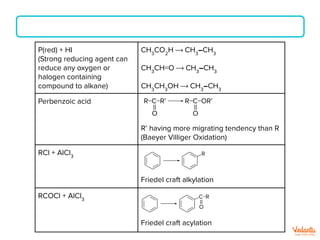
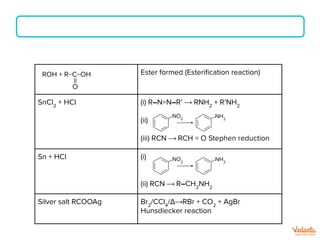
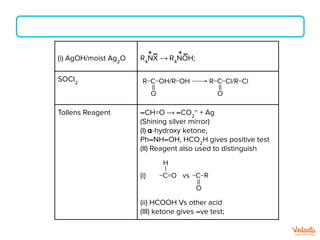
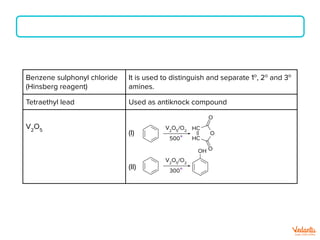
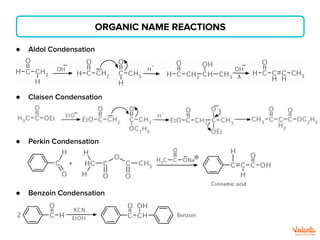
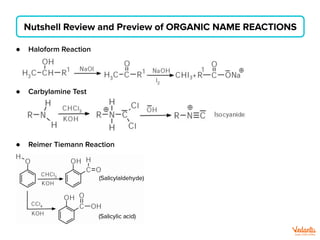
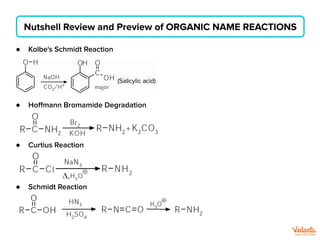
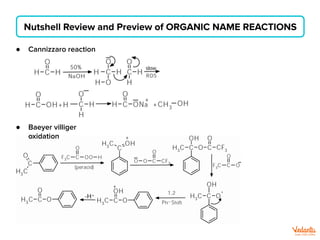
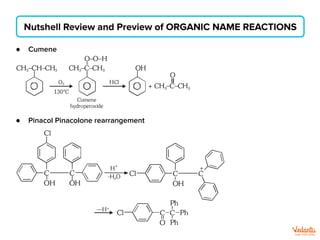
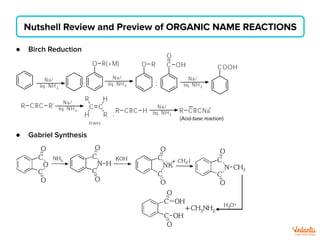
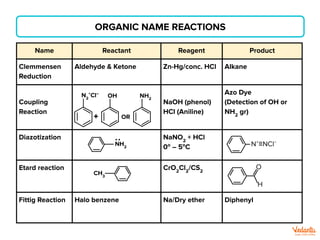
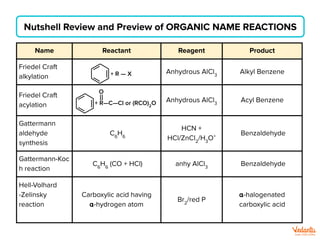
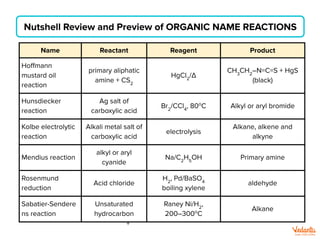
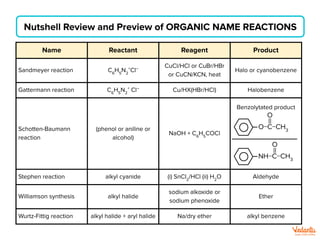
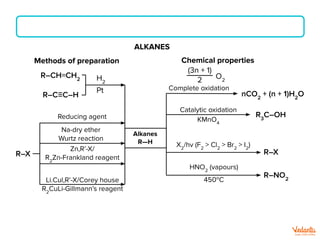
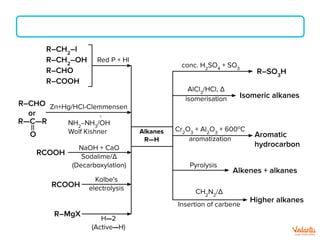
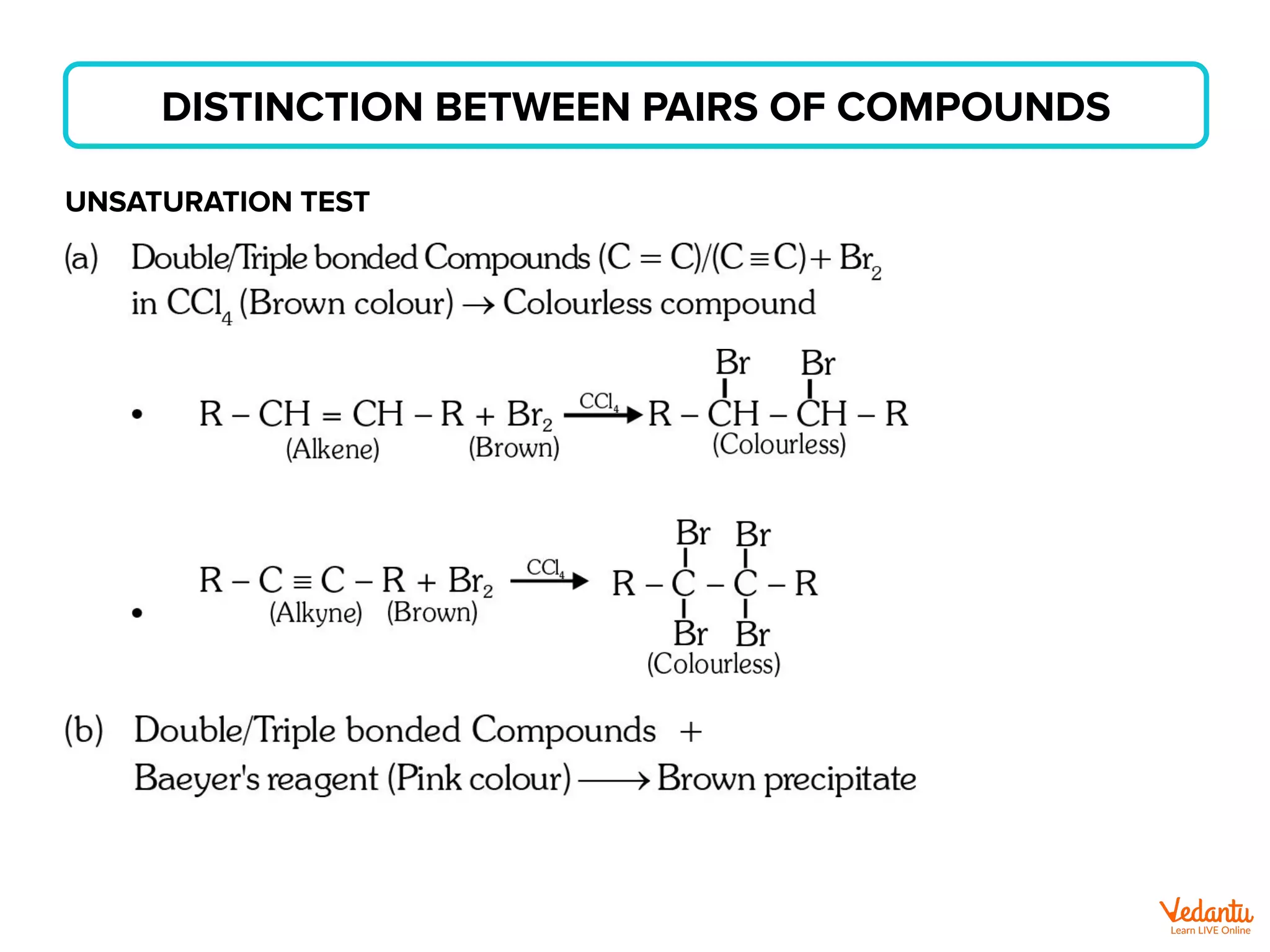
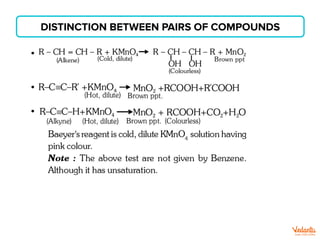
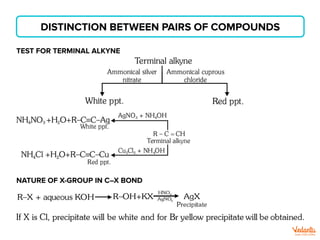
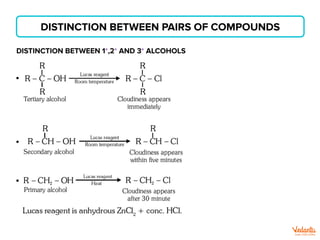
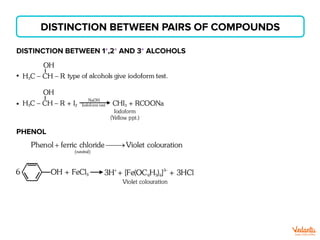
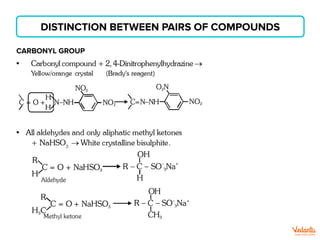
