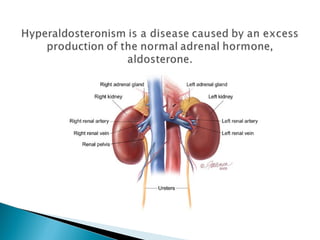
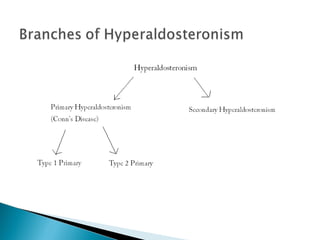
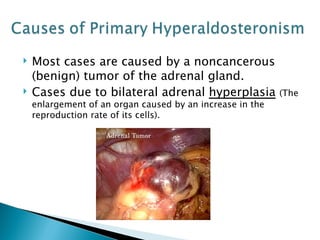
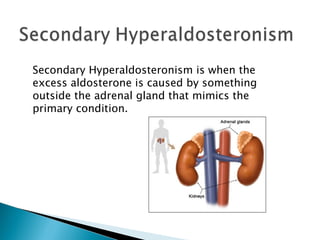
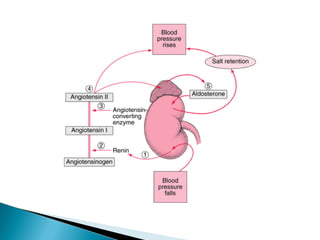
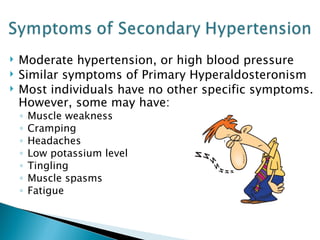
Aldosterone is a hormone that controls sodium and potassium levels in the blood. Too much aldosterone leads to high blood pressure. There are two types of hyperaldosteronism: primary, caused by tumors or overproduction in the adrenal gland; and secondary, caused by external factors that stimulate aldosterone production. Symptoms include high blood pressure, muscle weakness, and low potassium levels. The conditions are diagnosed through blood and urine tests and treated by addressing the underlying cause.