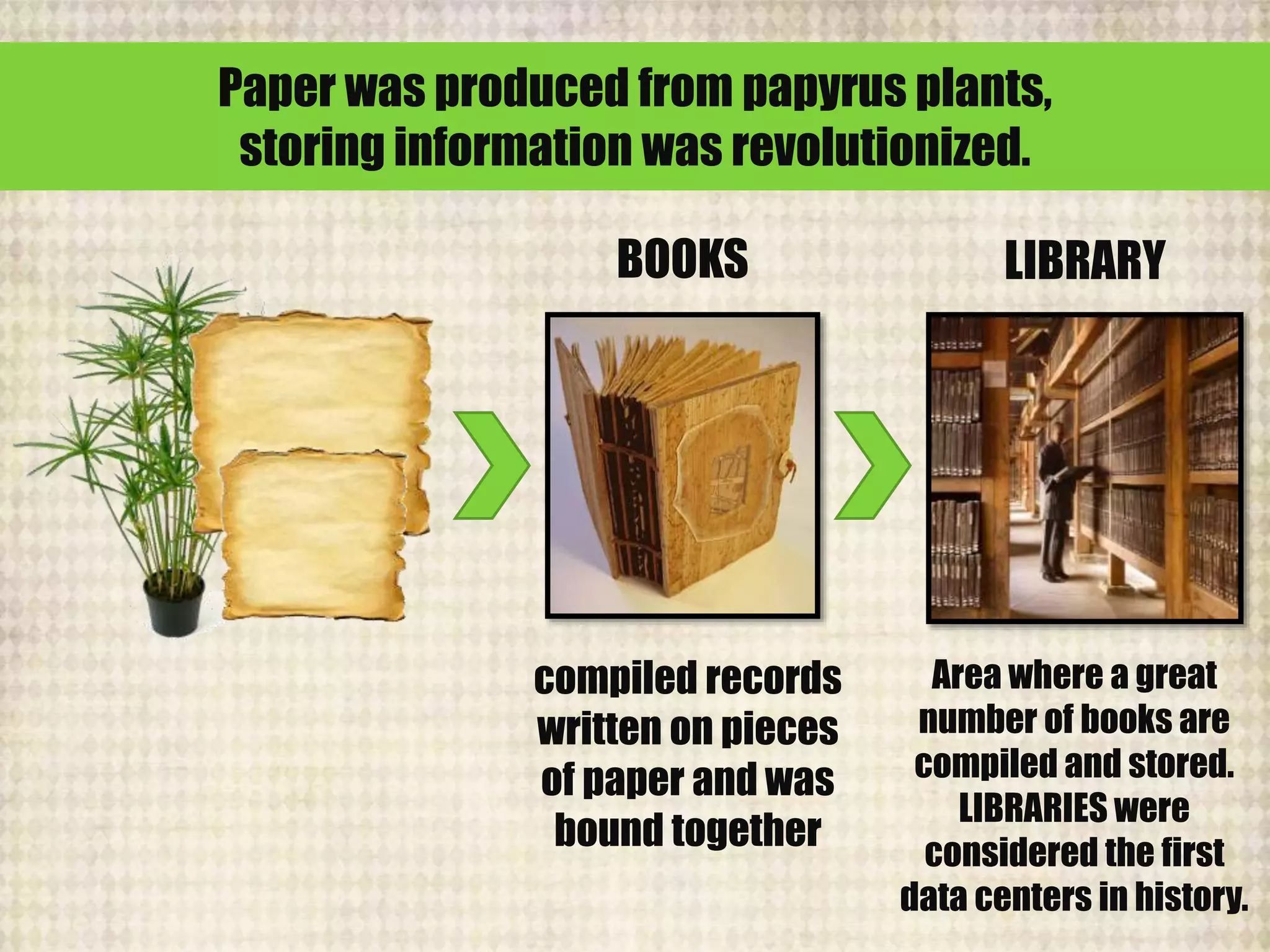
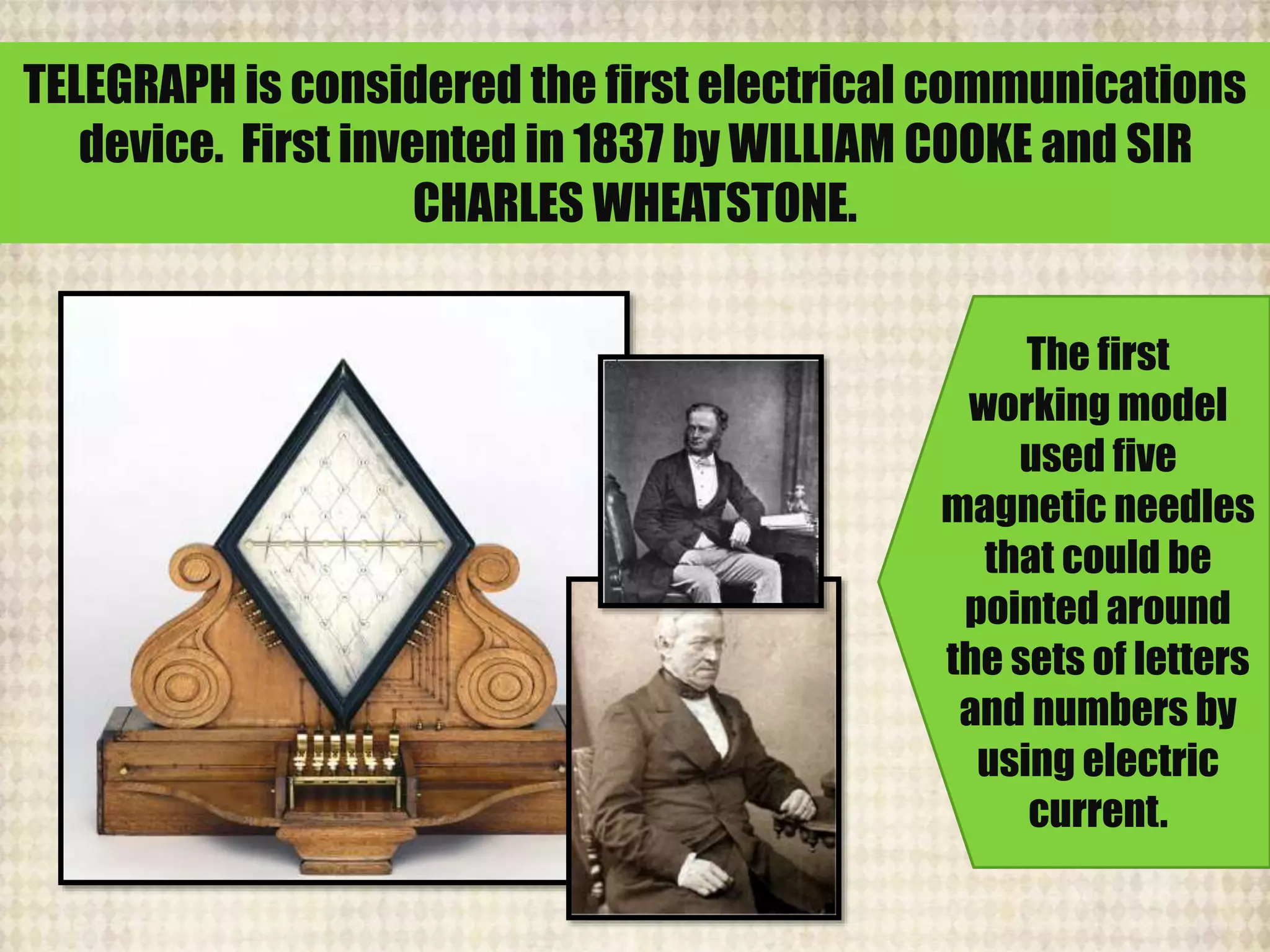
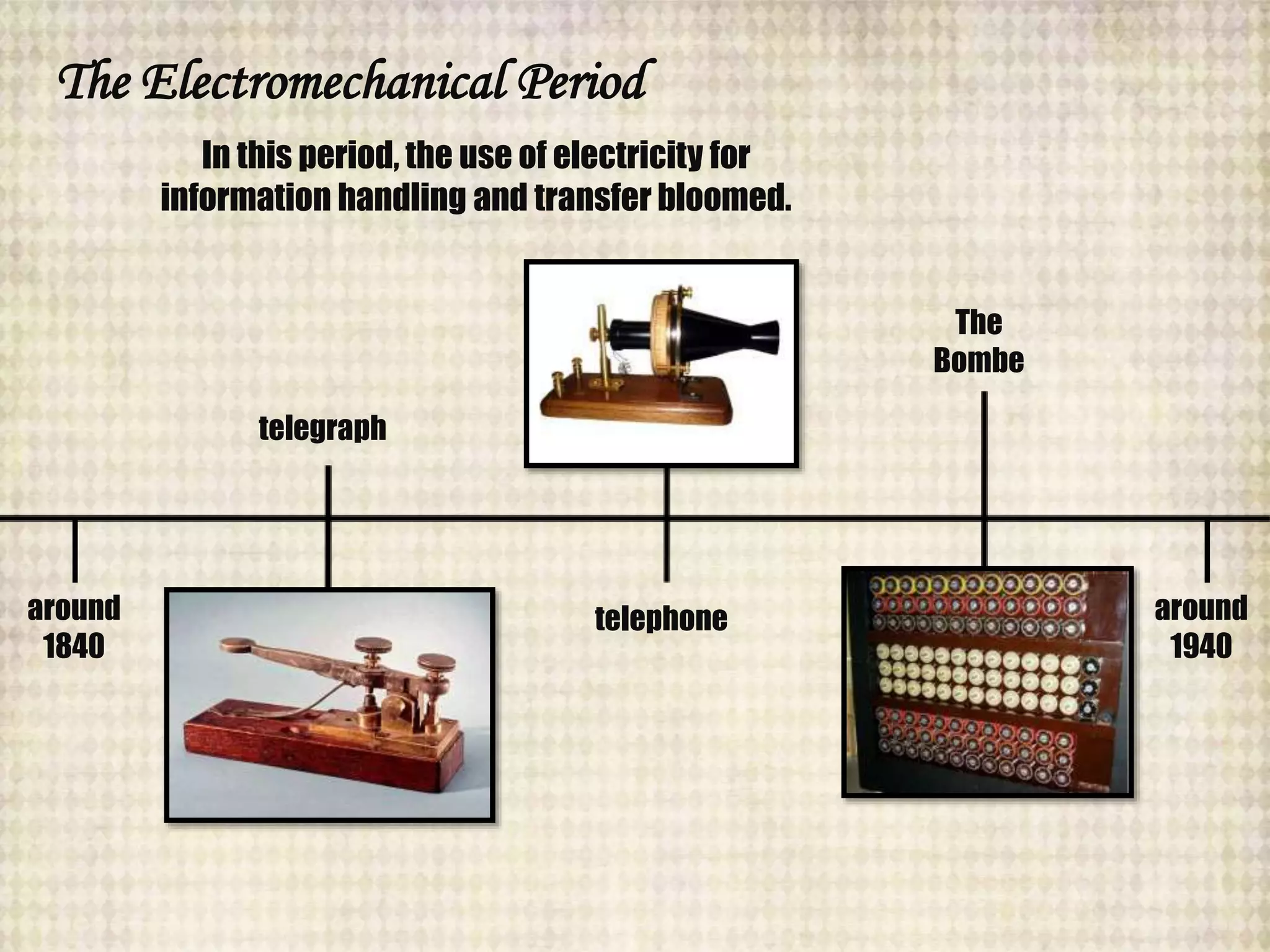
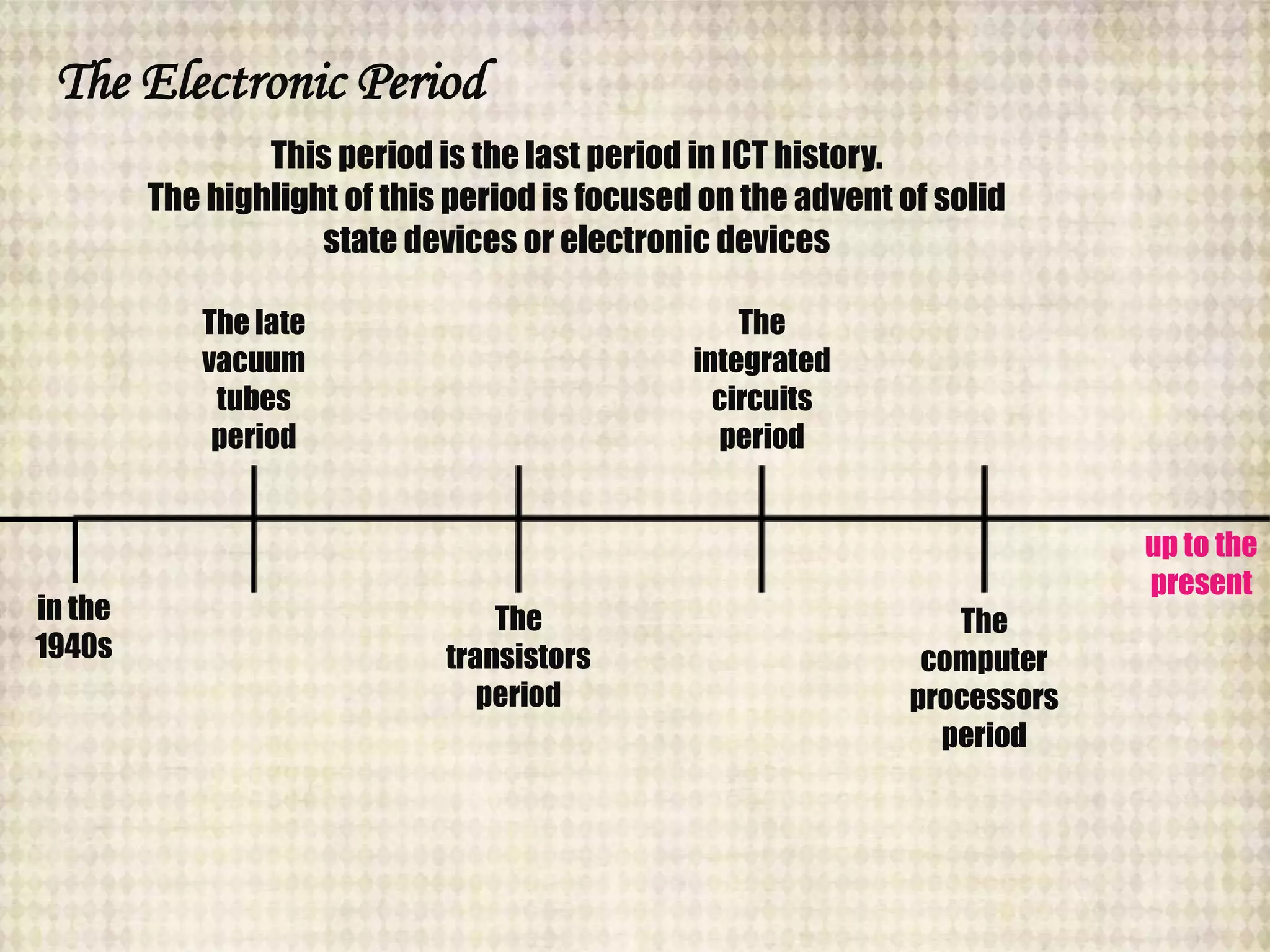
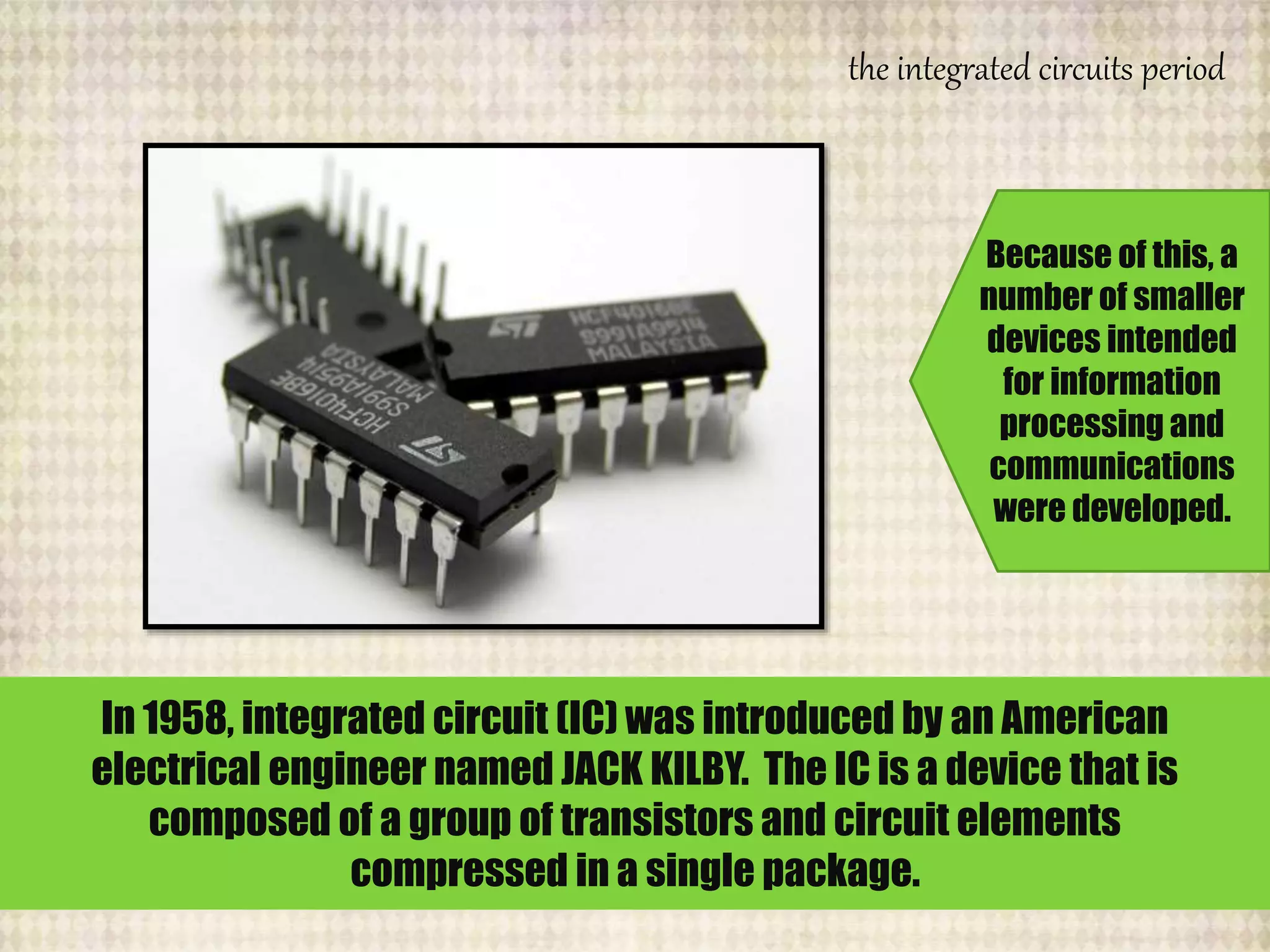
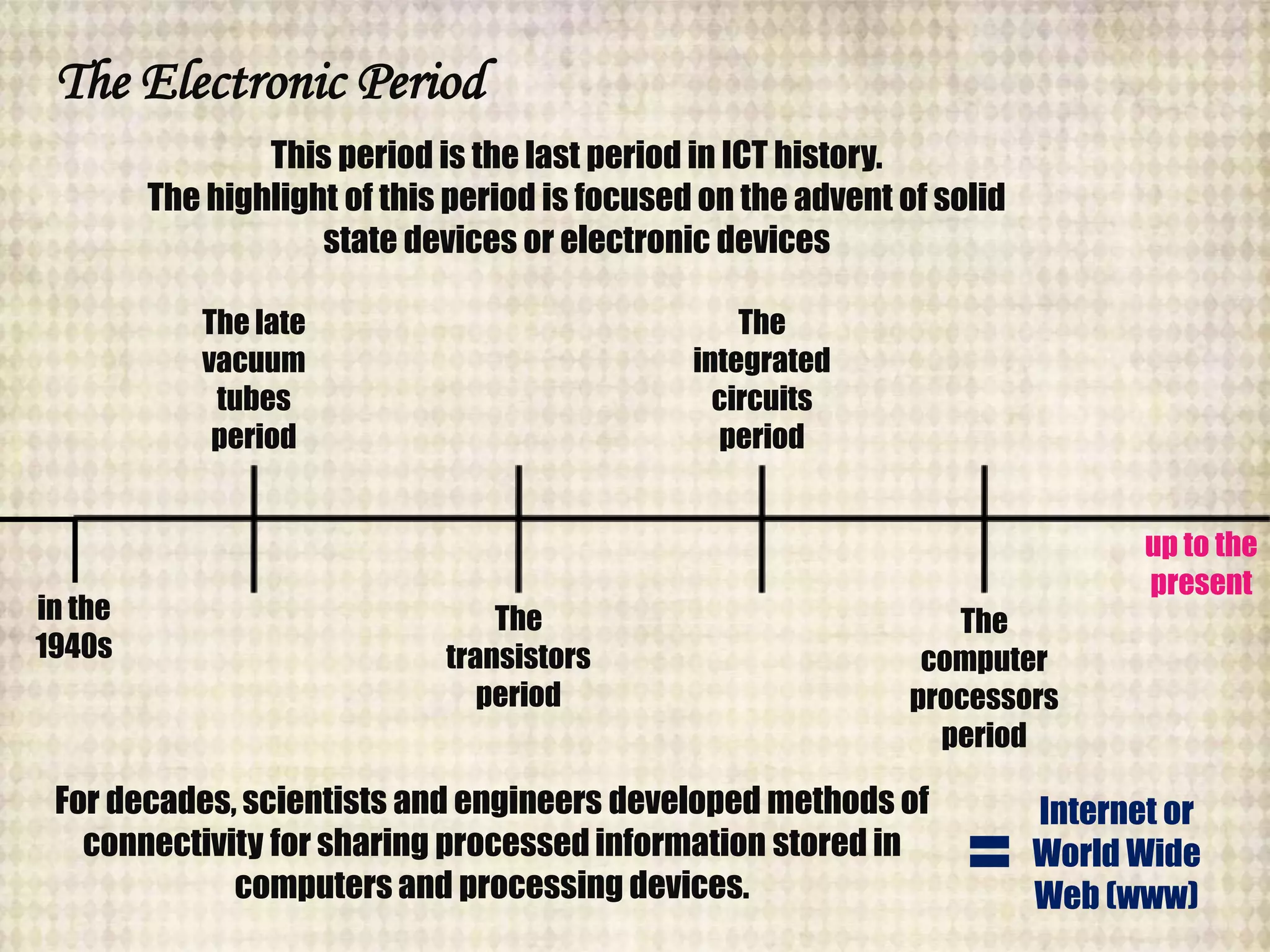
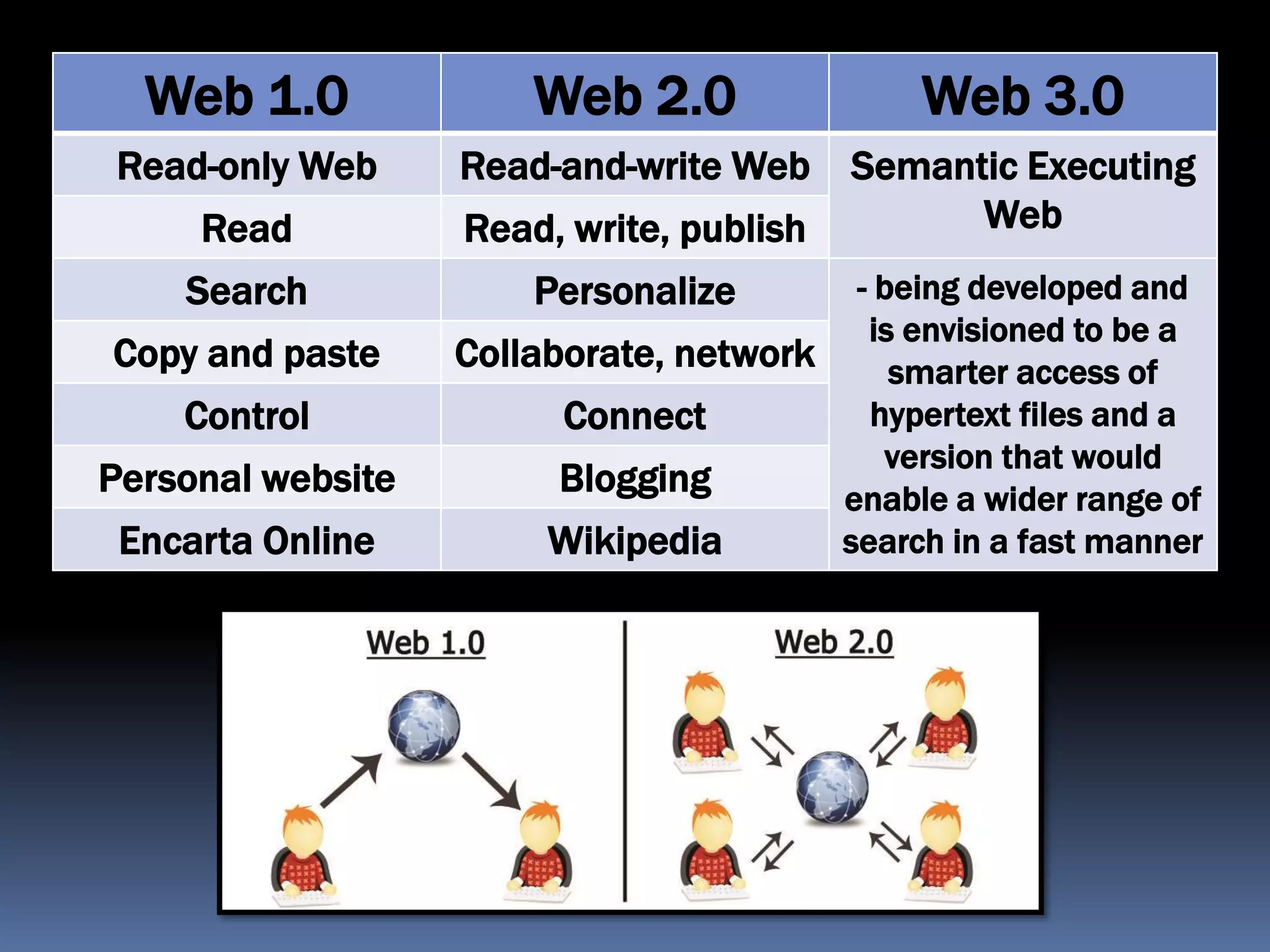
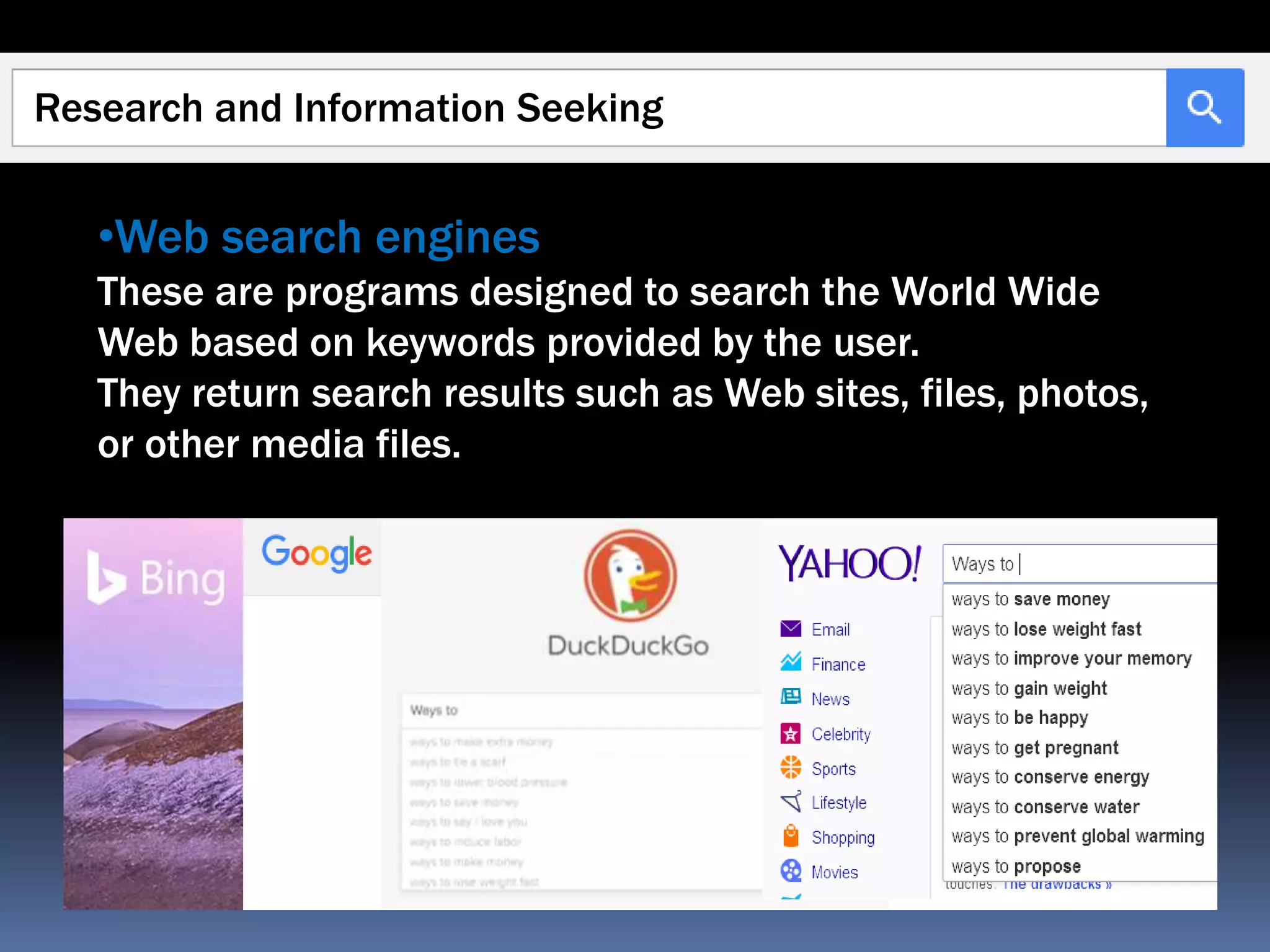
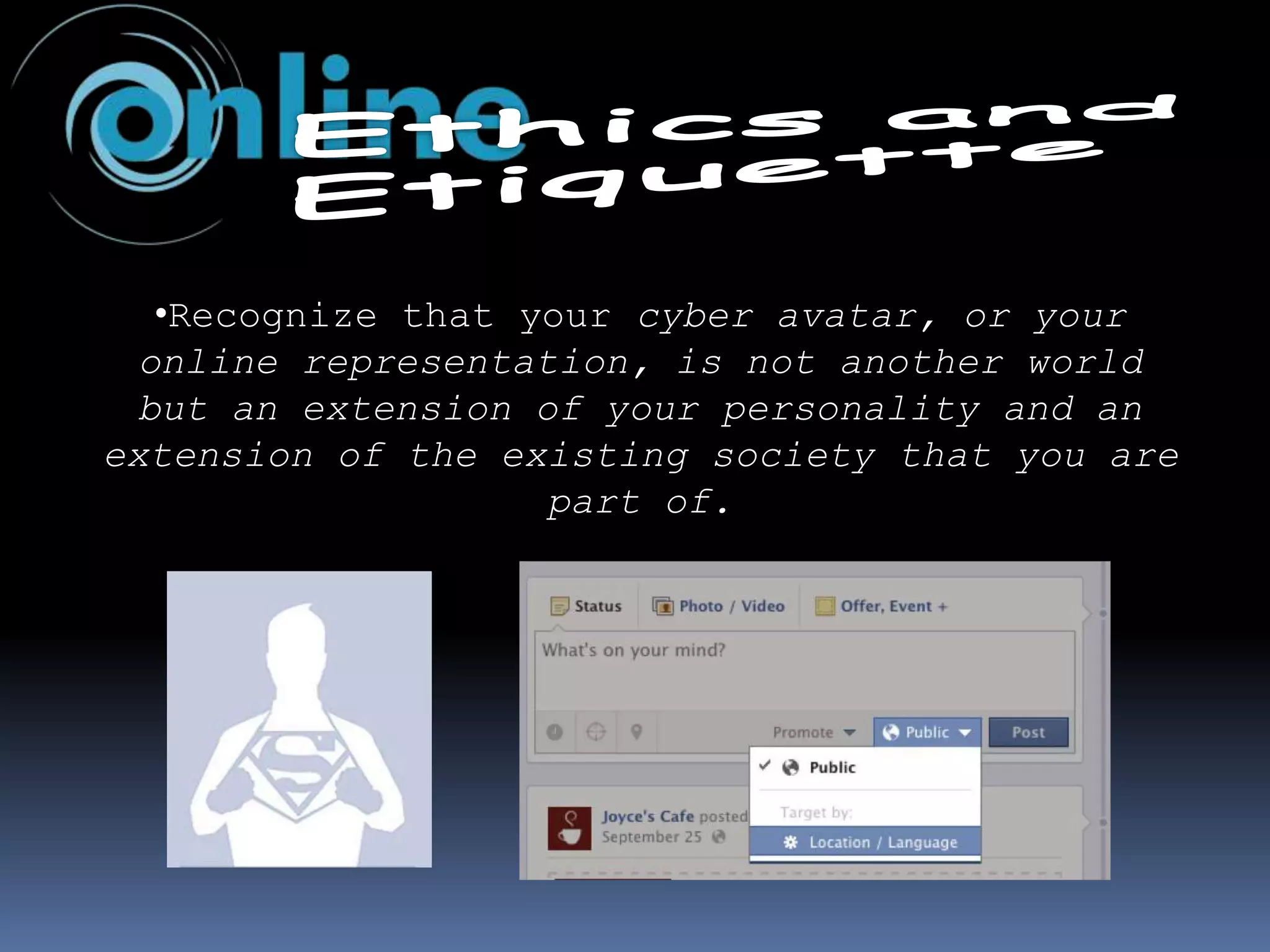
