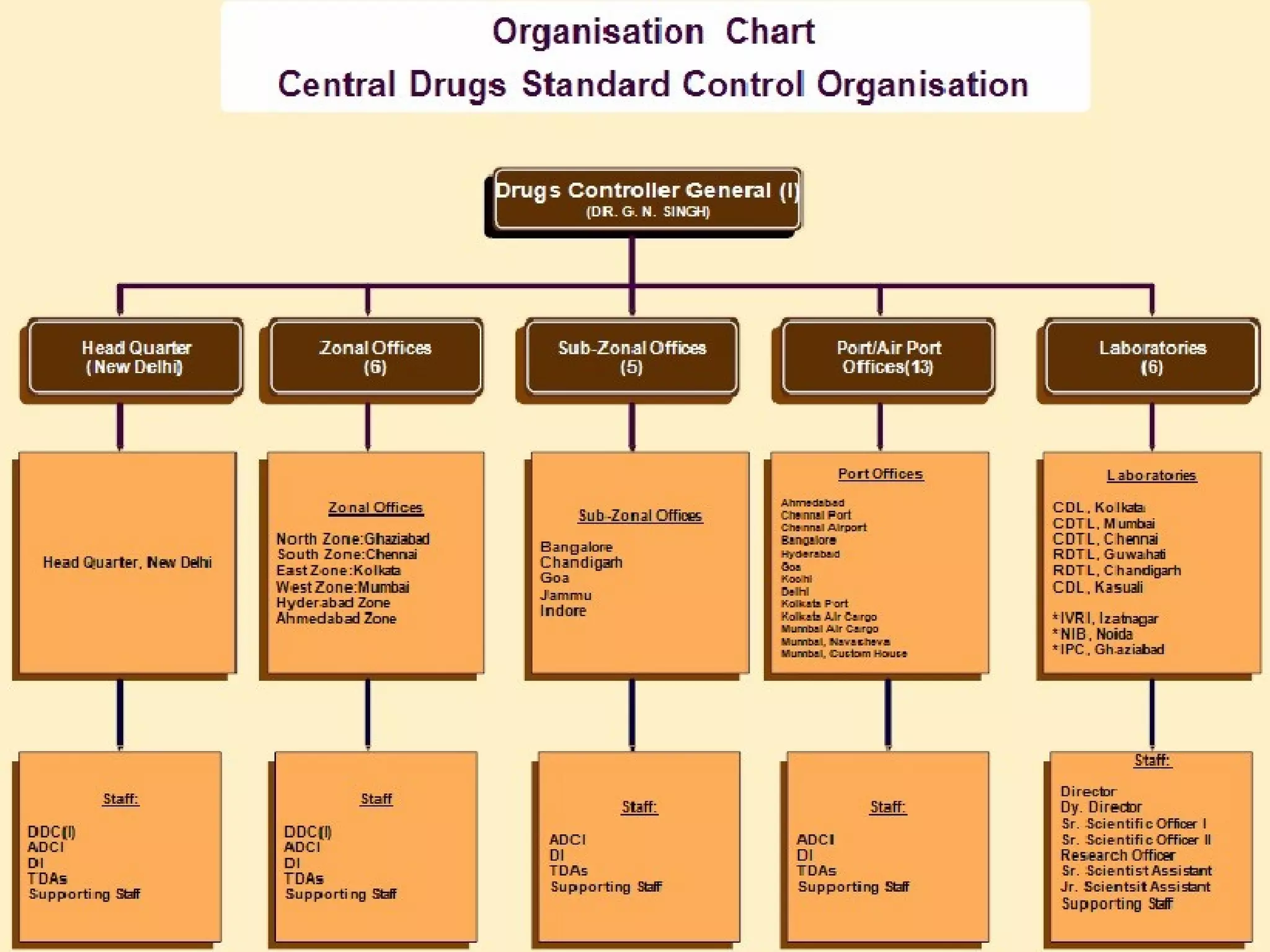
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the main regulatory body for pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and clinical trials in India. CDSCO approves new drugs, regulates import/export and manufacturing of drugs, medical devices, and cosmetics. It has various zonal and regional offices. The document outlines CDSCO's role in drug approval process, clinical trials, regulation of cosmetics, and the new Medical Device Rules of 2016.