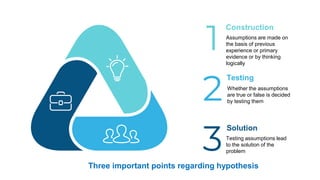
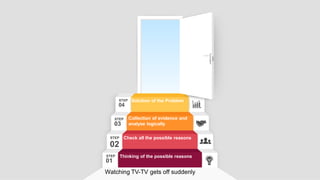
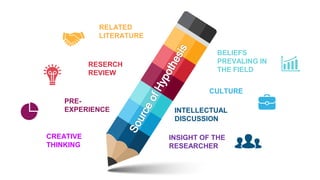
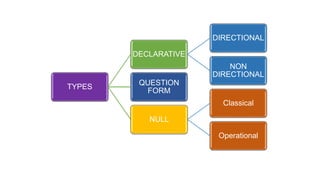
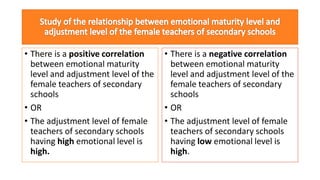
This document discusses the concept of a hypothesis, defining it as a proposition that can be tested for validity through various types such as declarative, directional, non-directional, null, and operational hypotheses. It outlines the characteristics of effective hypotheses, their formulation based on prior evidence, and their relationship to variables in research. Additionally, it provides examples related to teaching aptitude and instructional methods, emphasizing the importance of data collection and logical analysis in solving problems.