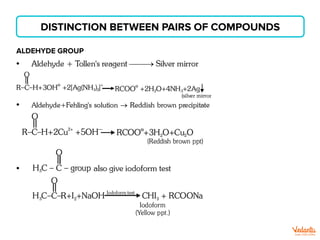
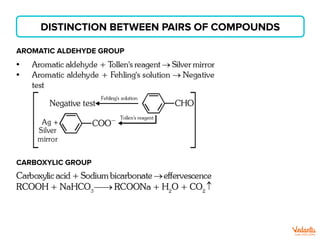
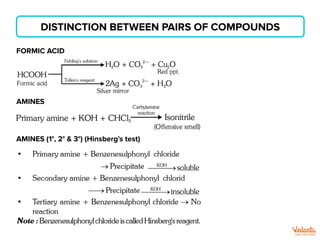
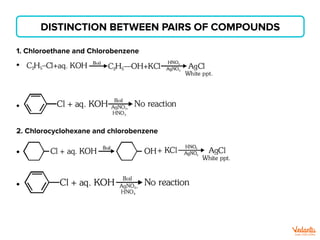
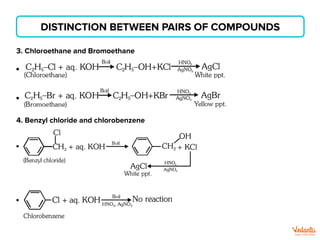
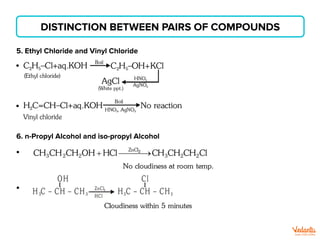
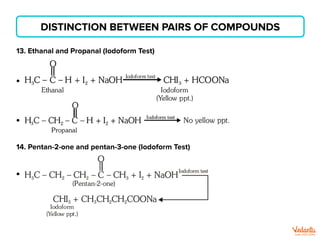
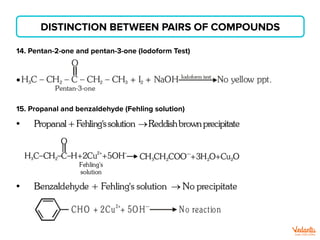
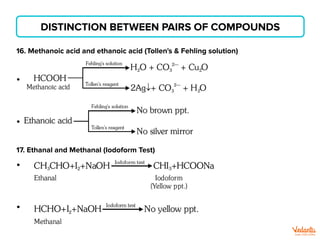
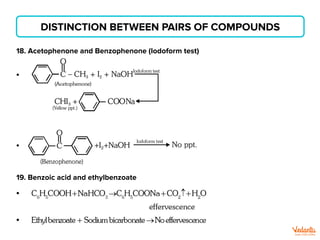
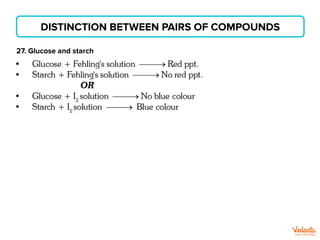
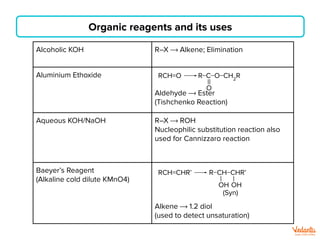
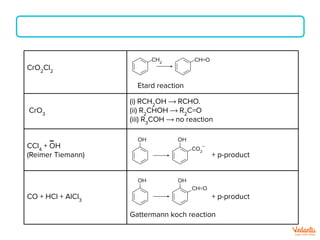
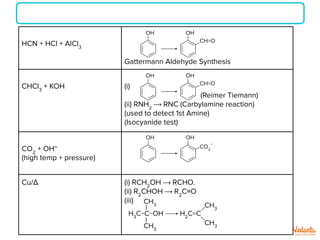
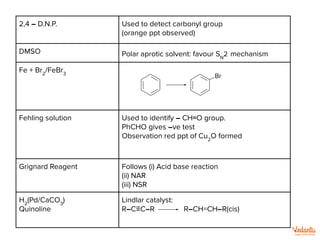
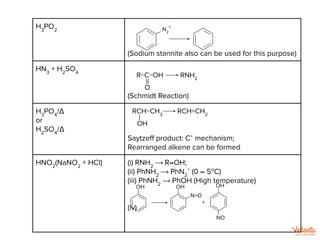
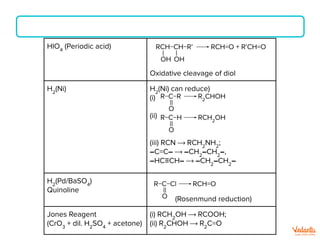
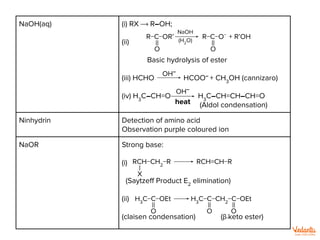
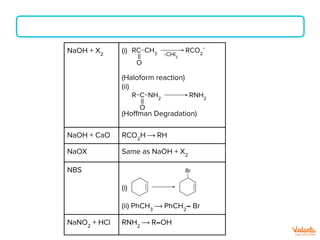
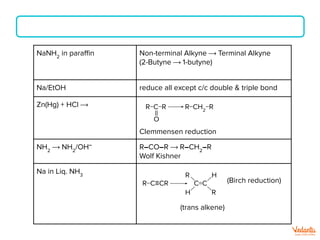
