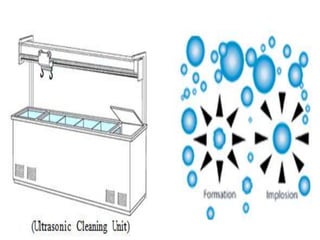
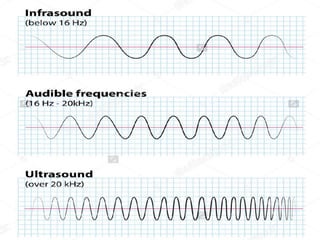
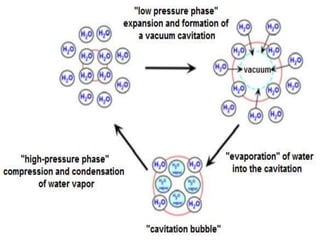
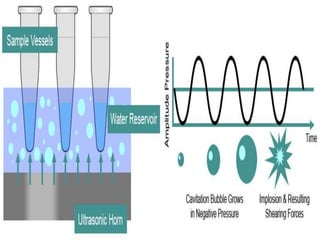
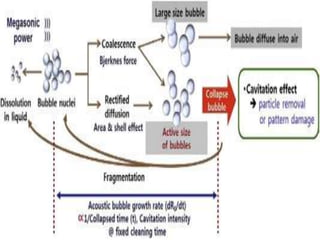
Ultrasonic technology uses high frequency sound waves to treat water and wastewater through a process called cavitation. Cavitation occurs when sound waves cause bubbles to form, grow, and violently collapse in the liquid, generating high temperatures and pressure that can break down organic compounds. This document reviews the science behind cavitation, including how piezoelectric transducers generate ultrasound, the formation of hydroxyl radicals, and the differences between transient and stable cavitation. Applications include suppression of algae growth and biofilm formation without using chemicals.