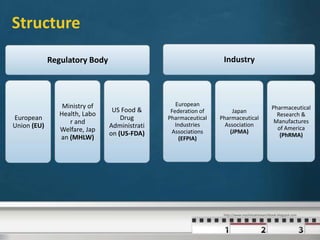
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) is a joint regulatory-industry initiative to harmonize technical requirements for pharmaceutical product registration. It aims to reduce duplication of testing by achieving greater harmonization in guidelines' interpretation between Europe, Japan, and the United States. ICH addresses safety, quality, efficacy, and other topics through guidelines developed by expert working groups representing regulators and industry. Over two decades, ICH has successfully harmonized guidelines through scientific consensus.