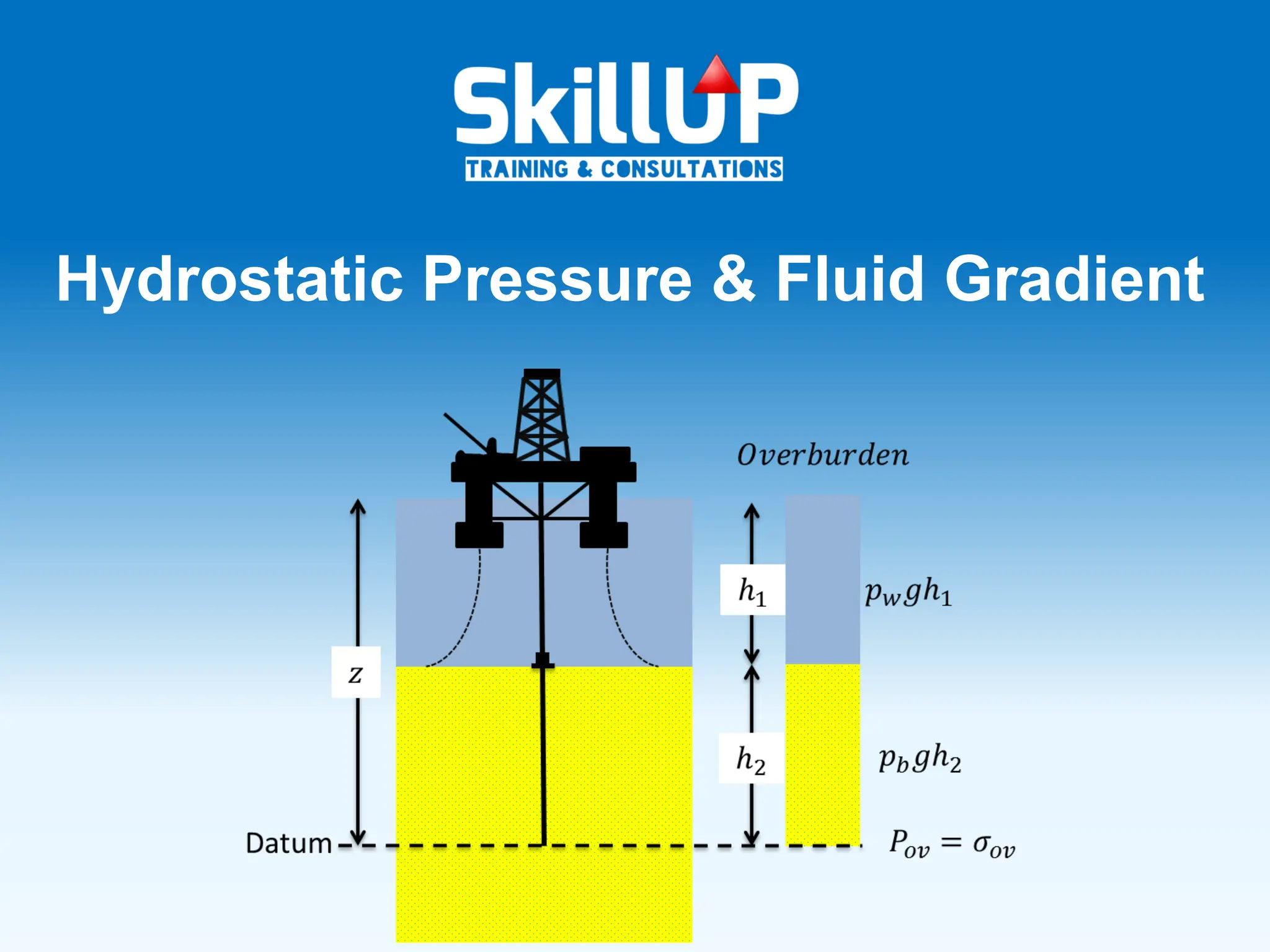
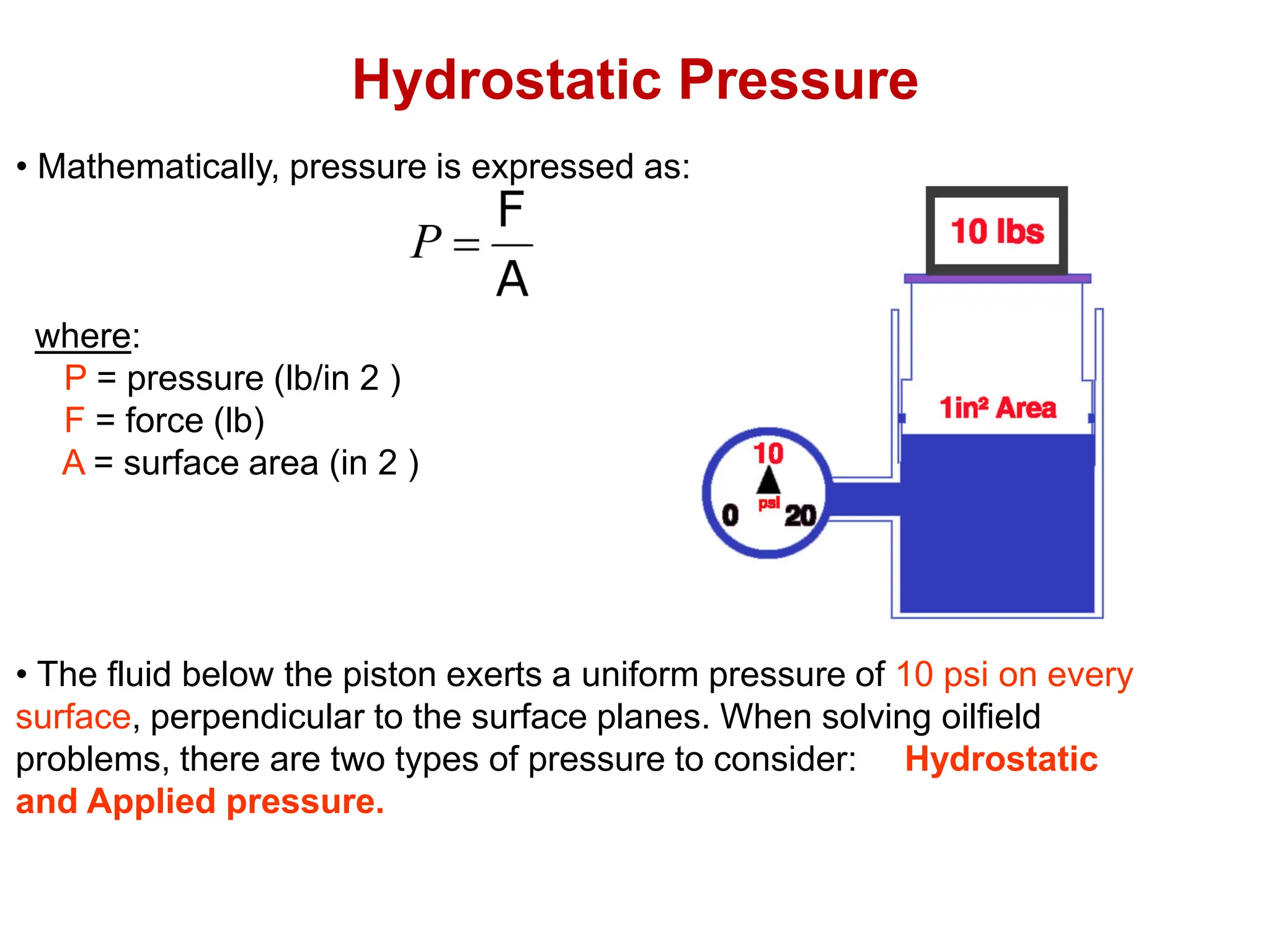
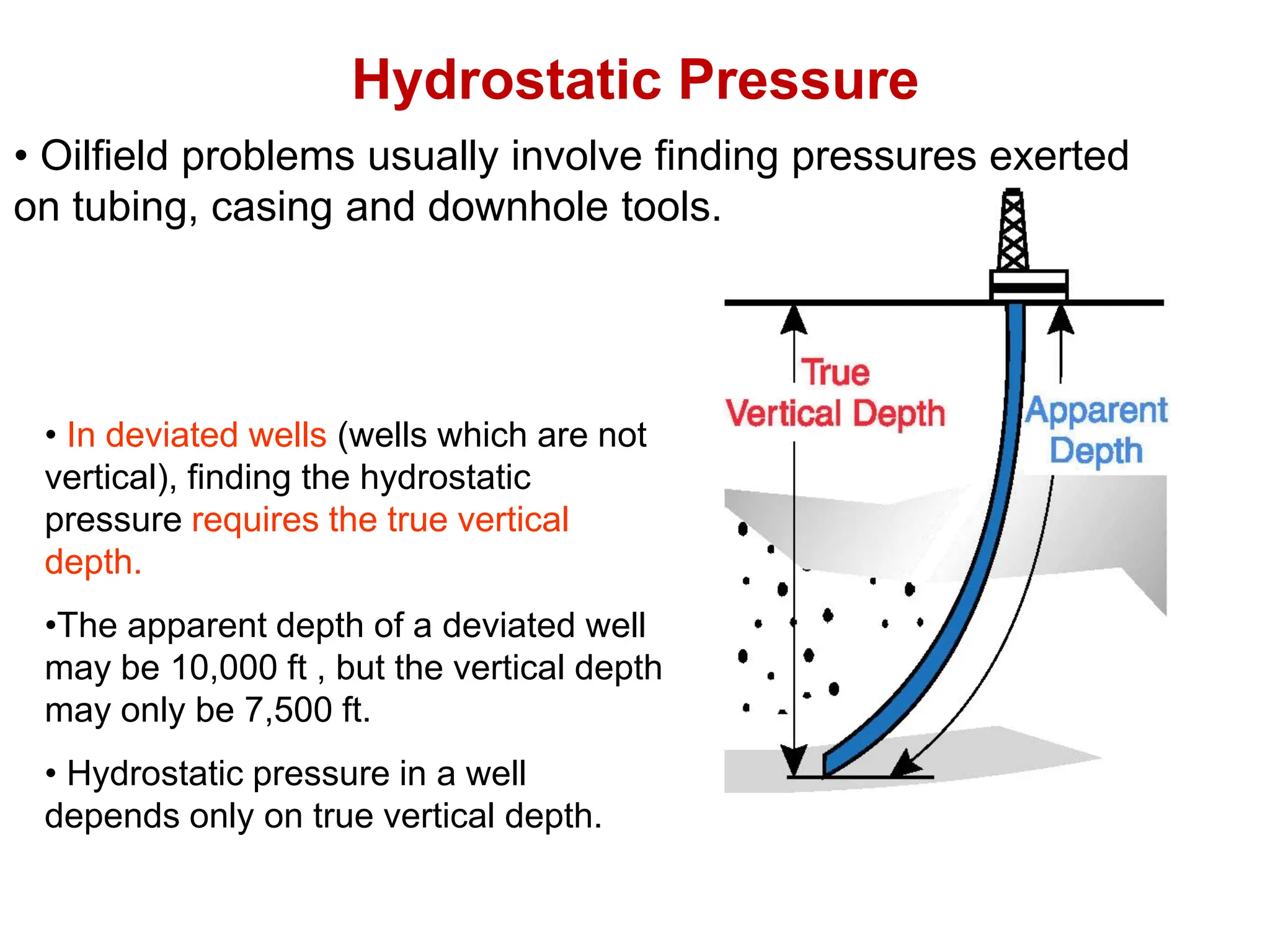
