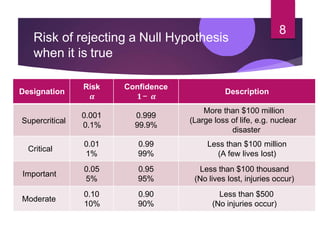
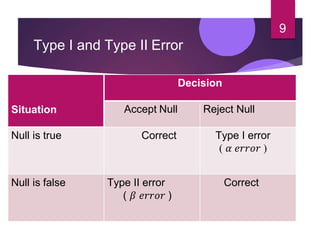
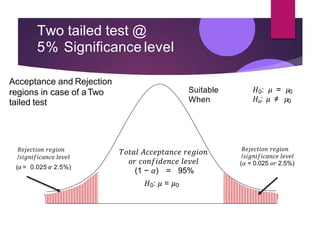
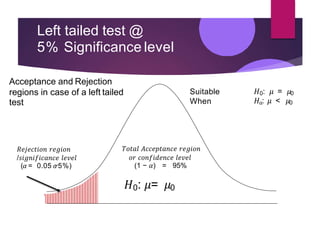
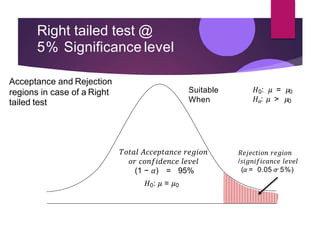
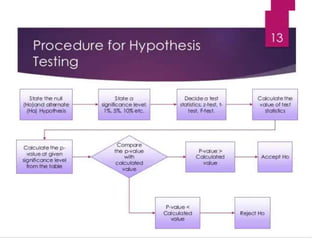
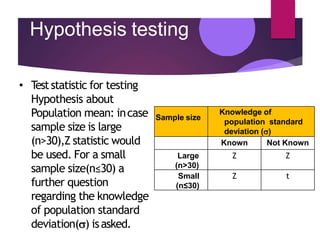
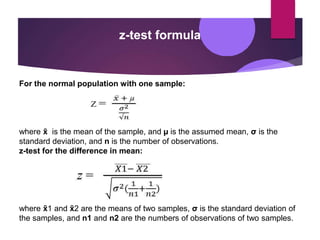
Hypothesis testing involves setting up a null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis, determining a significance level, calculating a test statistic, identifying the critical region, computing the test statistic value based on a sample, and making a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. The z-test is used when the sample size is large and the population standard deviation is known, while the t-test is used for small samples when the population standard deviation is unknown. Both tests involve calculating a test statistic and comparing it to critical values to determine if there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Limitations include that the tests only indicate differences and not the reasons for them, and inferences are based on probabilities rather than certainty.