The document lists various organic compounds and reagents and their uses in distinguishing between compound pairs or performing common organic reactions. It includes tests to identify functional groups like carbonyls, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Common reactions mentioned are halogenation, hydrolysis, oxidation, reduction, substitution, elimination, condensation and rearrangement reactions.
![Bromine water (i) used to detect unsaturation.
(ii)
(iii)
2,4,6-tribromophenol
Benedict’s solution Used to detect aldehyde group
RCHO ⟶ RCO3
–
[ketone gives –ve test]
Cu2
Cl2
+ NH4
OH
(Fehling solution)
Used to Detect Terminal Alkyne
Red Precipitate observed.
NH2
Br
Br
Br
NH2
OH
Br
Br
Br
OH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/namereactionsformains-230202160421-7e35314d/85/Name-reactions-for-mains-pdf-27-320.jpg)
![KHSO4
Dehydrating Reagent
K2
Cr2
O7
/H+
(i) RCH2
OH ⟶ RCO2
H;
(ii) R2
CHOH ⟶ R2
C = O
MnO2
(i) CH3
–CH=CH–CH2
–OH ⟶ CH3
–CH=CH–CH=O
(ii)PhCH2
OH ⟶ PhCH=O
To oxidise allylic/benzylic hydroxyl group into
corresponding carbonyl.
NaHCO3
NaHSO3
[White crystals, soluble in water used to separate
carbonyl from non-carbonyl compound]
CH2
=CH−CH=O
CH2
−CH−CH2
−OH
|
OH
|
OH
14
RCO2
−Na+
+
CO2
↑
RCO2
H
14
NaHCO3
RC
R−C−R
||
O
|
R
OH
SO3
−
Na+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/namereactionsformains-230202160421-7e35314d/85/Name-reactions-for-mains-pdf-33-320.jpg)
![OsO4
+ H2
O ⟶
(syn-addition)
O3
R–CH=CH–R R⟶CHO + R–CHO
[Ozonolysis process]
Oxirane followed by H+
RMgX ⟶ RCH2
–CH2
–OH
PCC (i) RCH2
OH ⟶ RCHO,
(ii) R2
CHOH ⟶ R2
C=O
(iii) R3
COH ⟶ no reaction
[Mild oxidizing reagent]
P(red) + Br2
(i)
(HVZ reaction)
(ii) ROH ⟶ R-Br
RCH=CHR RCH−CH−R
|
OH
|
OH
CH3
CO2
H H2
C−CO2
H
|
Br
O3
H2
OZn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/namereactionsformains-230202160421-7e35314d/85/Name-reactions-for-mains-pdf-37-320.jpg)