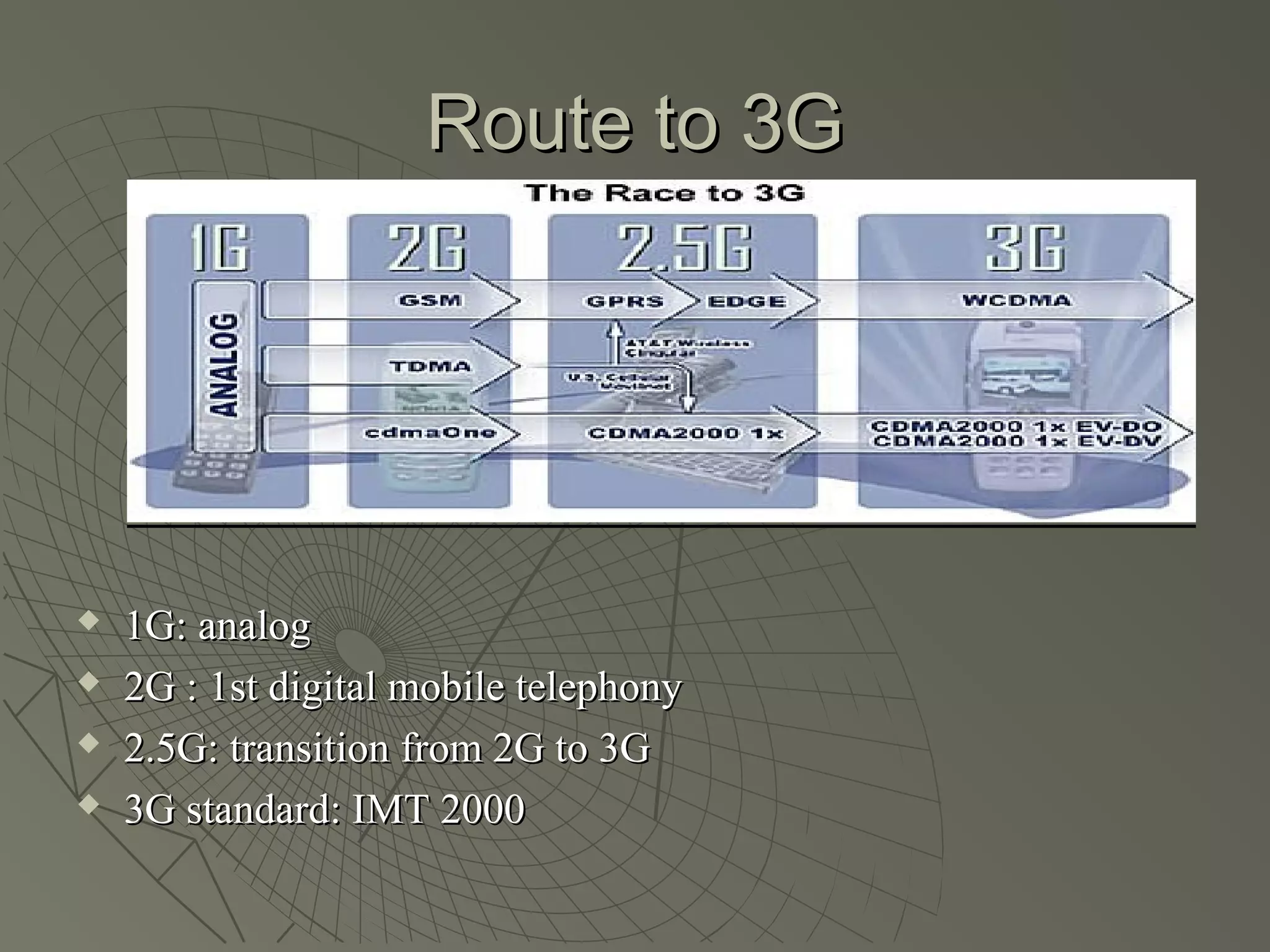
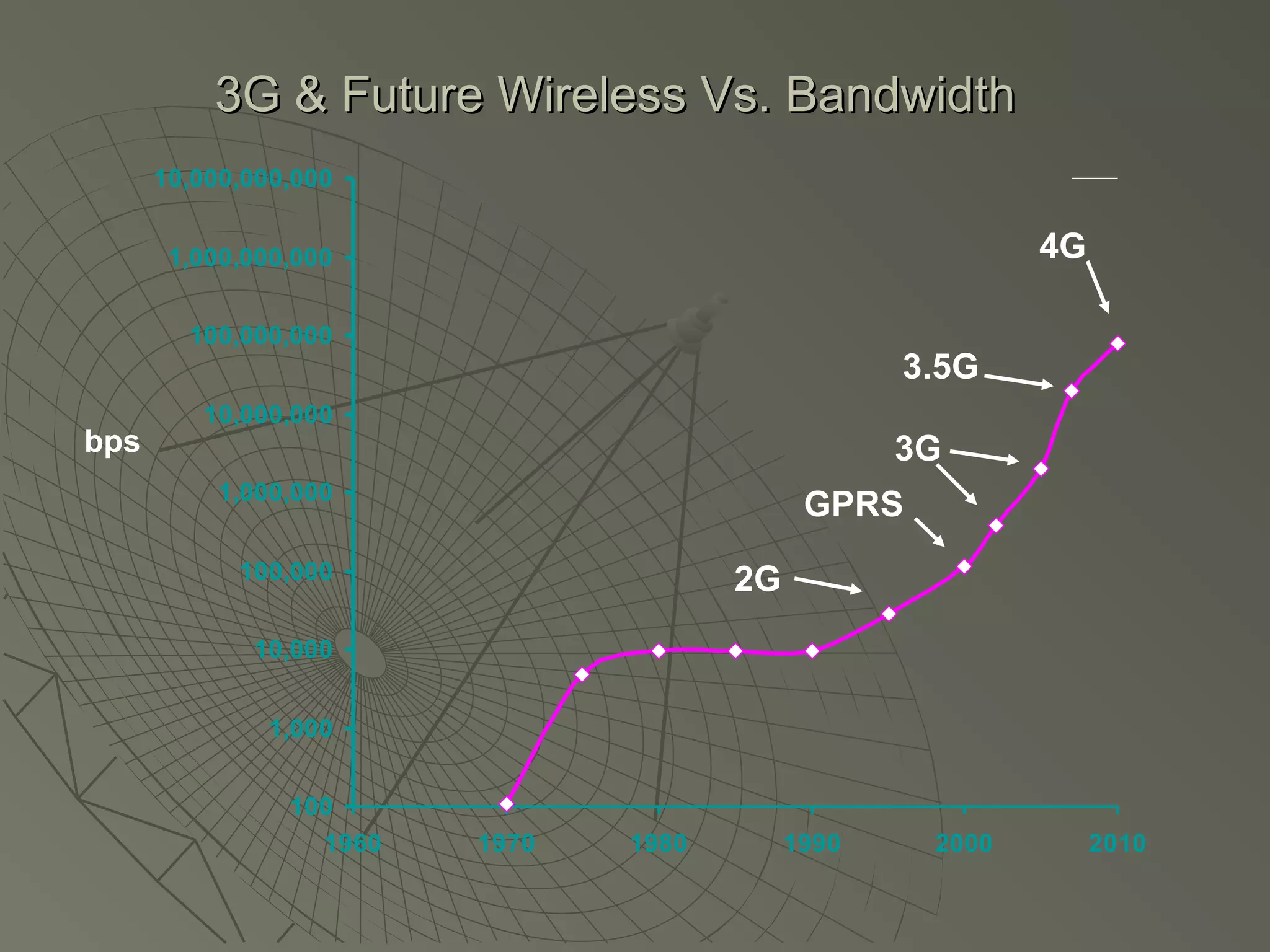
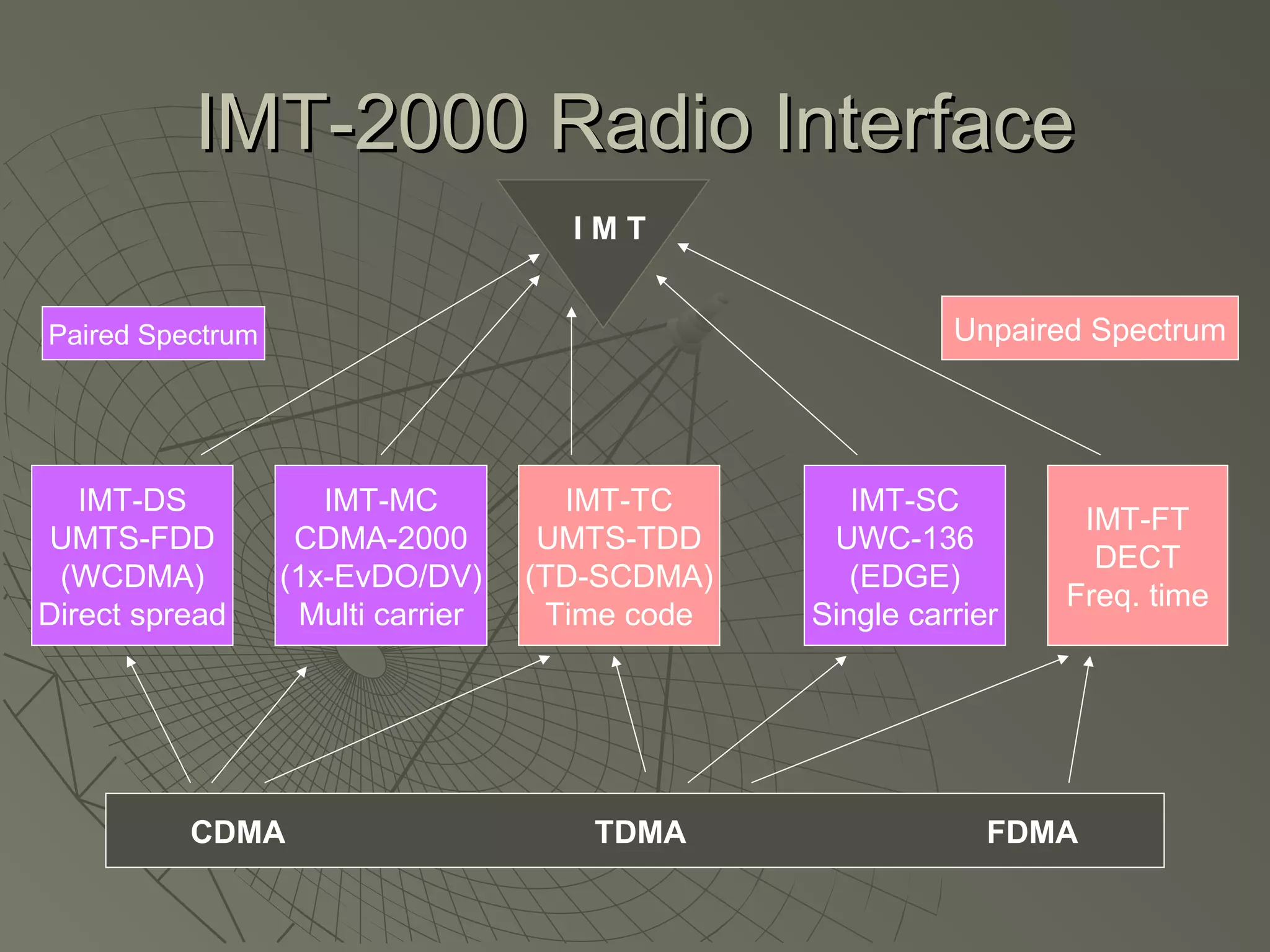
