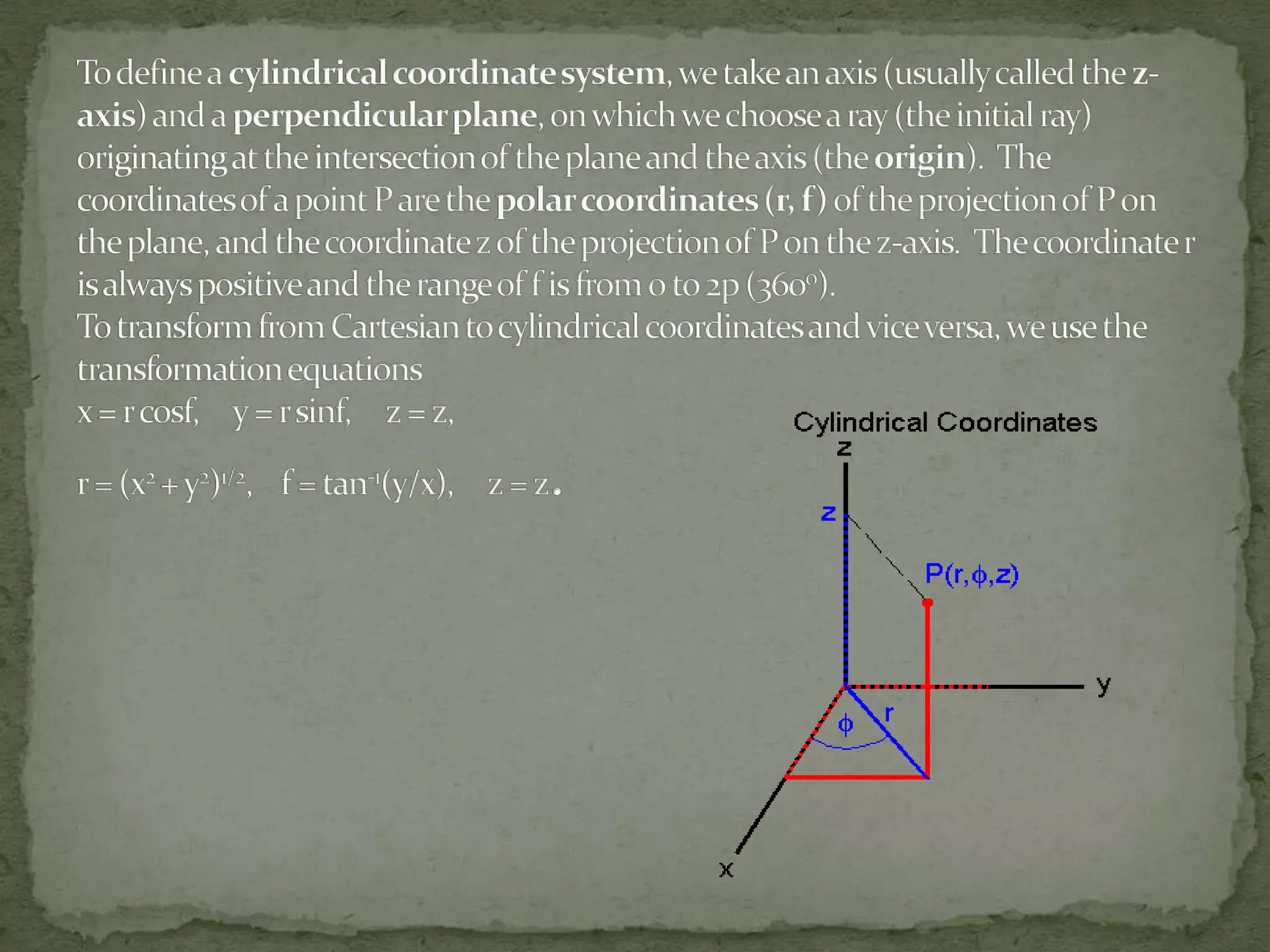
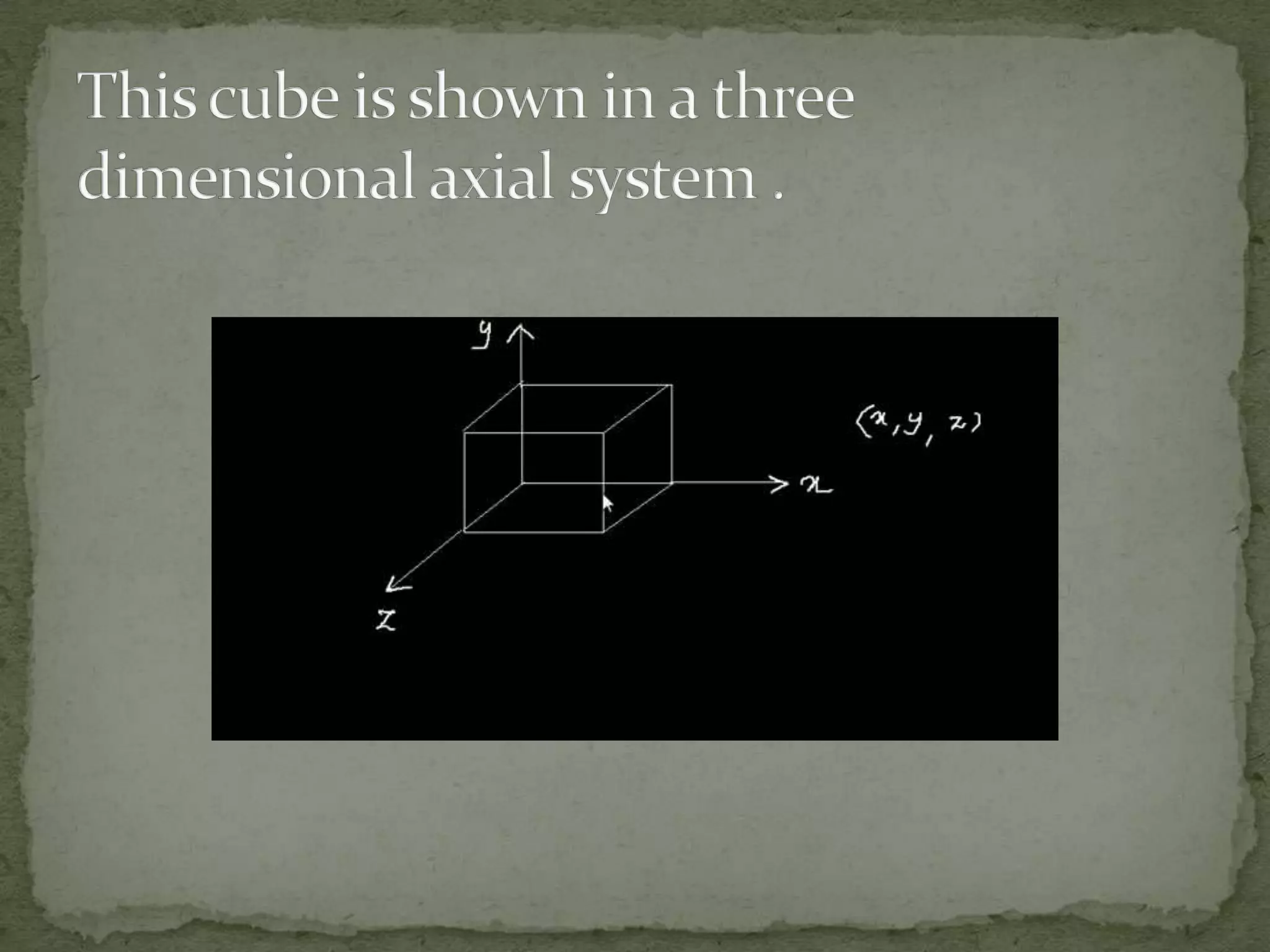
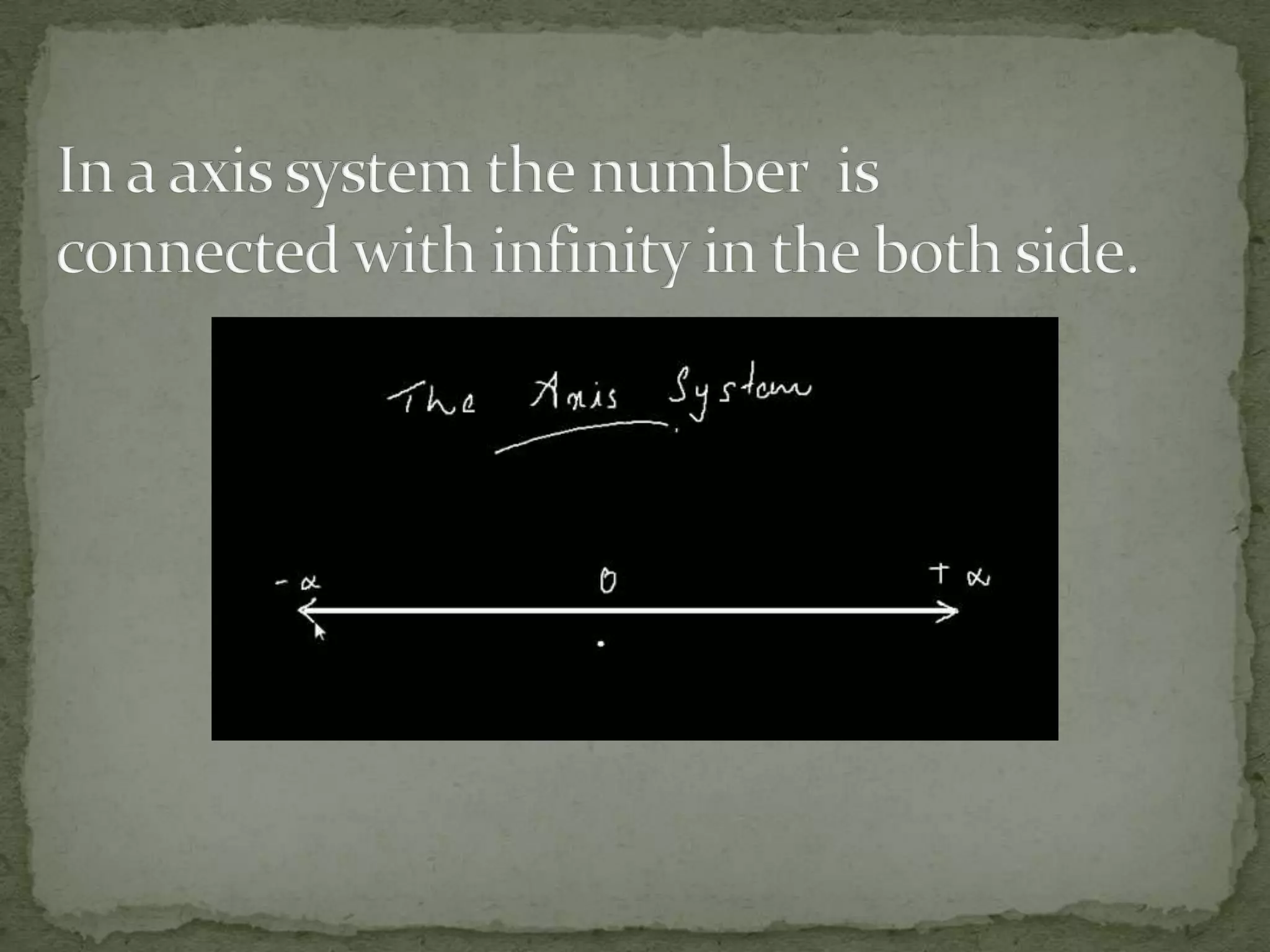This document discusses different coordinate systems including Cartesian, polar, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. It explains that the Cartesian system uses perpendicular axes that intersect at right angles, with one point defined as the origin. Polar coordinates represent a point using its distance from the origin and the angle from the x-axis. The document also describes how the axial system is used to find distances between points and know positions relative to the axes in different dimensional systems.