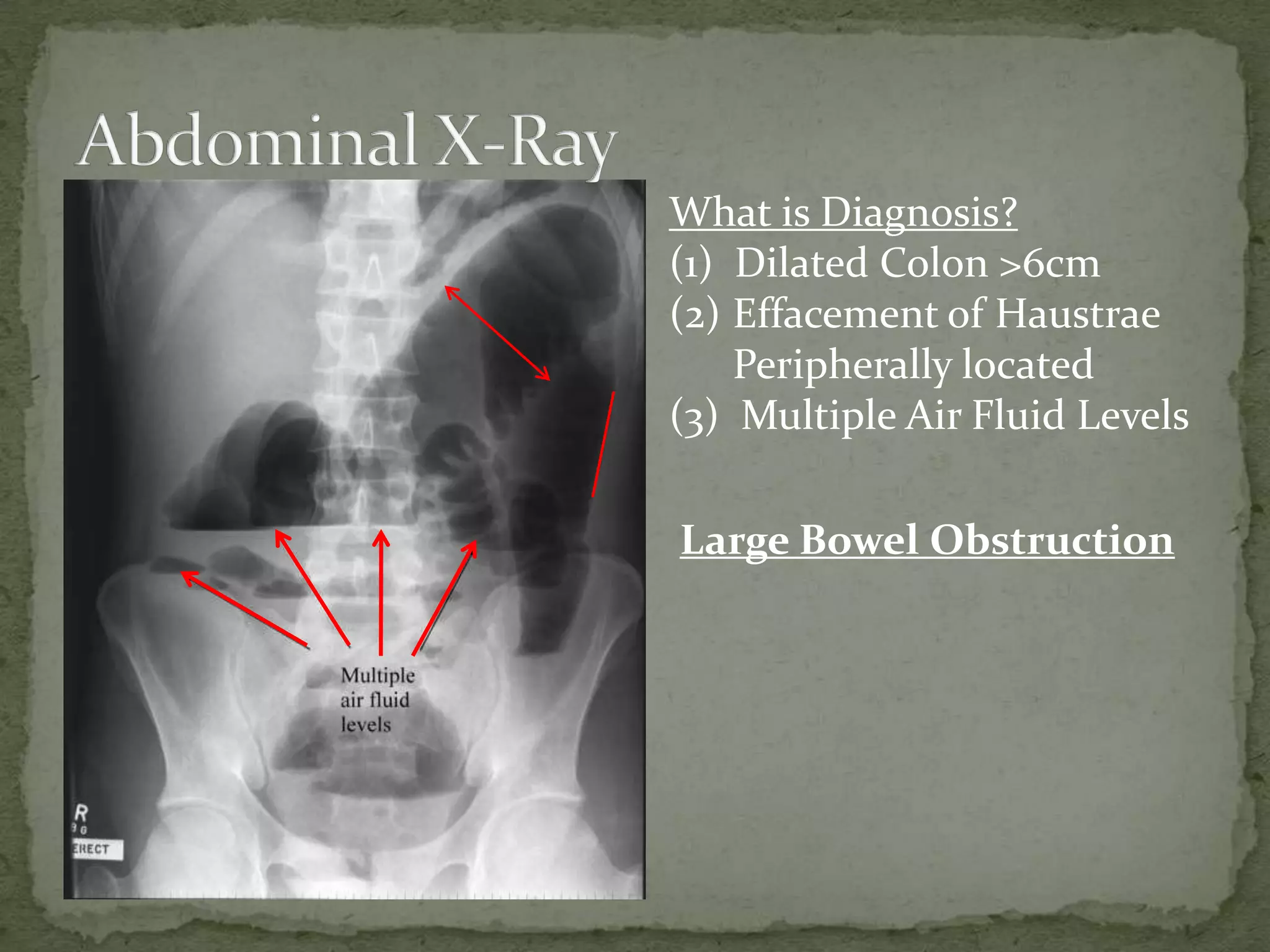
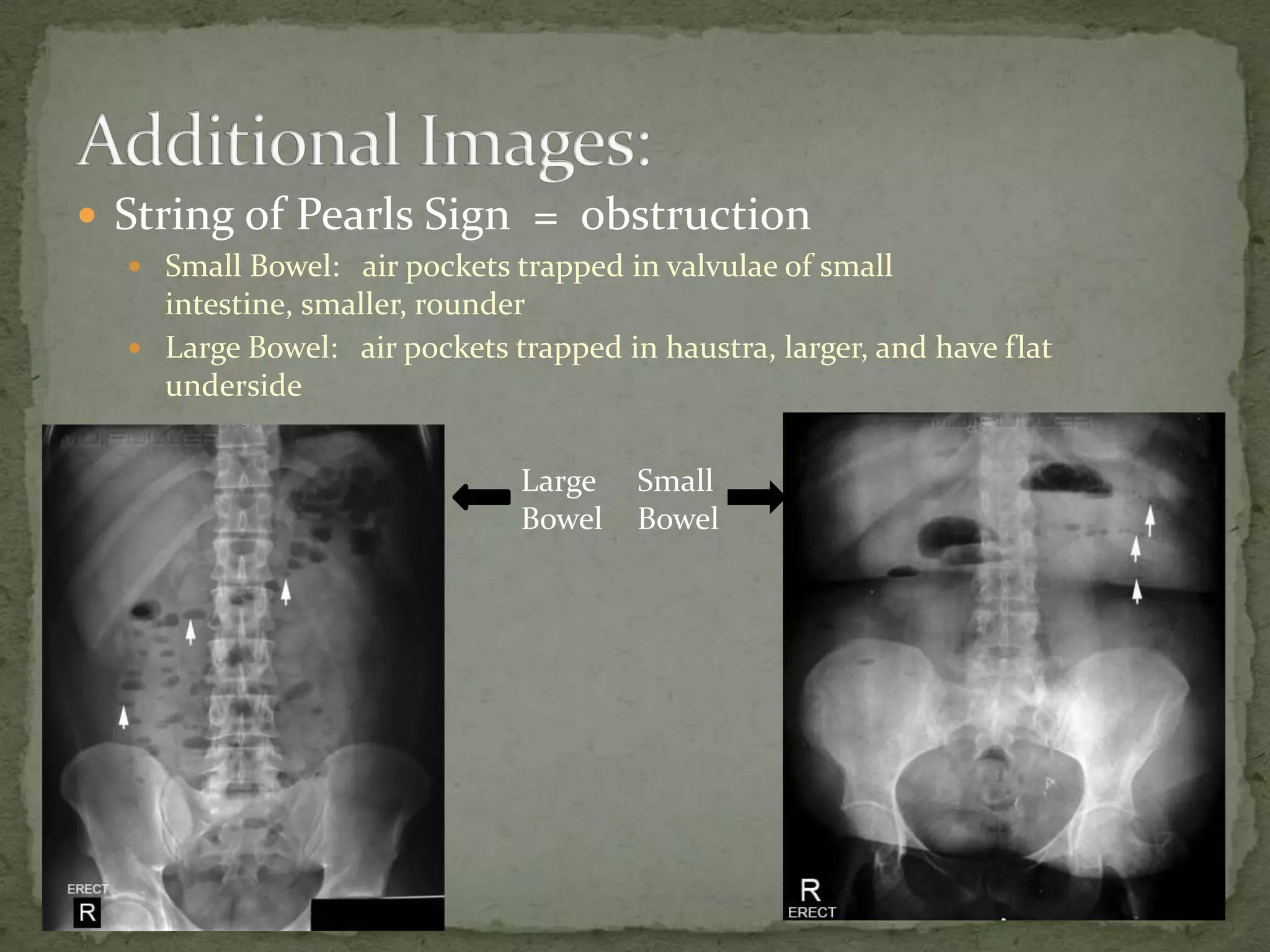
(2) X-ray findings include dilated colon over 6cm, effacement of haustrae peripherally located, and multiple air fluid levels consistent with large bowel obstruction.
(3) Treatment includes IV fluids, analgesics, NG tube, antibiotics, and surgery consult with emergency laparotomy if signs of peritonitis, free air, or sepsis are present.