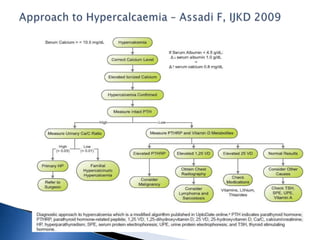
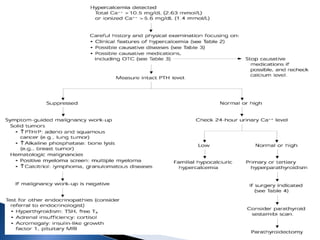
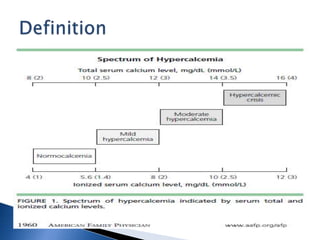
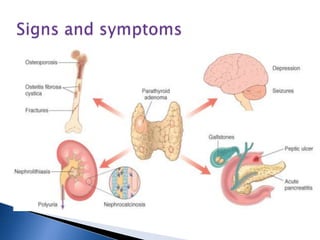
Hypercalcemia is a common condition seen in up to 4% of hospitalized patients. The most common causes are primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy-associated hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia occurs when calcium influx into the extracellular fluid exceeds renal excretory capacity. It is defined as a total serum calcium level greater than 10.2 mg/dL. Treatment involves stabilizing the patient with intravenous fluids, promoting calcium excretion with diuretics, and administering bisphosphonates to reduce bone resorption in malignancy-associated cases. Surgical removal of parathyroid adenomas is required for symptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism.


![ Bone
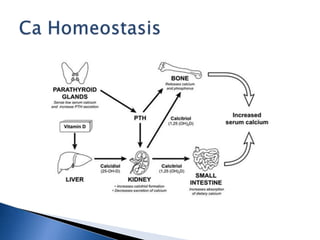
◦ Inhibits osteoblasts
◦ Accelerates osteoclastic bone resorption
Kidneys
◦ Increases renal tubular reabsorption of Ca
◦ Increases PO4 excretion
◦ Increases calcitriol activity (1-hydroxylation) indirectly
raises [Ca]
Gut
◦ Does not directly affect GIT absorption of Ca
◦ Effects are mediated indirectly through regulation of
synthesis of calcitriol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypercalcemiaatee-130819074055-phpapp02/85/Hypercalcemia-atee-8-320.jpg)






![ Diagnosis = Hypercalcaemia + raised [iPTH]
Additional lab findings
- ↓ serum phosphate
- urinary excretion of Ca2+ ( PTH amount of filtered
Ca2+ > normal resorptive capacity of the kidney xs Ca2+
secreted in urine)
-↑ Se ALP (when bone disease present)
-↑ se Cl and ↓ se Bicarb
- ↑1,25 (OH)2D
-bone markers(↑bone specific ALP,osteocalcin)
Other Ix
◦ Sestamibi scan of the Parathyroid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypercalcemiaatee-130819074055-phpapp02/85/Hypercalcemia-atee-21-320.jpg)



![ Thiazide diuretics:
◦ Enhance ca reabsorption in the distal tubule
↓urinary ca excretion.
• Rarely cause Ca in N persons, but lead to Ca in
pt with underlying bone resorption (eg in
hyperparathyroidism)
• Mild hypercalcaemia,↓/N PTH
Lithium therapy:
◦ Increased PTH secretion Increasing set point
of PTH, hence higher [Ca] to switch off PTH
◦ Lab ix: high Ca, PTH, low urinary 24(h) calcium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypercalcemiaatee-130819074055-phpapp02/85/Hypercalcemia-atee-25-320.jpg)