Embed presentation
Download to read offline
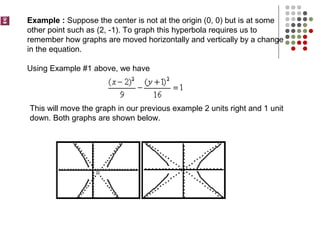
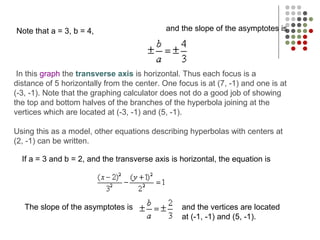

The document discusses how to graph hyperbolas when the center is not at the origin. It provides an example of a hyperbola with center (2, -1), which shifts the original graph 2 units right and 1 unit down. It then discusses key features of the hyperbola like vertices, foci, asymptotes, and their locations relative to the shifted center point.



