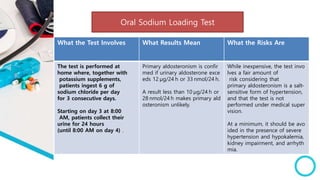
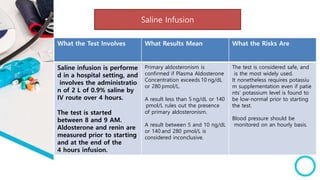
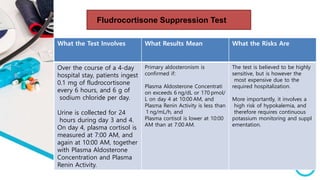
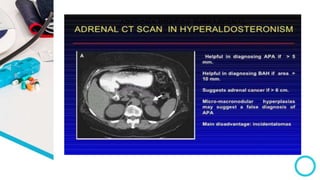
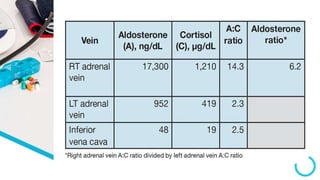
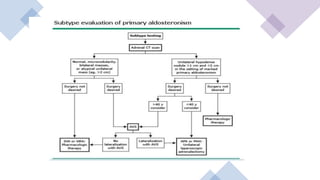
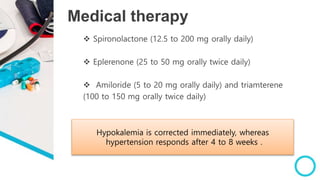
The document discusses primary hyperaldosteronism, characterized by inappropriate aldosterone overproduction, its epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, treatment options, and post-surgical care, emphasizing its prevalence in hypertensive patients and the associated risks of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Diagnosis involves biochemical screening tests like plasma aldosterone concentration and plasma renin activity, while imaging and adrenal vein sampling help localize the source of excess aldosterone for targeted therapy. Treatment typically includes surgical resection for unilateral cases and medical therapy for bilateral or inoperable cases, with close monitoring required post-operation.