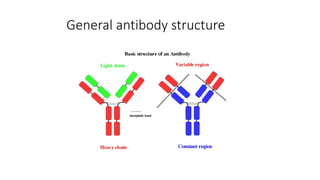
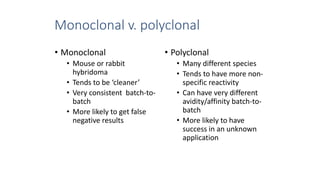
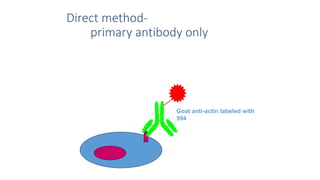
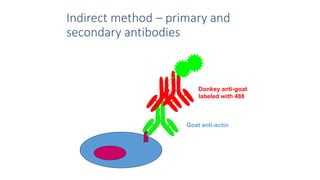
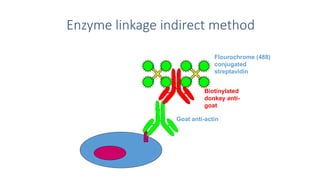
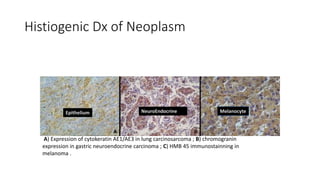
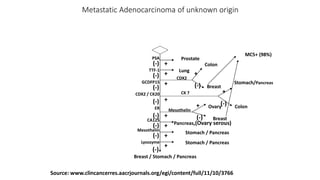
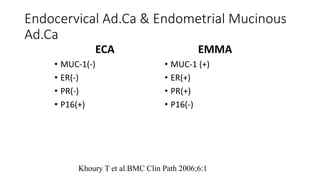
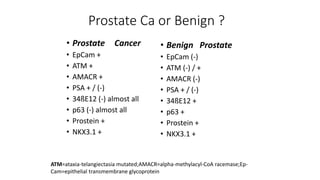
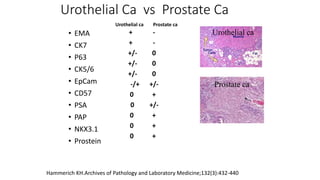
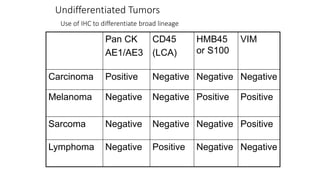
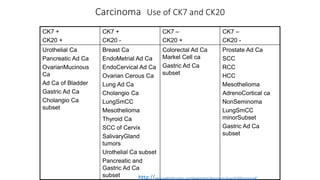
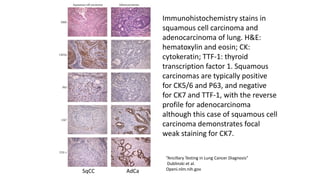
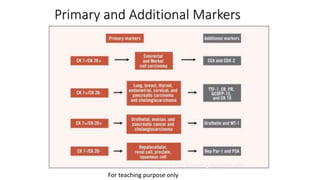
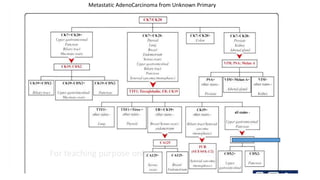
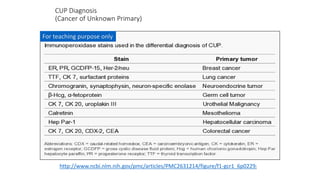
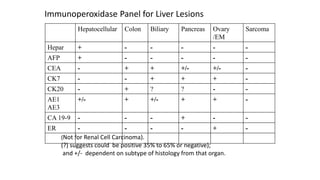
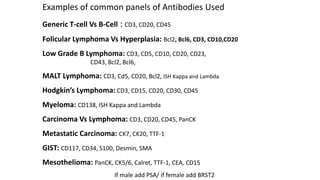
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) combines histological and immunological techniques to identify specific tissue components using antigen-antibody reactions tagged with visible labels. IHC allows visualization of the distribution and localization of cellular components. Antibodies bind specifically to antigens, providing spatial location of particular cells and proteins. Important considerations for IHC include antibody selection, fixation, antigen retrieval, controls, and detection methods such as direct, indirect, and enzyme-linked methods. IHC is useful for tumor diagnosis, classification, predictive markers, and distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions.