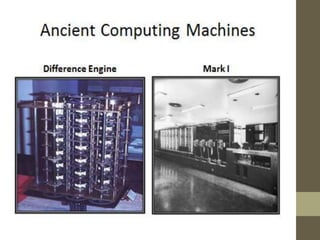
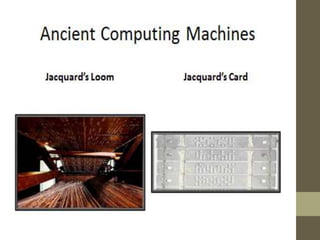
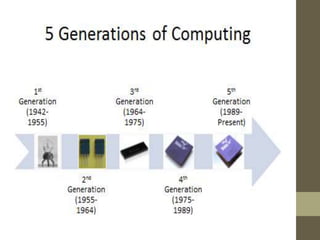
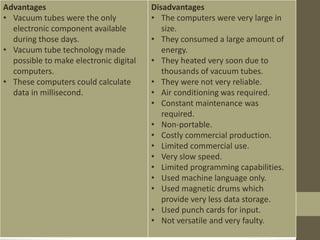
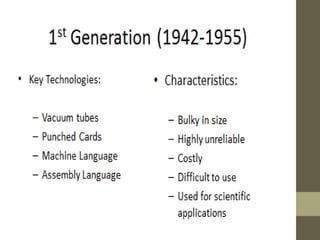
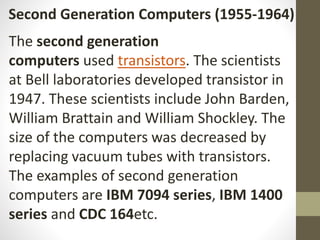
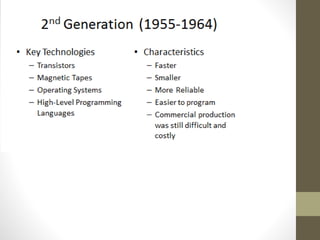
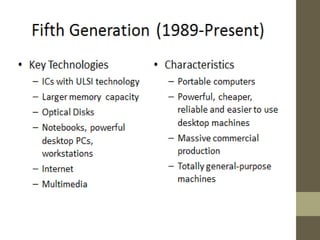
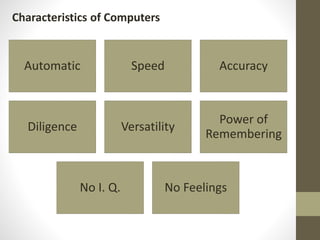
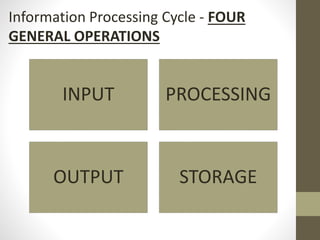
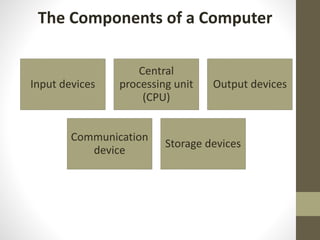
The document provides an introduction to information and communication technology (ICT). It defines ICT as the technology required for information processing, particularly using electronic computers, communication devices, and software applications. It discusses how information is used to make decisions and predictions. The document also defines communication and provides a brief history of computers from early mechanical devices like the Antikythera mechanism and abacus to modern computers based on integrated circuits. It summarizes the characteristics and components of computers as well as their uses in fields like science, medicine, education, banking, crime investigation, and entertainment.