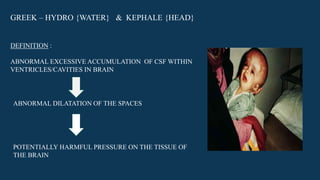
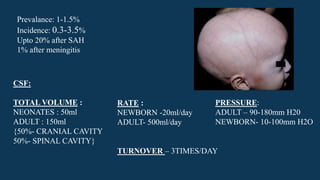
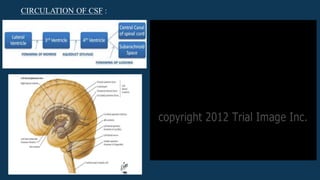
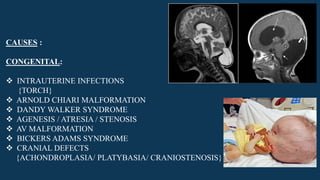
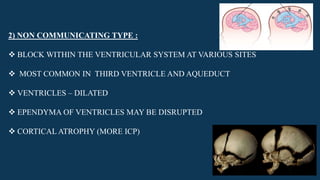
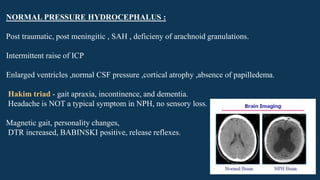
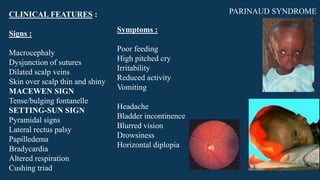
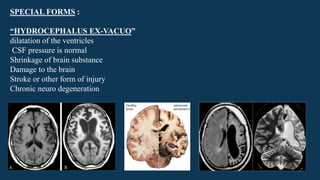
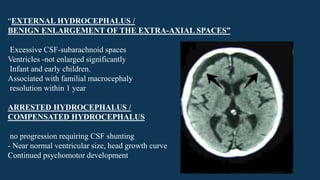
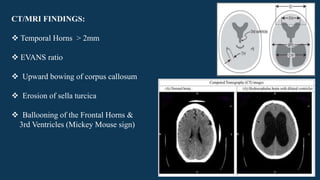
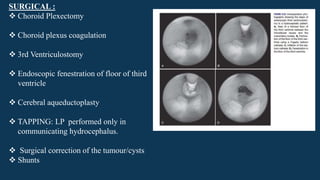
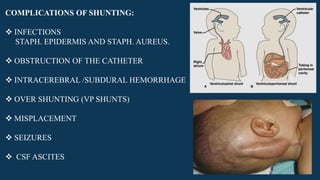
Hydrocephalus is characterized by abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain's ventricles, leading to potentially harmful pressure on brain tissue. It has a prevalence of 1-1.5% and causes can be congenital or acquired, with various types classified as communicating or non-communicating. Treatment options include medical management with diuretics and surgical interventions such as shunting, with prognosis dependent on the underlying cause.