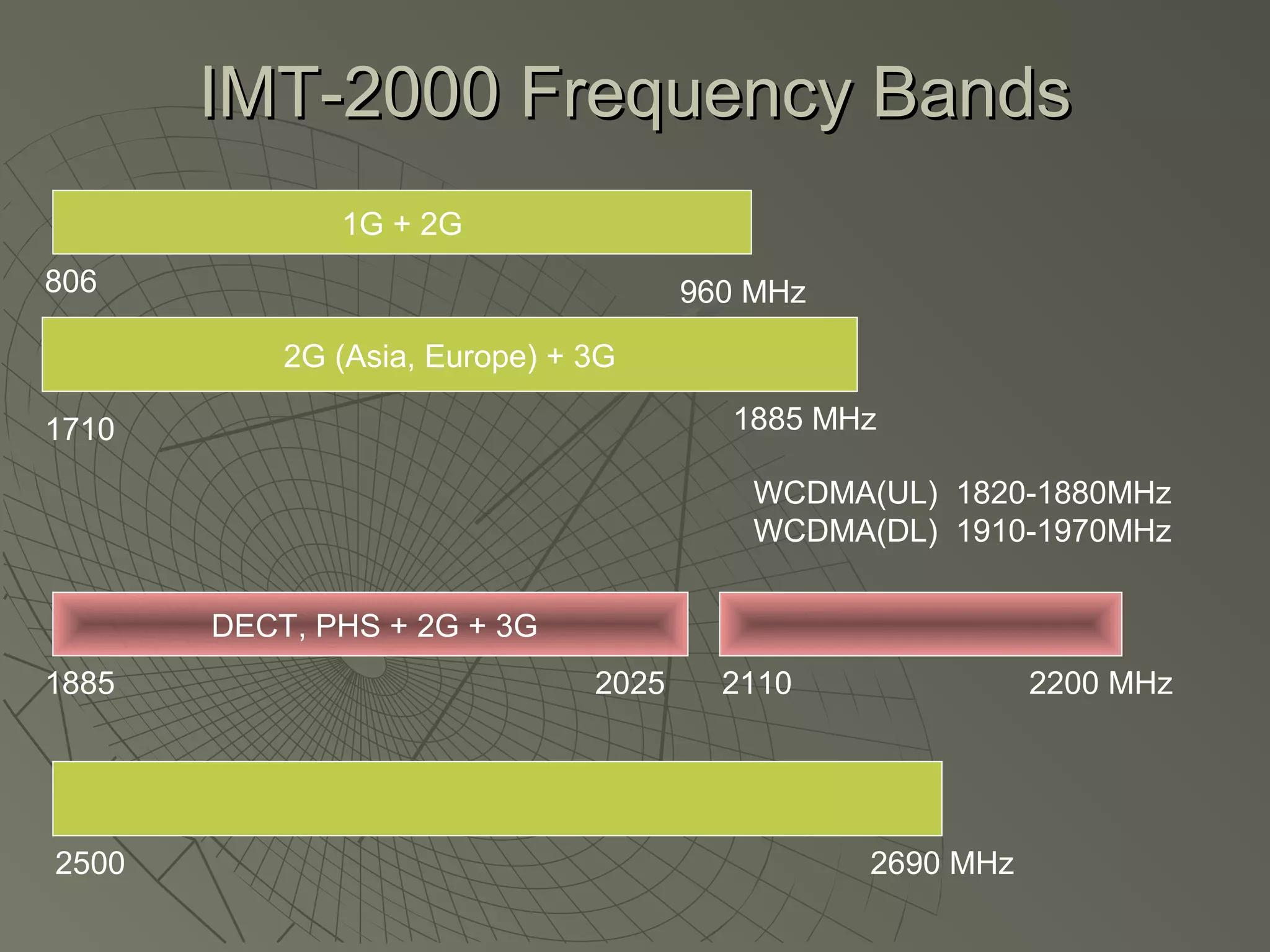
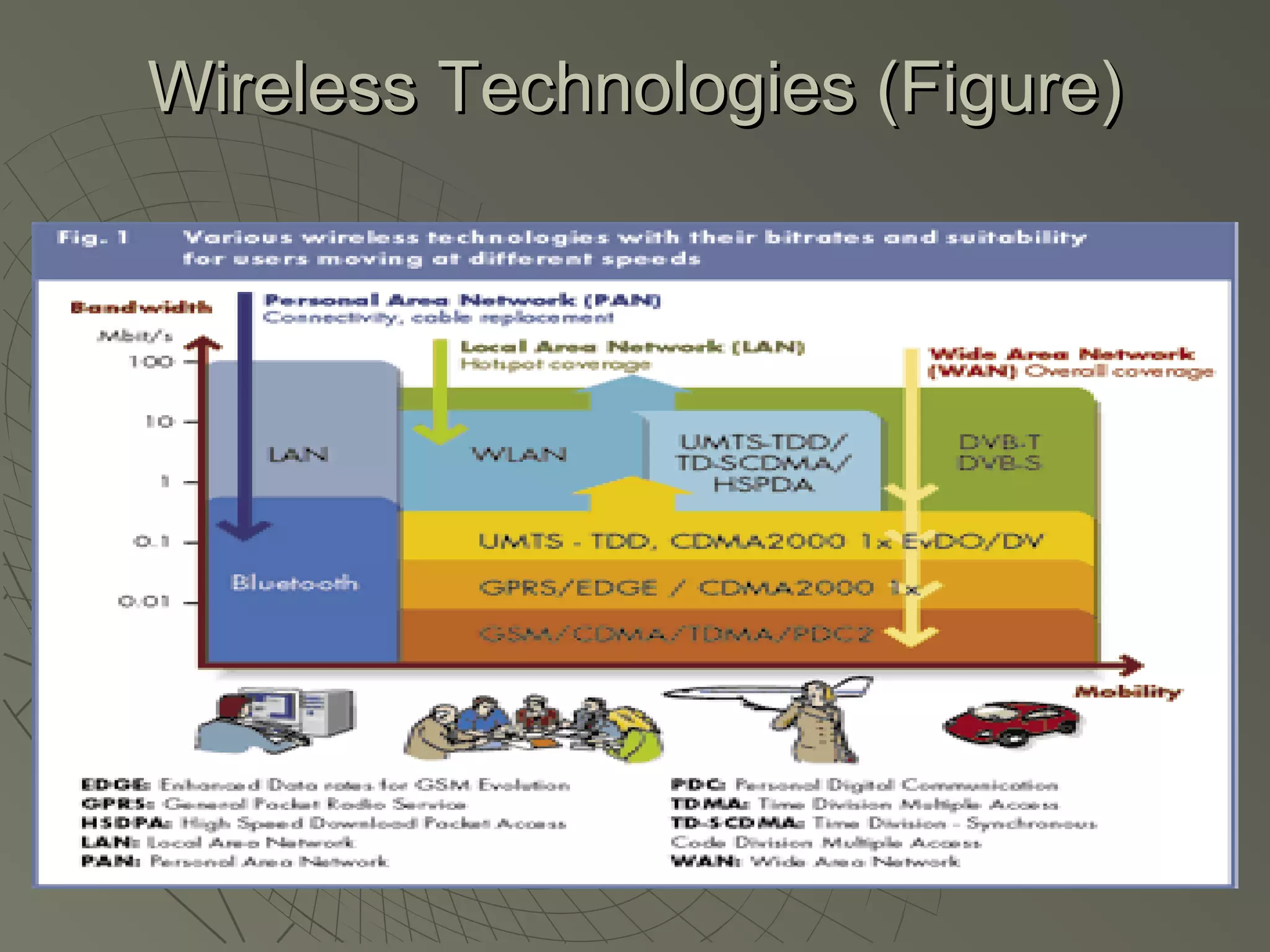
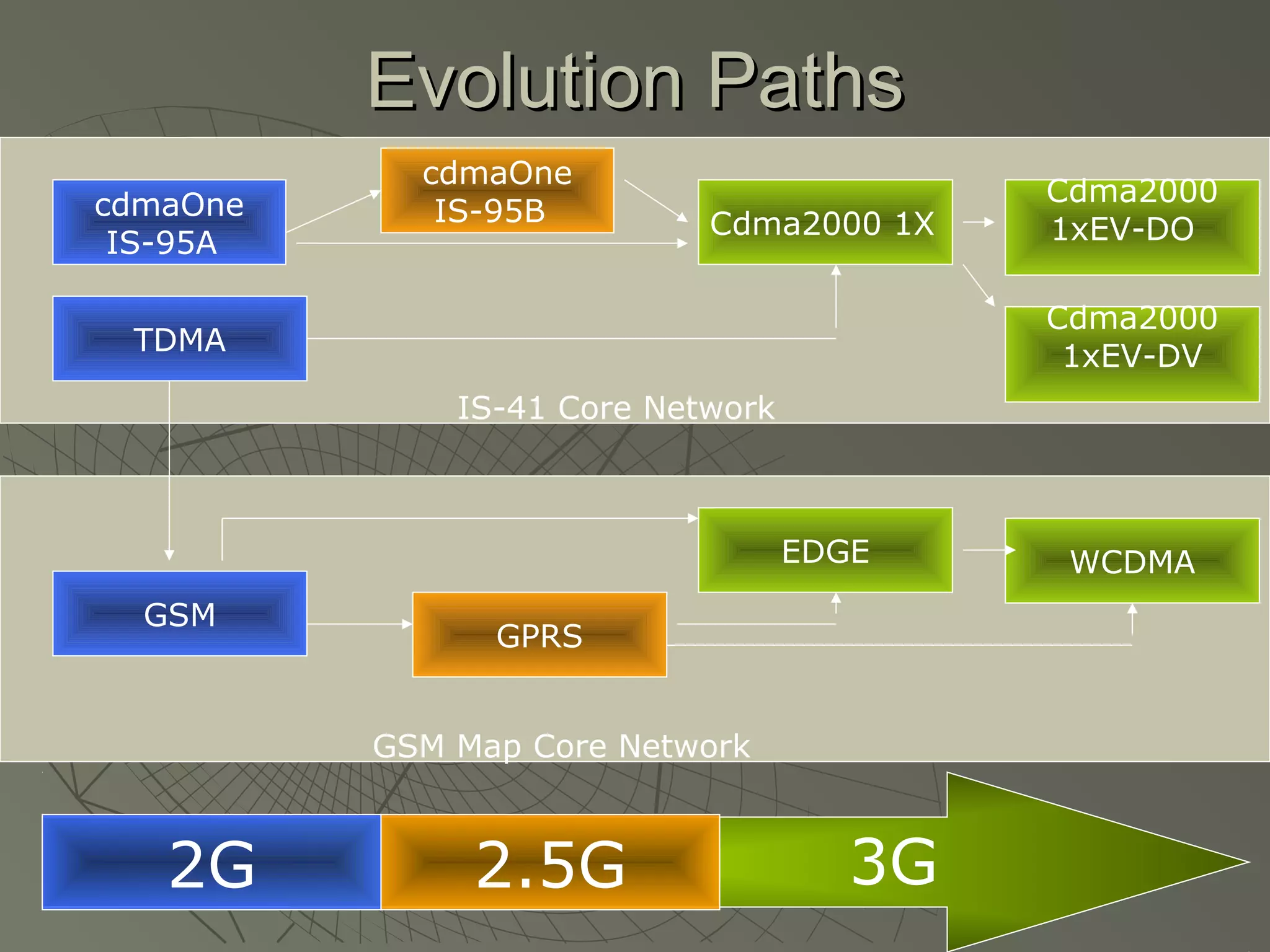