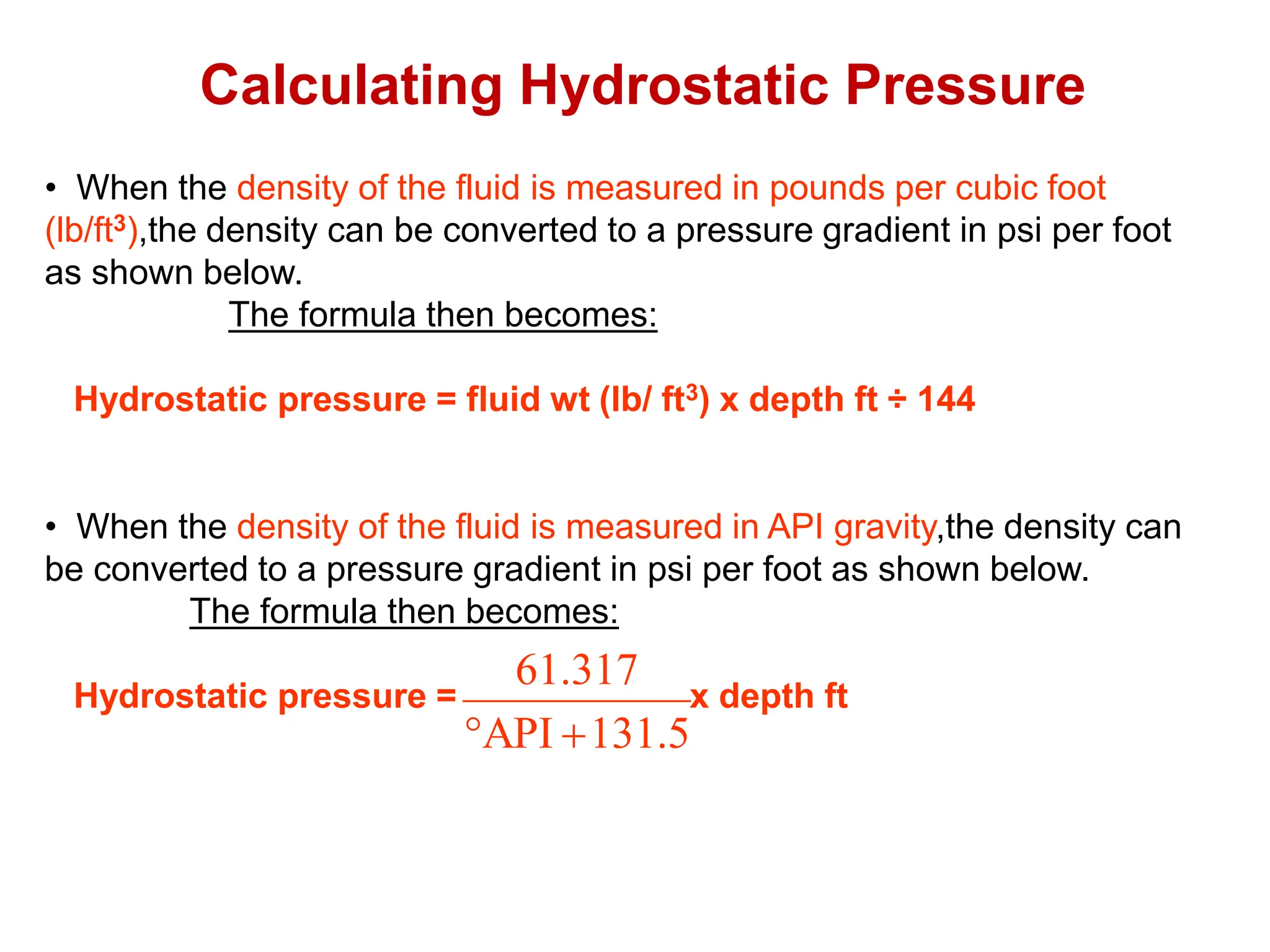
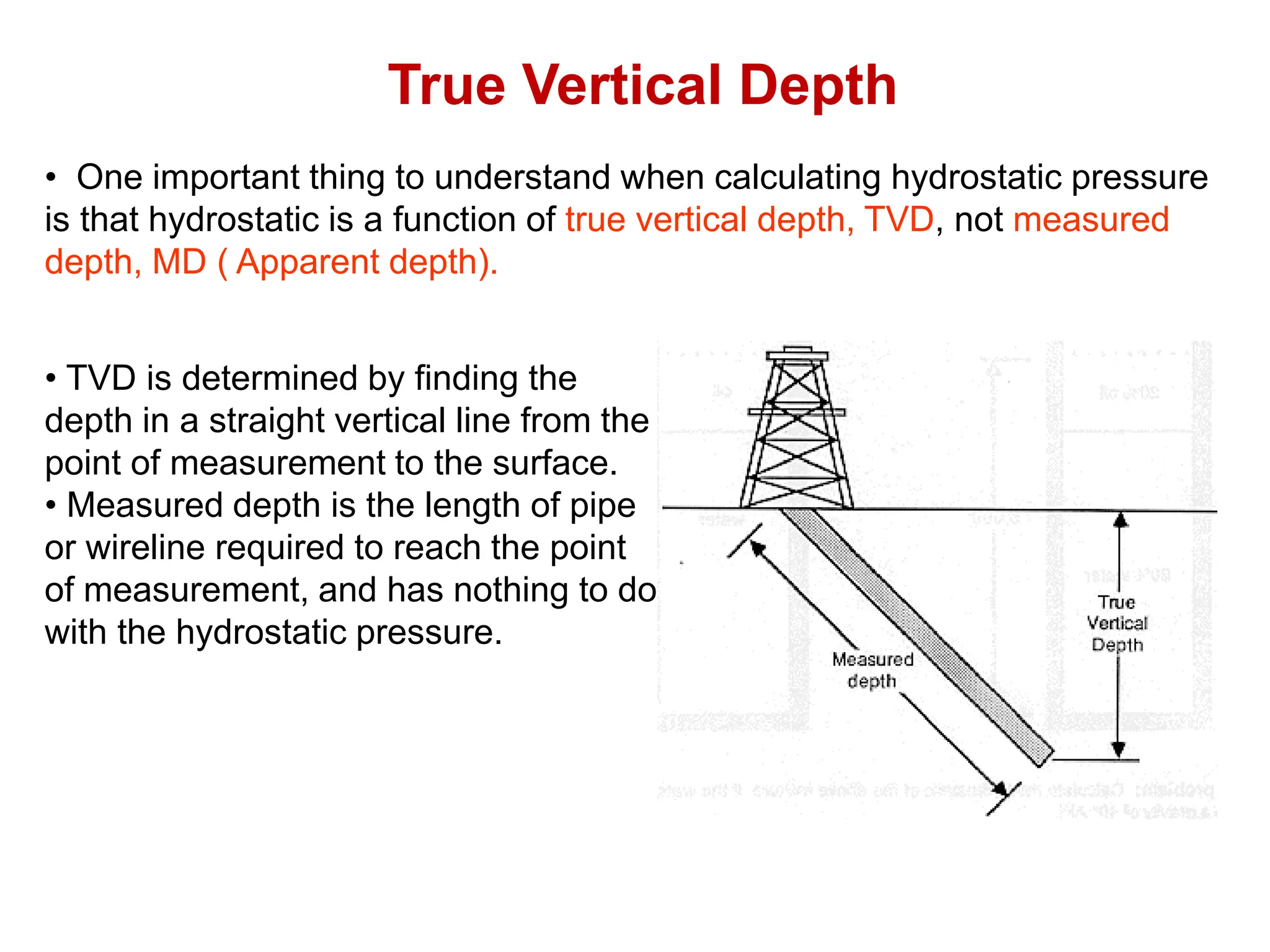
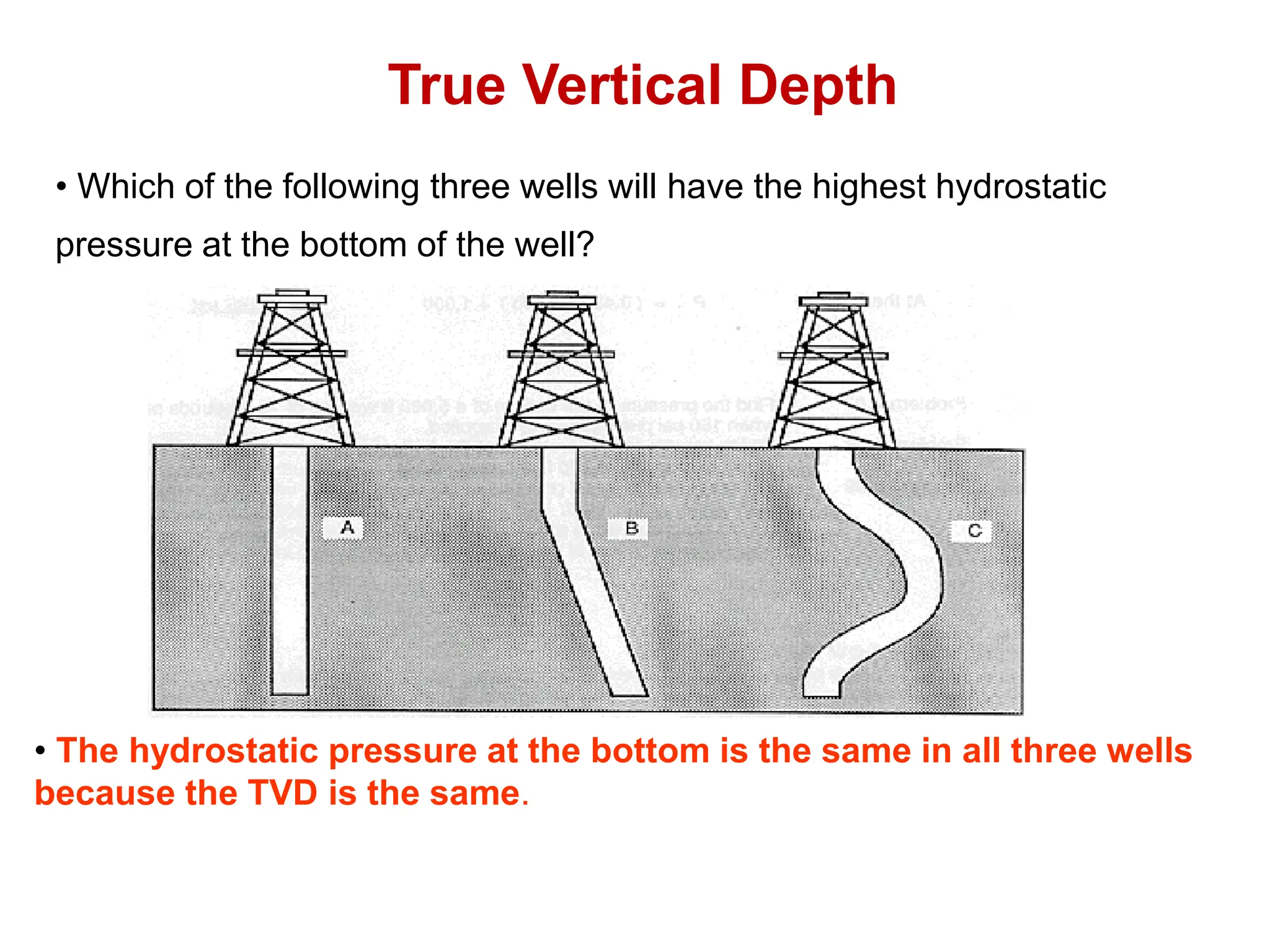