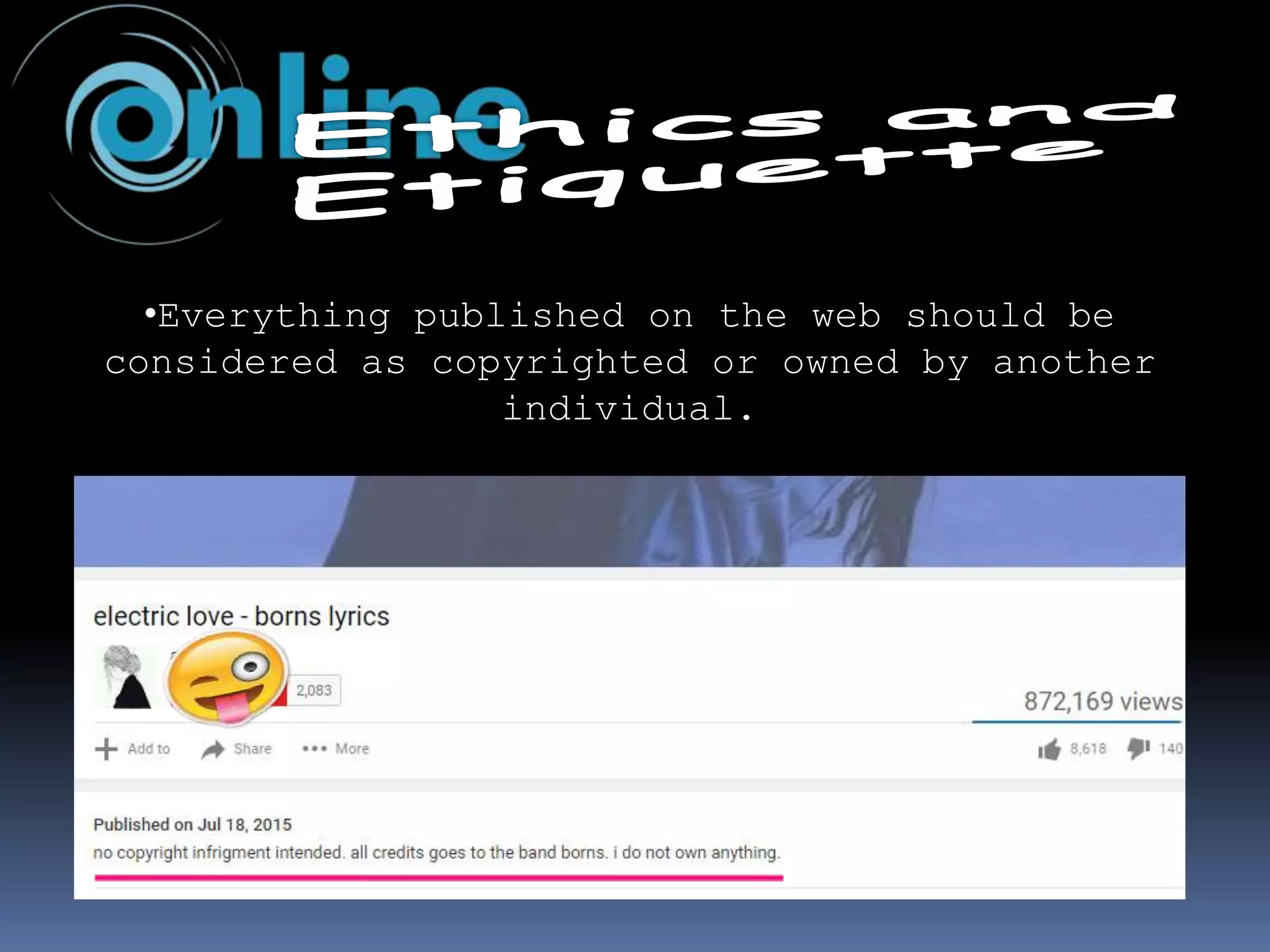
The document outlines the historical evolution of information and communication technology (ICT) from the pre-mechanical period around 3000 BCE to the electronic period of today. It details significant inventions such as the abacus, the telegraph, and the first electronic computer ENIAC, while also discussing the development of the World Wide Web across different phases, including Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and the emerging Web 3.0. The content emphasizes the importance of credible information verification online and outlines netiquette for respectful online communication.