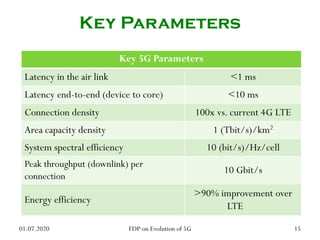
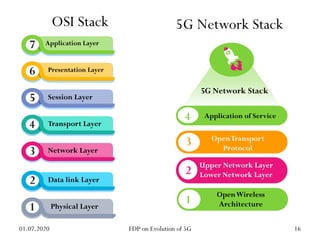
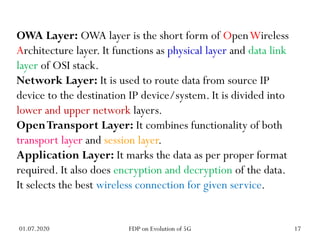
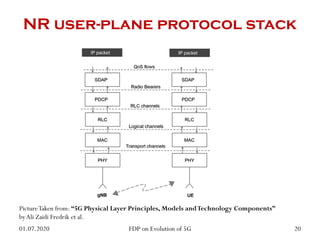
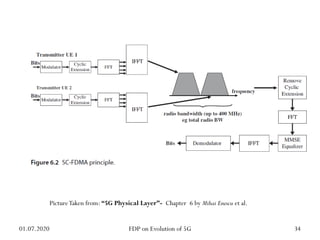
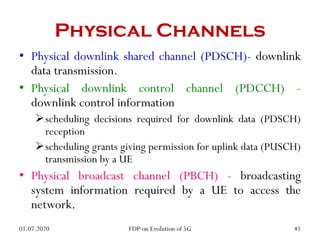
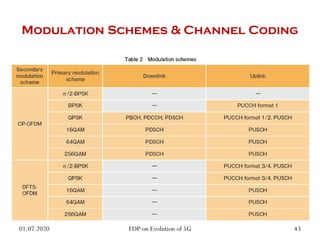
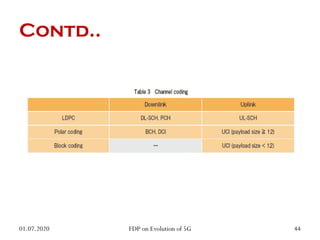
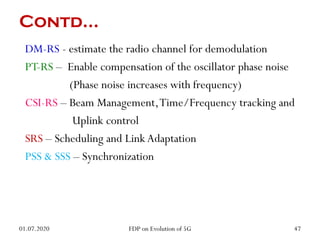
The physical layer of 5G will differ significantly from 4G LTE in several ways to improve spectral efficiency and data rates. It will utilize a much larger number of active antennas and antenna arrays to support beamforming and millimeter wave signals. New modulation and coding schemes, components for power amplification and noise reduction, and channel models need to be developed. The 5G physical layer protocol stack separates the layer into PHY, MAC, RLC, PDCP and SDAP layers to handle functions like error correction, scheduling, security, and QoS flow mapping between layers.