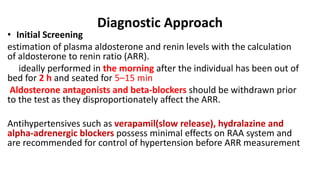
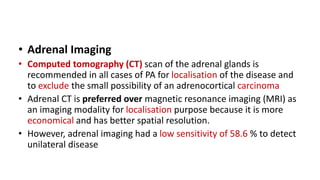
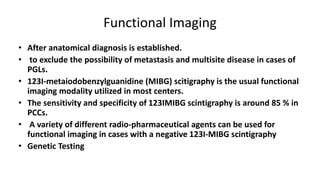
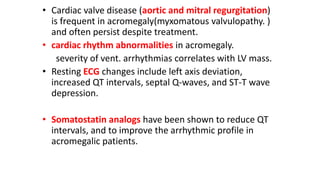
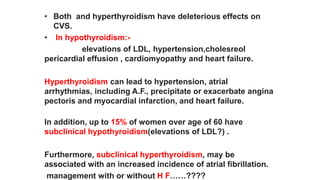
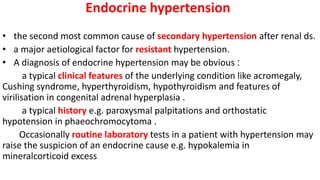
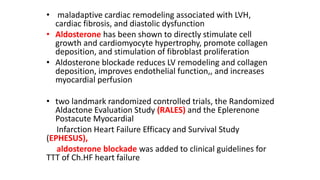
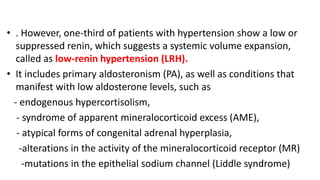
This document discusses endocrine causes of hypertension, including primary aldosteronism, pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, thyroid disorders, and others. It provides details on the pathophysiology, diagnostic approach, and management of primary aldosteronism in particular. Primary aldosteronism is one of the most common causes of secondary hypertension and can lead to hypokalemia, sodium retention, and cardiac damage if left untreated. Diagnosis involves measuring aldosterone and renin levels with calculation of the aldosterone-renin ratio, followed by confirmatory testing and imaging of the adrenal glands. Treatment options include adrenalectomy for localized disease or mineralocorticoid receptor














![Primary Mineralocorticoid Excess
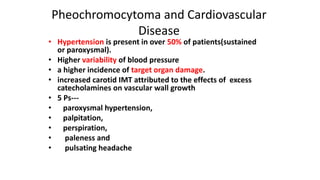
• Primary Aldosteronism (PA)
5–13 % of cases of hypertension between 30-60 years
About 10 % of cases in hypertension clinics.
4 % in the community .
20 % with resistant hypertension .
.
Nearly 60–65 % of cases of PA are from idiopathic hyperaldosteronism
(IHA)
30–35 % aldosterone producing adrenal adenoma (APA)
5 % of cases of PA are familial [FH-I, II and III]) with clear
genetic background .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endohtn-copy-231115164900-787c87a7/85/endo-htn-Copy-pptx-19-320.jpg)