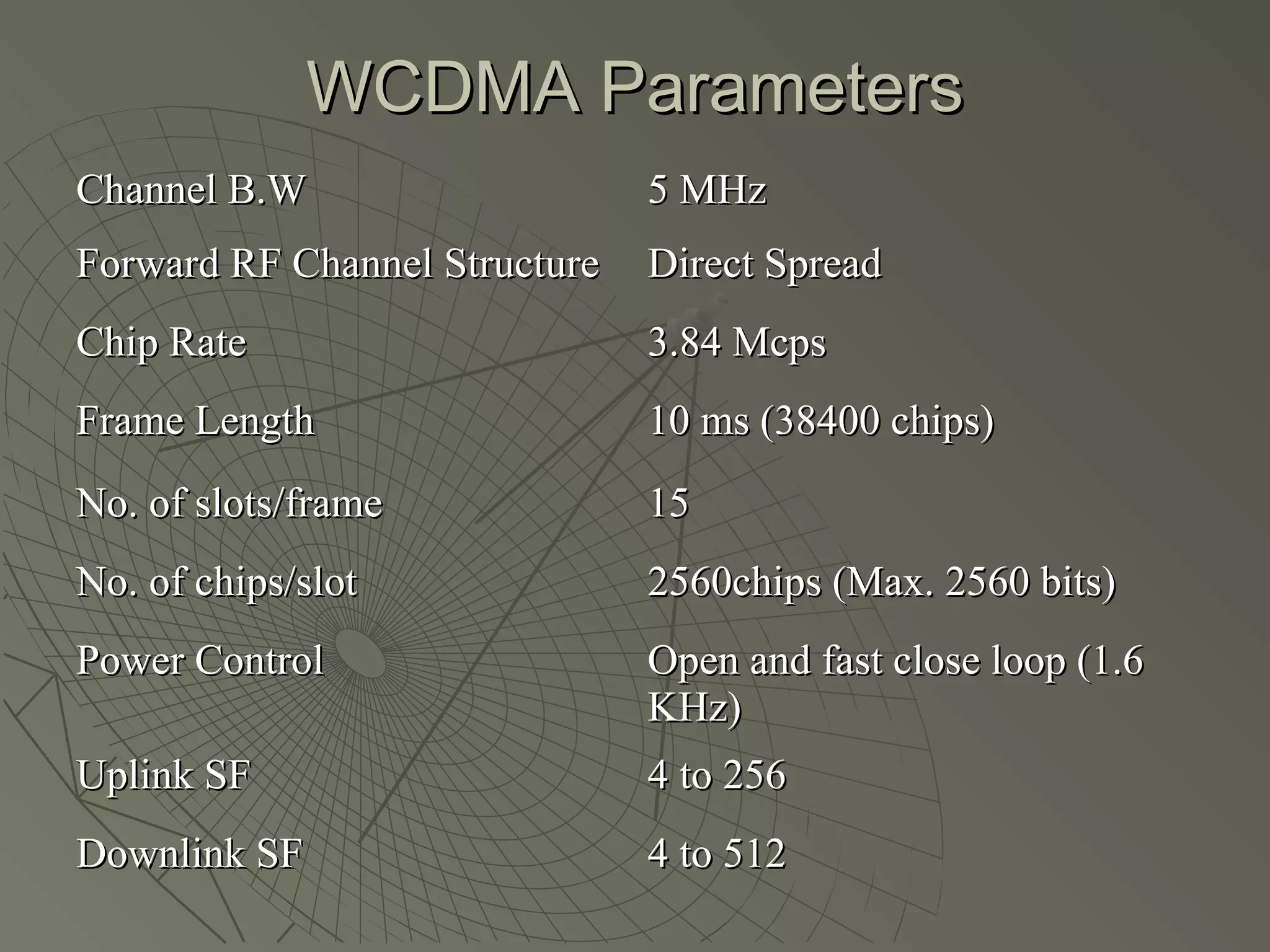
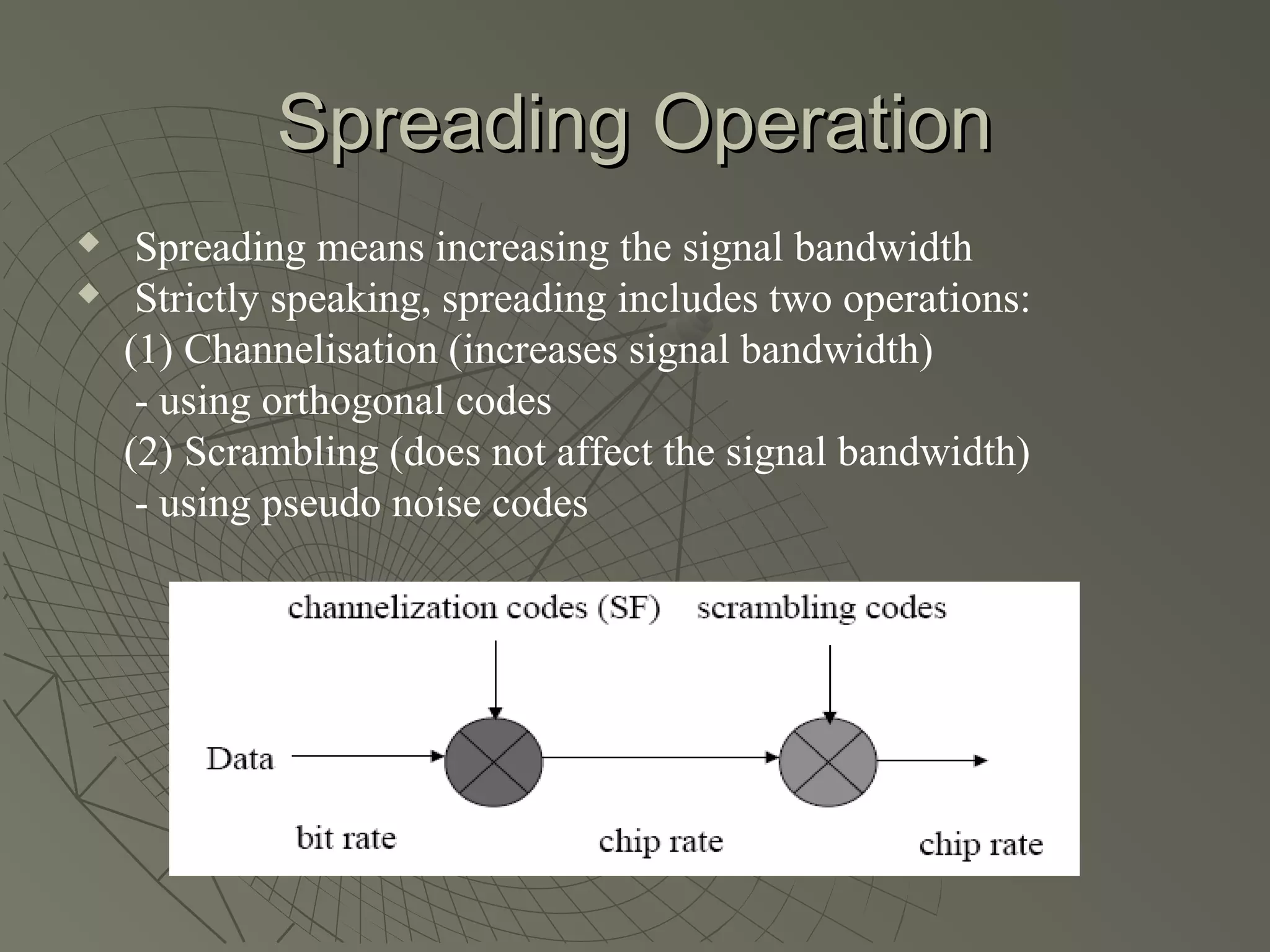
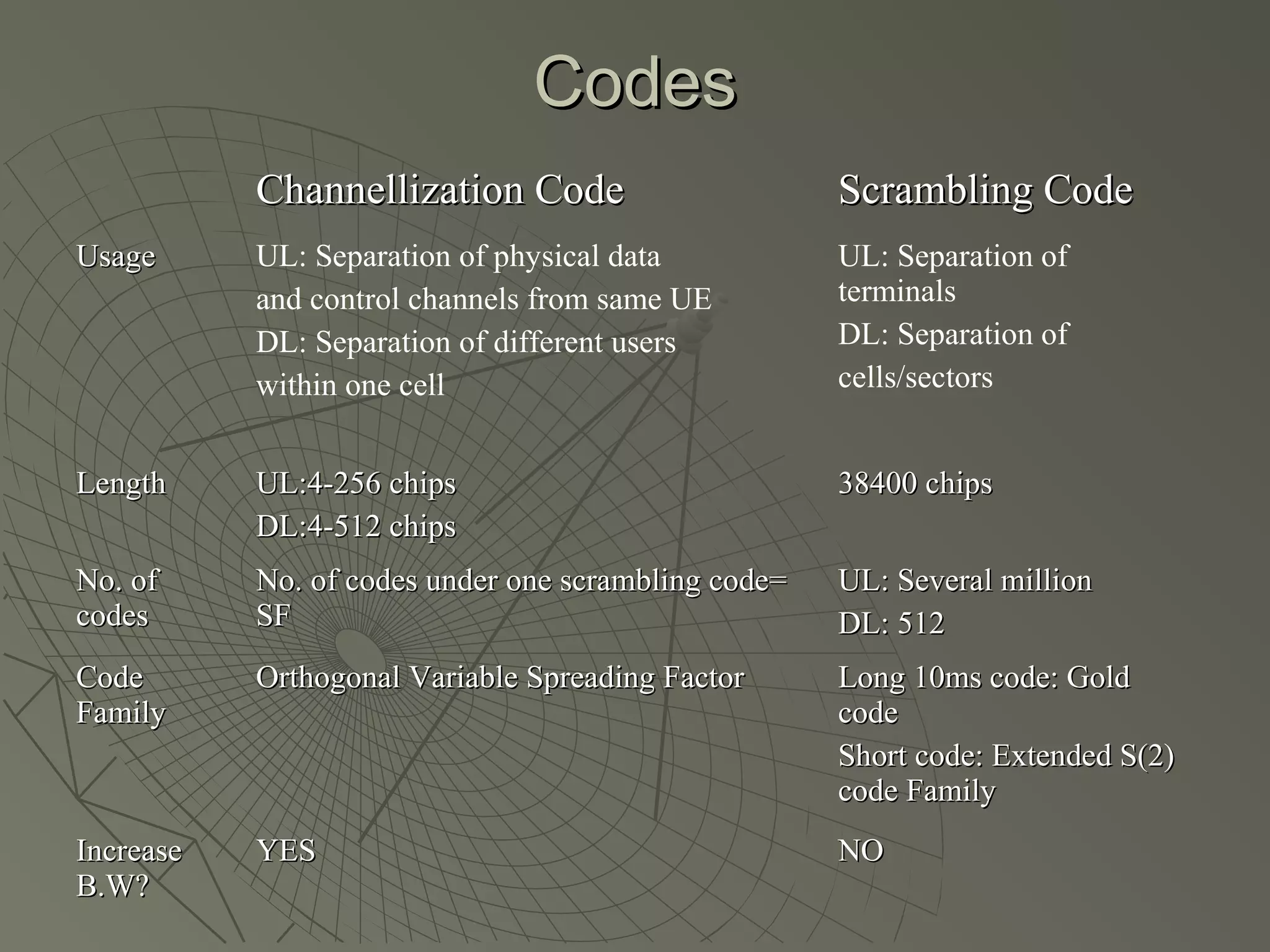