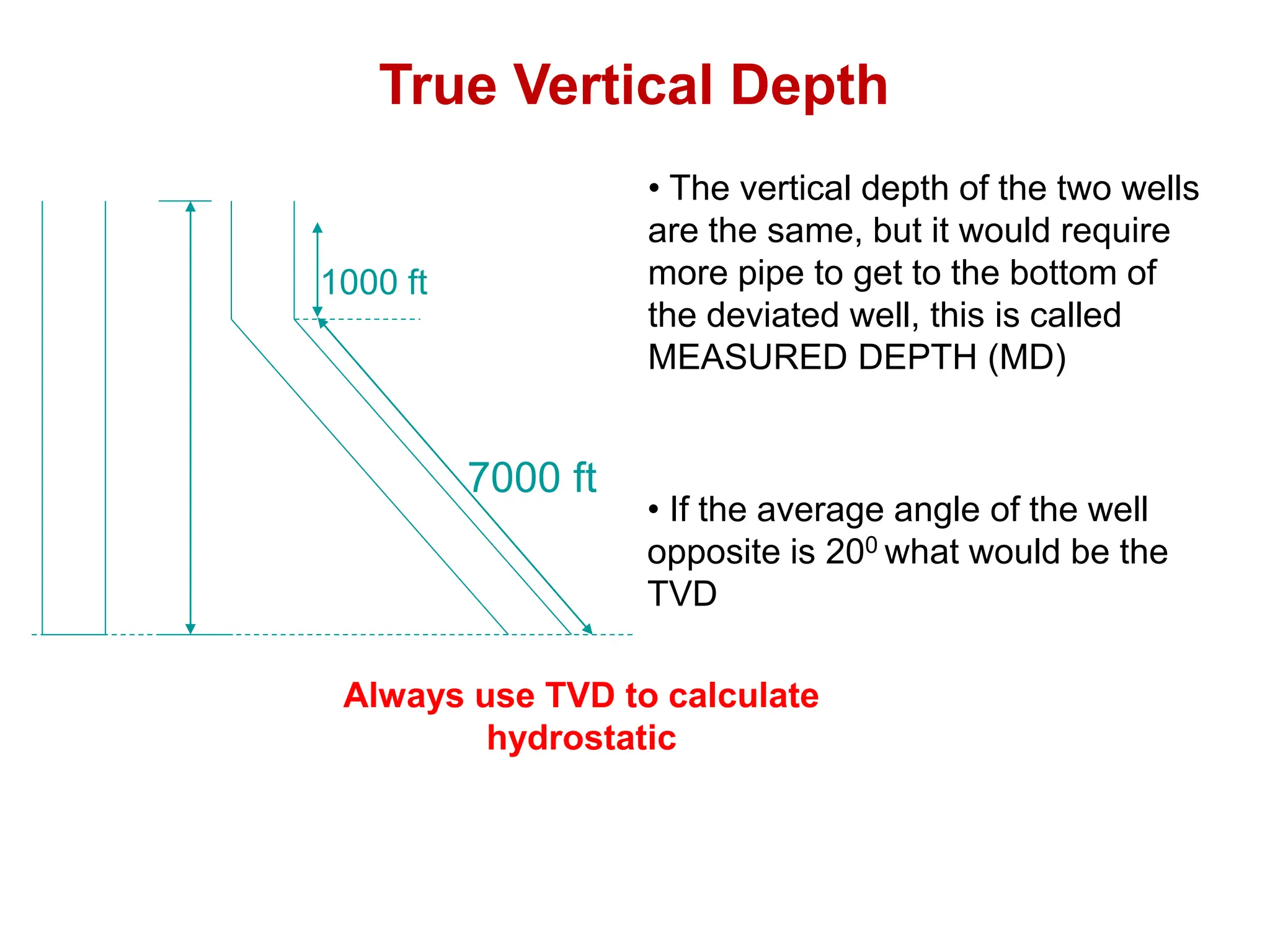
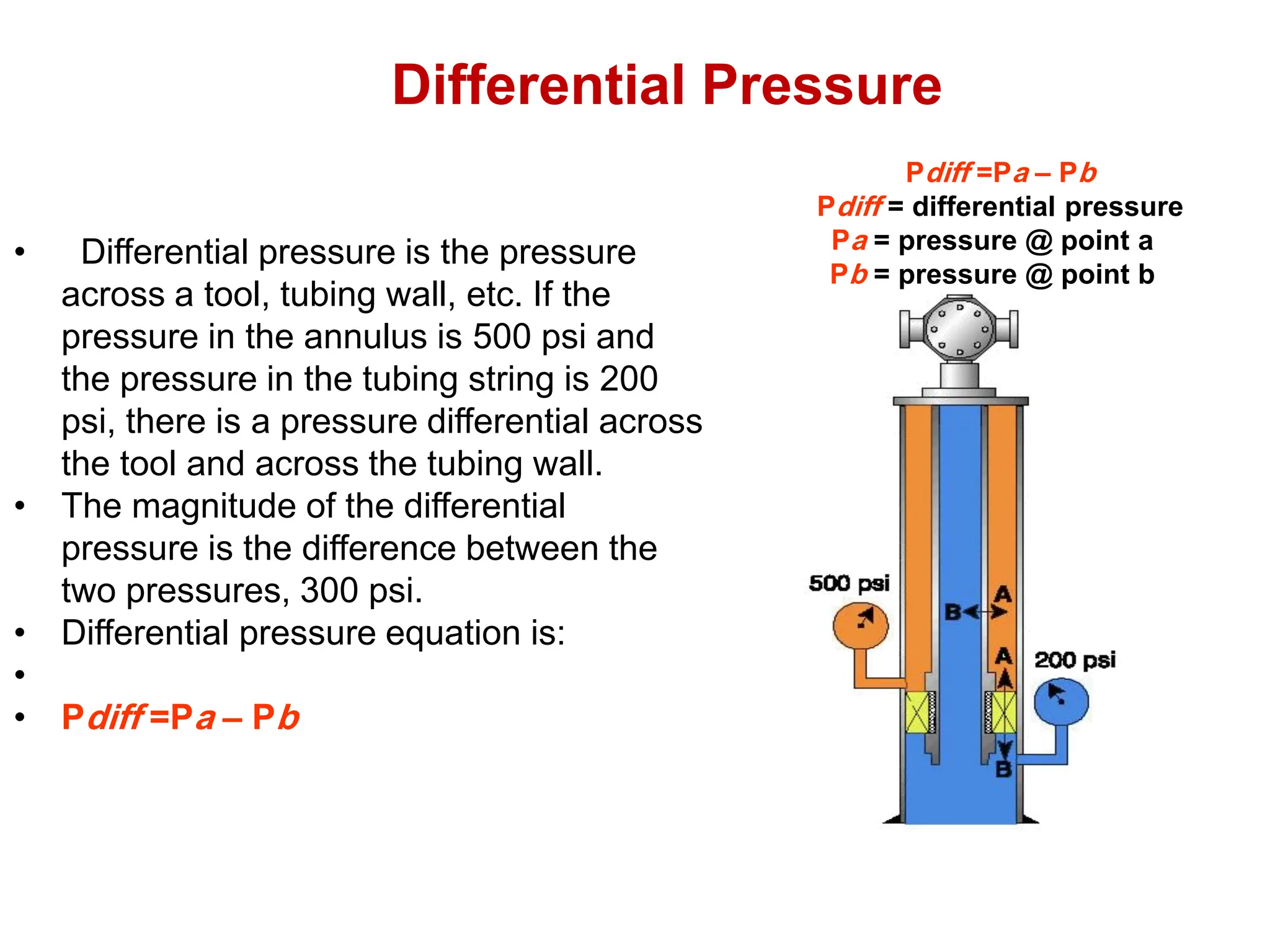
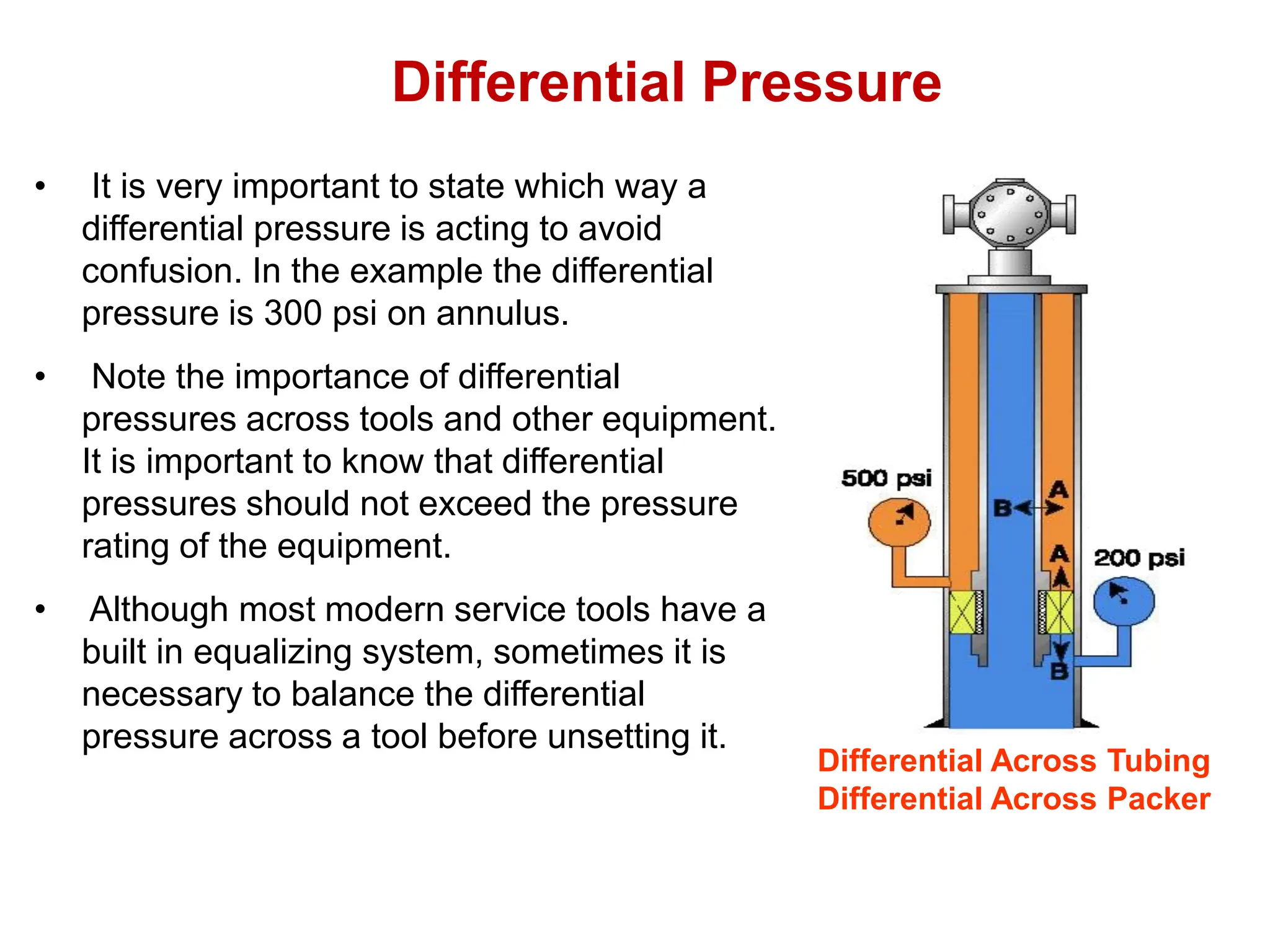
