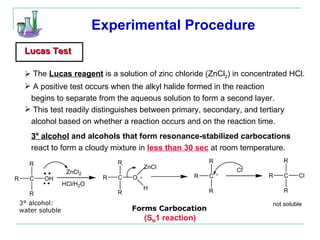
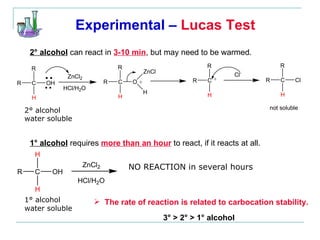
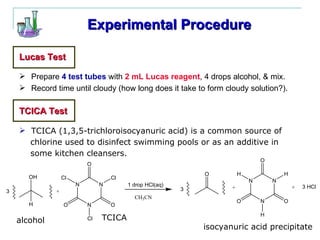
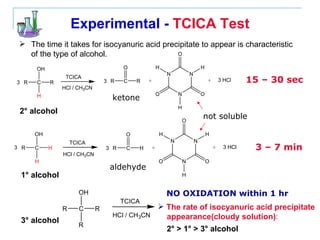
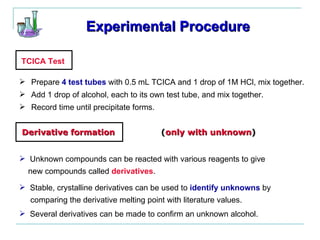
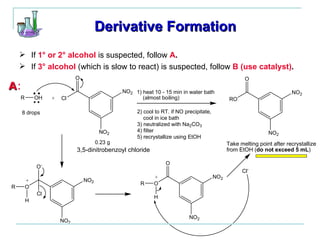
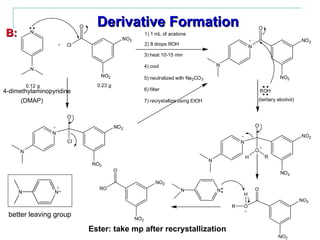
This document provides instructions for using classification tests to identify an unknown alcohol sample. It describes performing the Lucas test, TCICA test, and derivative formation to determine if the alcohol is primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the reaction times and results. The order of the experimental procedures is changed, with specific waste containers for different solutions. Identification of the unknown alcohol type must be stated in the lab report.