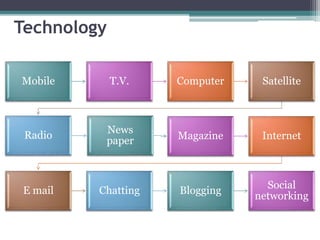
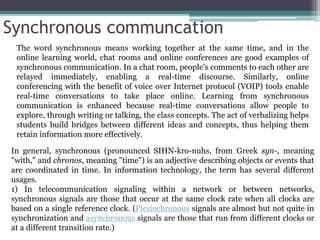
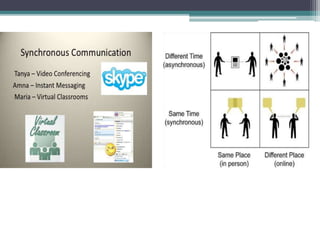
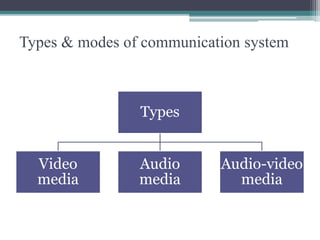
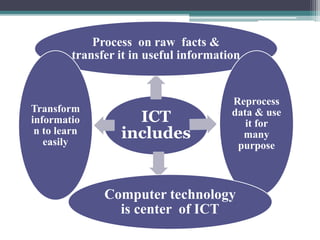
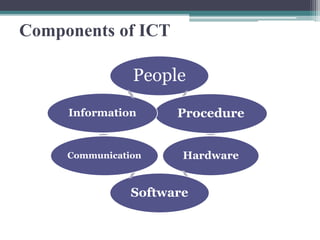
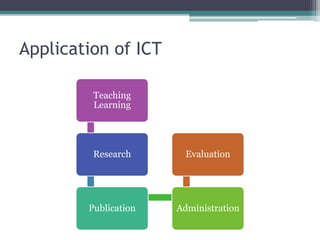
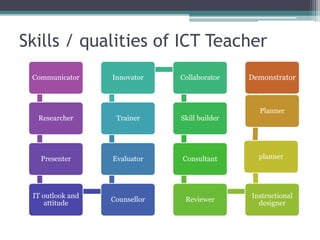
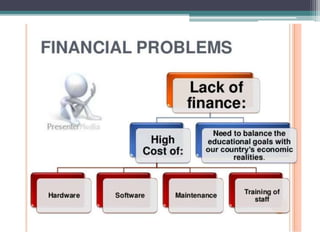
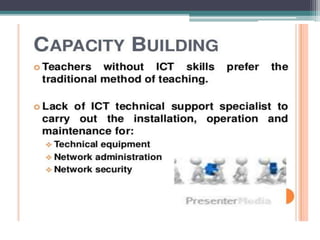
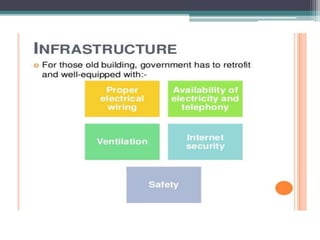
The document discusses ICT (Information and Communication Technology) in education. It outlines the objectives of understanding ICT, its features, the role of ICT teachers, and tools for evaluation. ICT is defined as digital technologies used for communication, and includes computers, the internet, and other communication mediums. The use of ICT in education provides benefits like global access to knowledge, self-paced learning, and making learning interactive. However, integrating ICT into schools also presents challenges related to infrastructure, funding, teacher training, and remote areas with limited access.





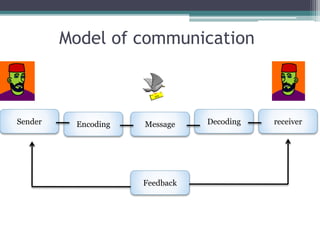
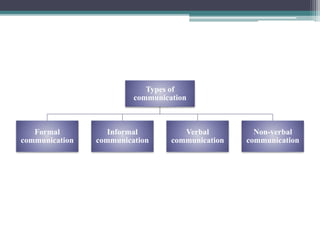


![Nonverbal communication
• Nonverbal communication between people
is communication through sending and receiving
wordless clues.
• It includes the use of visual cues such as body
language (kinesics), distance (proxemics) and
physical environments/appearance, of voice
(paralanguage) and of touch (haptics).[1] It can also
include chronemics (the use of time)
and oculesics (eye contact and the actions of looking
while talking and listening, frequency of glances,
patterns of fixation, pupil dilation, and blink rate).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictineducation-161121105909/85/Ict-in-education-10-320.jpg)