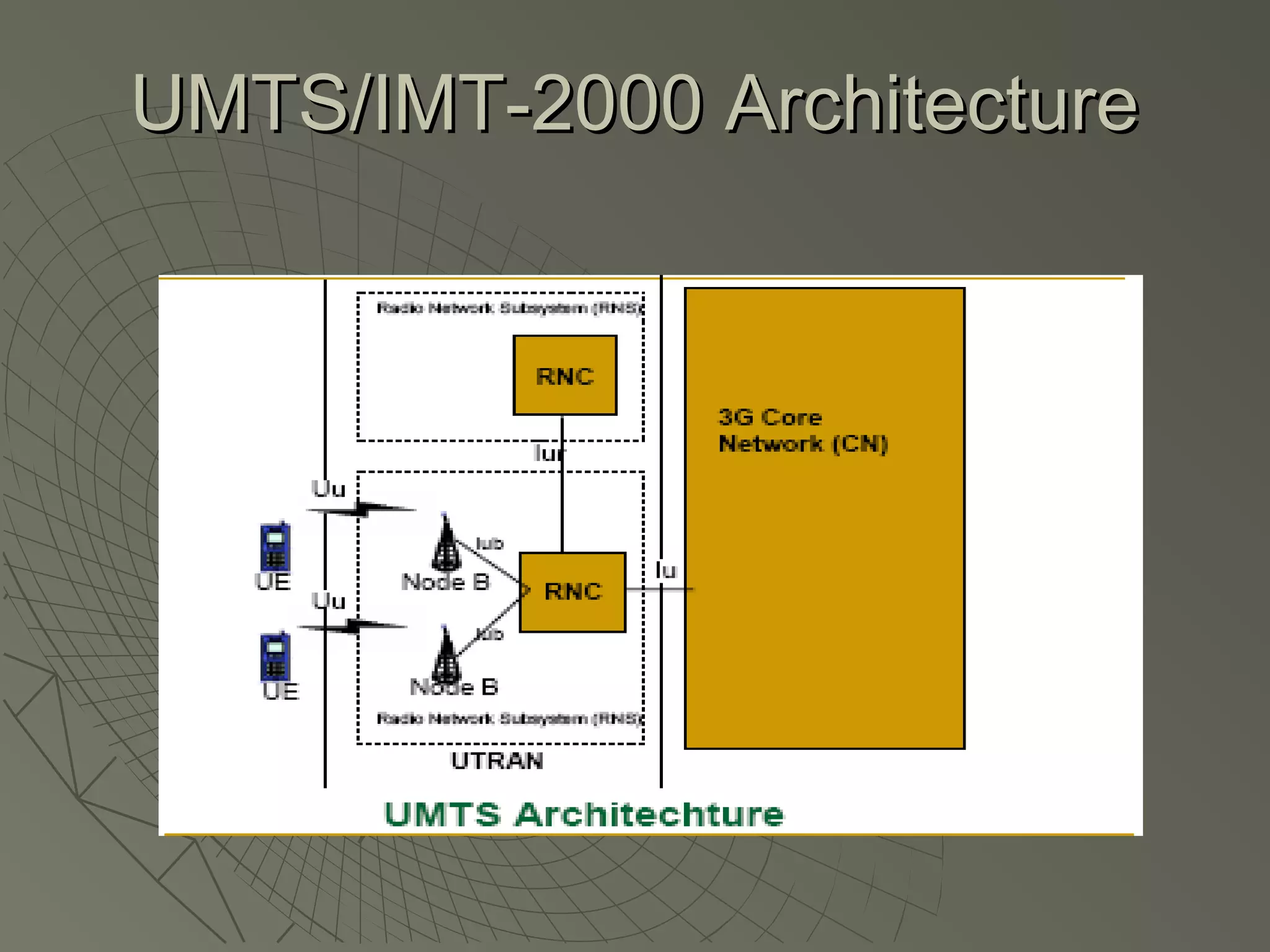
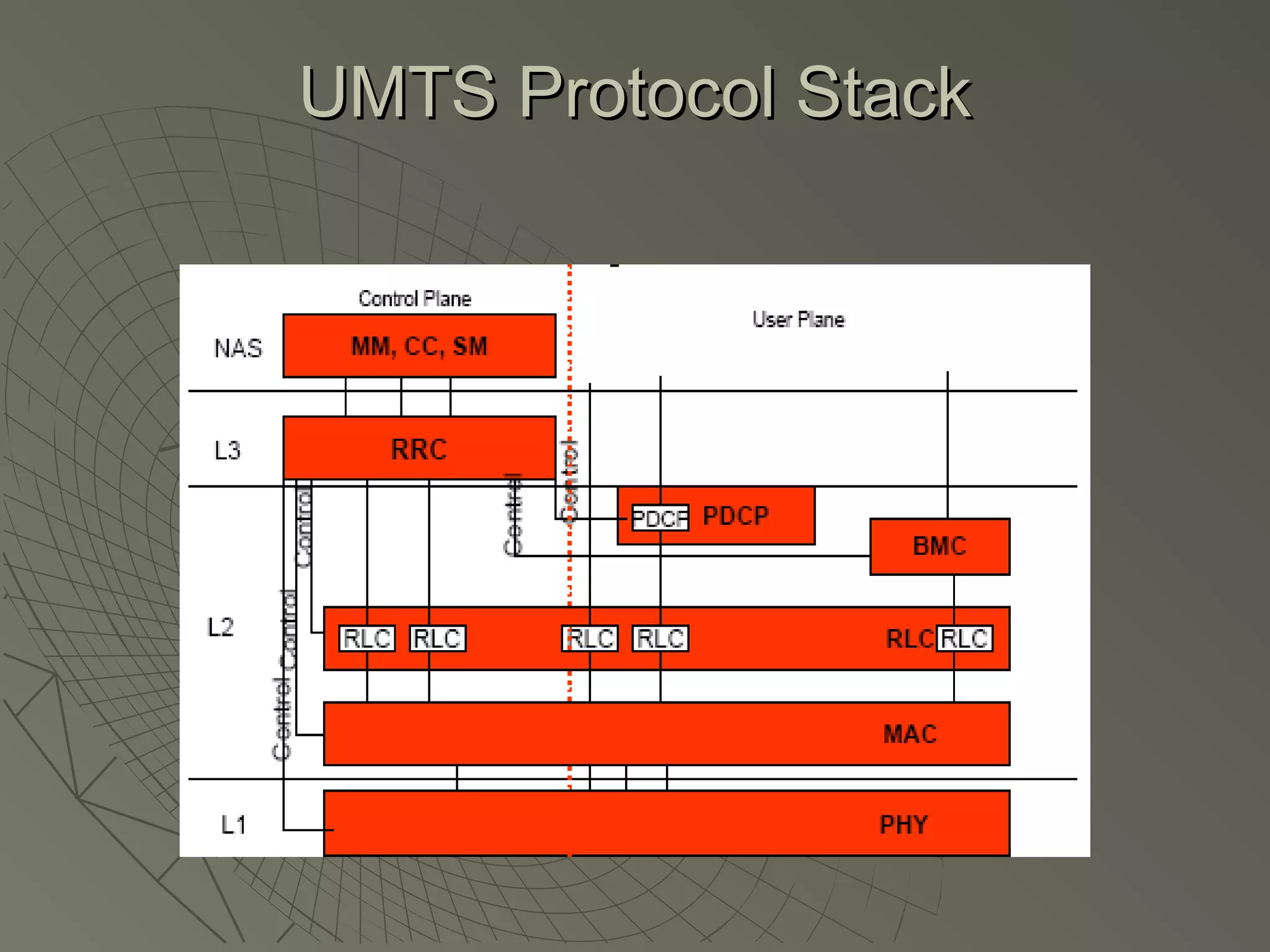
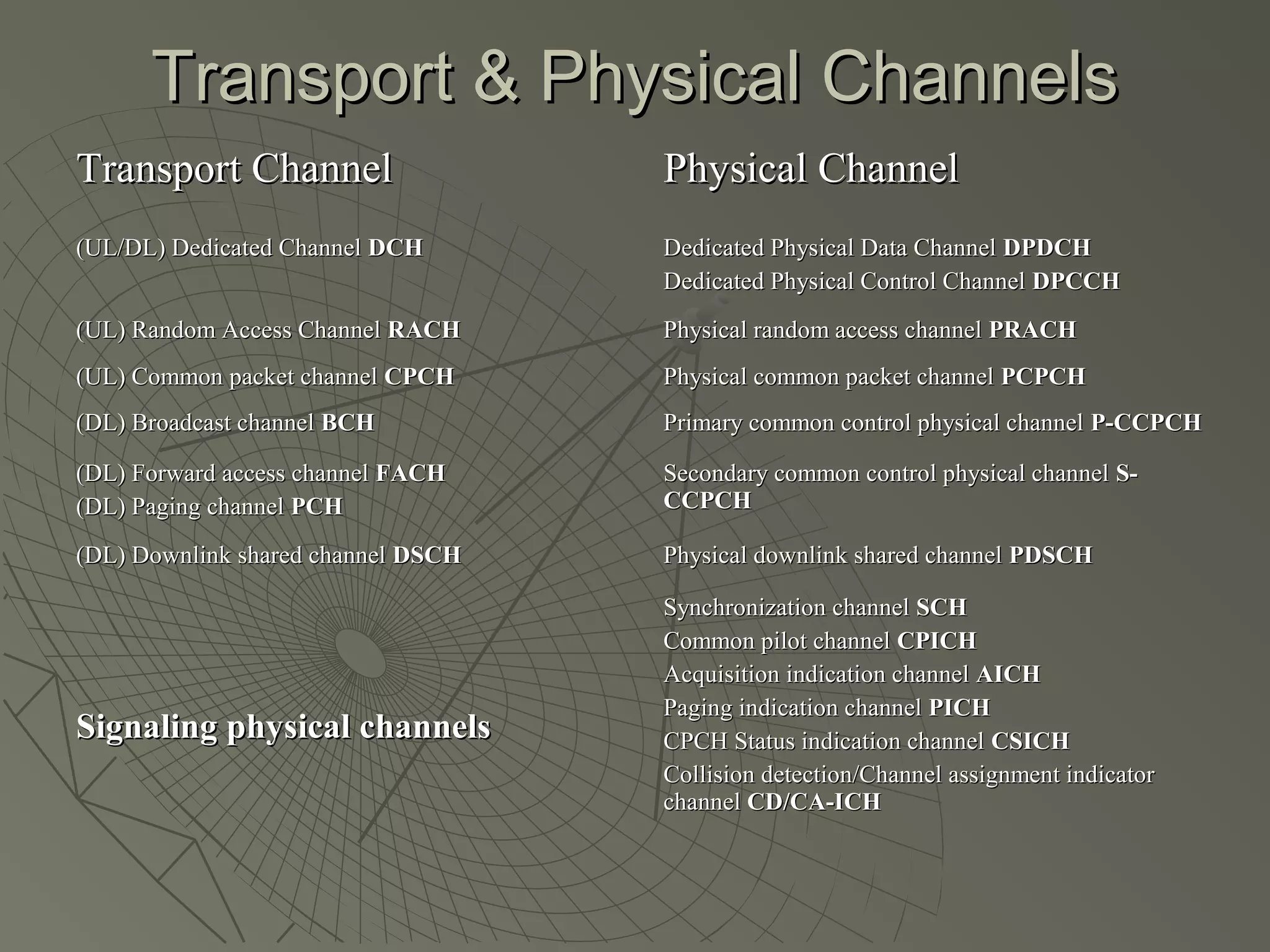
This document provides an overview of 3G wireless systems and the transition to 4G. It describes the advantages of 3G including higher data rates and bandwidth. The key 3G technologies are identified as WCDMA, CDMA2000, and UMTS. The document outlines aspects of the WCDMA protocol including the physical, MAC, RLC, and RRC layers. It also discusses handover, power control, and quality of service support in 3G. 4G is predicted to provide even higher data rates while using smaller cell sizes and frequency bands below 5 GHz.