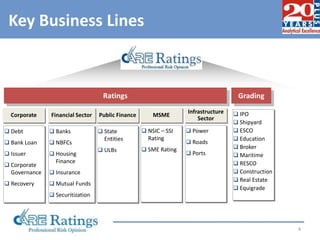
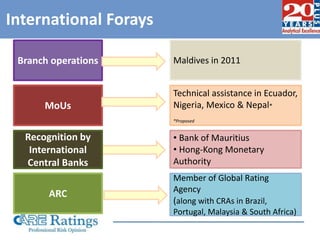
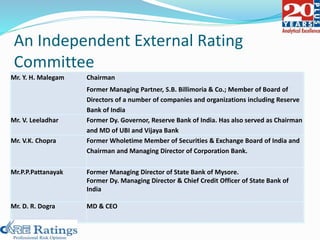
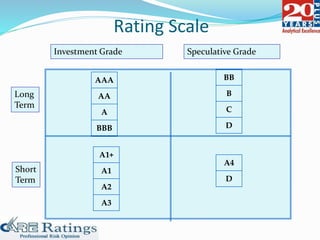
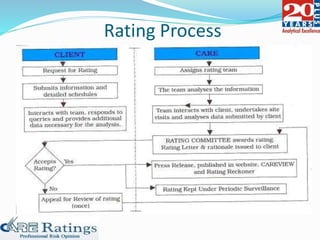
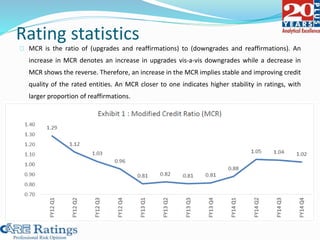
This document summarizes a presentation made by CA Smita Rajpurkar on rating concepts and methodologies at CARE. It discusses CARE's key business lines of ratings for corporates, financial sectors, public finance and infrastructure. It then outlines CARE's rating process, key risk factors considered, and approach to ratings surveillance. The document also provides details on CARE's rating scale and committee, and concludes with highlights of key rating factors for construction, roads and real estate sectors.