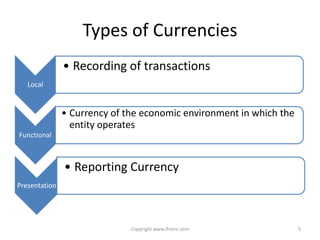
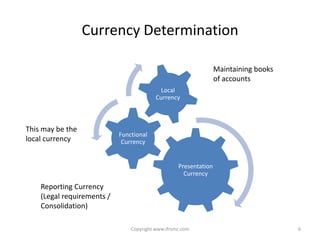
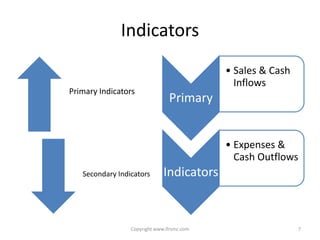
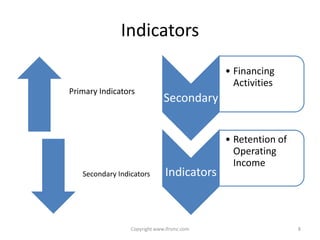
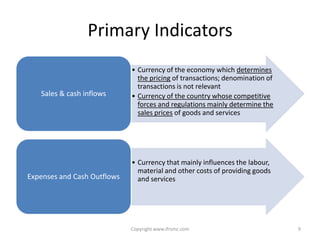
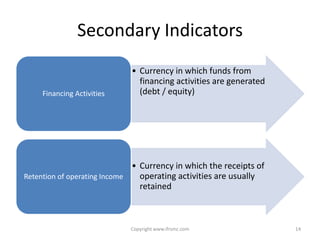
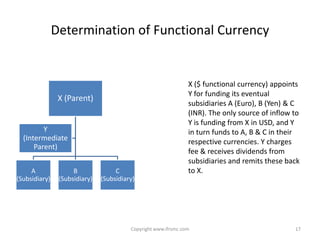
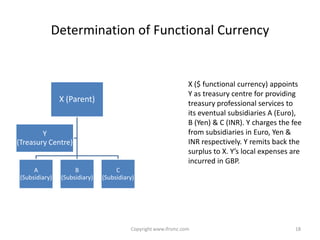
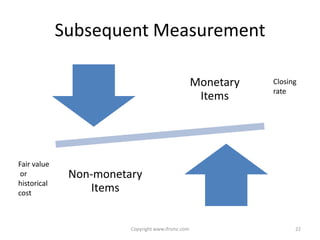
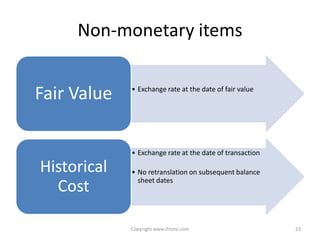
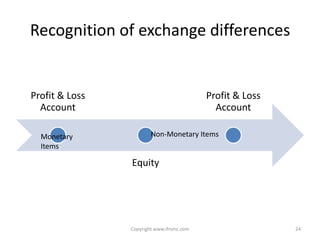
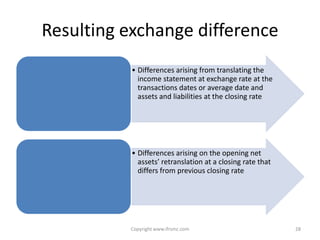
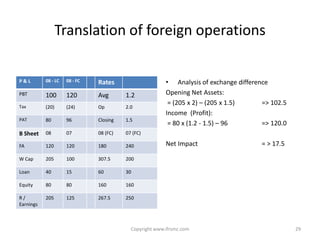
This document provides an overview of IAS 21 - Foreign Currencies. It discusses key aspects such as the objective, scope and types of currencies including local currency, functional currency and presentation currency. It explains how to determine functional currency based on primary and secondary indicators. It also covers foreign currency transactions, translation to presentation currency, consolidated financial statements and disclosure requirements.