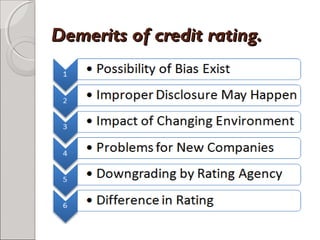
Credit ratings evaluate a debtor's ability to repay debt and the likelihood of default. They are assigned by credit rating agencies and provide an objective opinion on an issuer's financial obligations. India's first credit rating agency, CRISIL, was established in 1987 and the first private rating agency was Duffs & Phelps Credit Rating India in 1995. Credit ratings use methodologies including business, financial, management and fundamental analysis to assess issuers and establish a link between risk and return for investors.