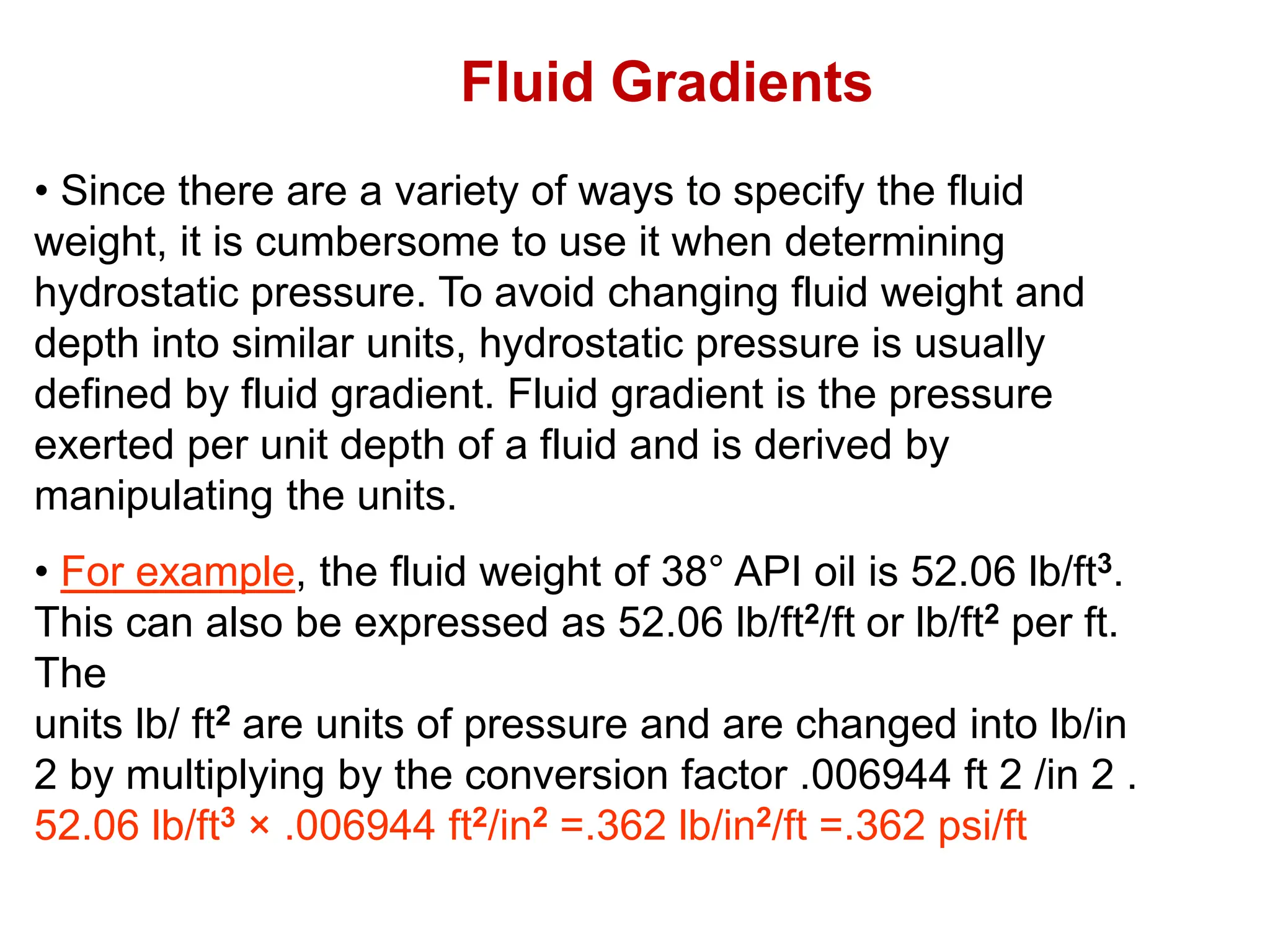
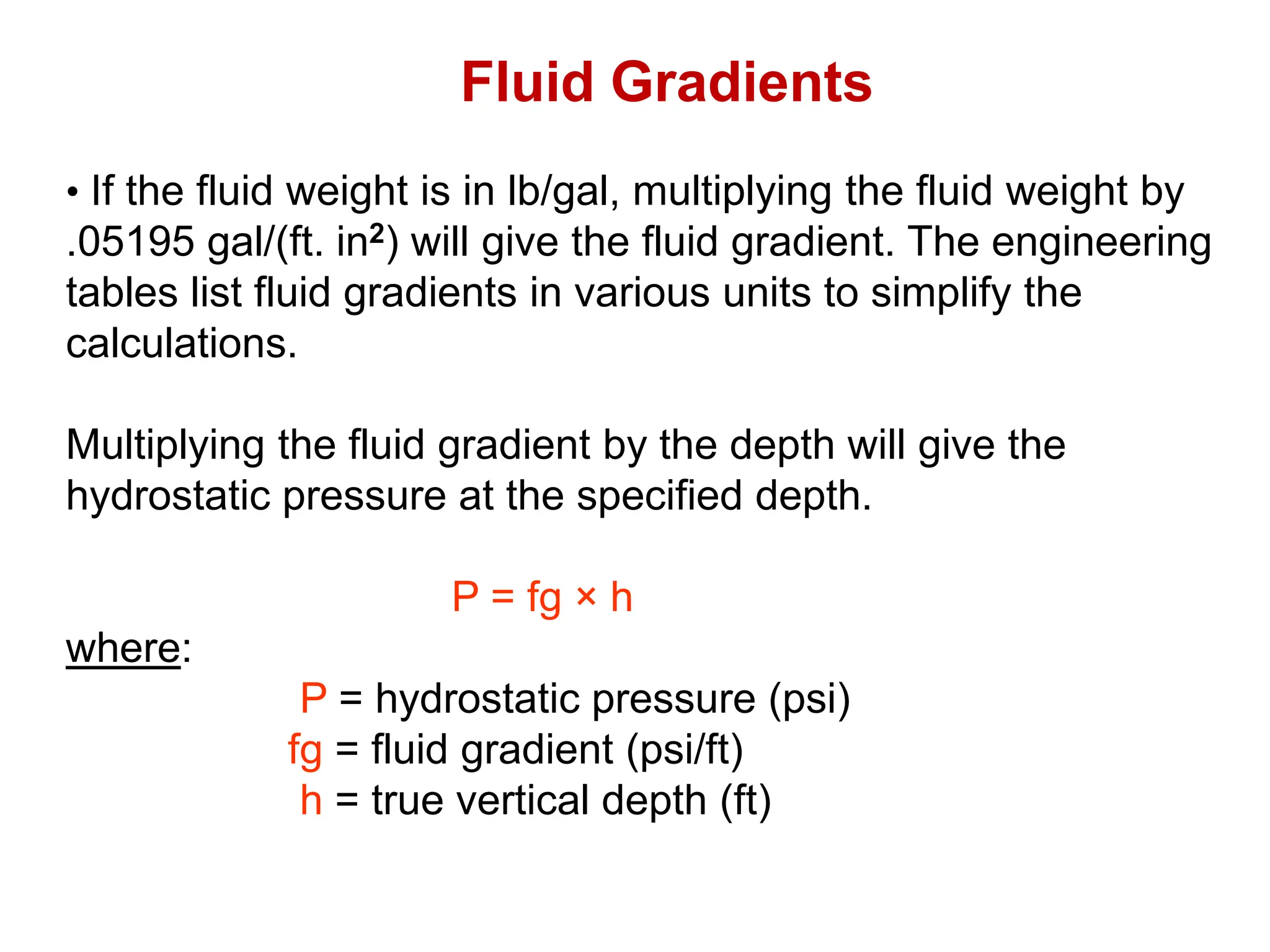
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid due to the weight of the fluid above it. It depends on the density of the fluid and the depth below the surface. To calculate hydrostatic pressure, use the formula: P = W x H, where P is pressure, W is fluid weight, and H is true vertical depth. True vertical depth, not measured depth, must be used because hydrostatic pressure only depends on the direct vertical distance through the fluid column. Fluid gradients are used instead of fluid weights to simplify hydrostatic pressure calculations.