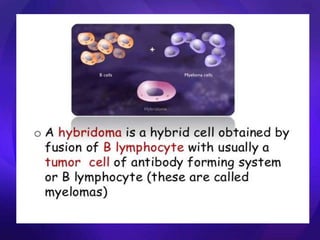
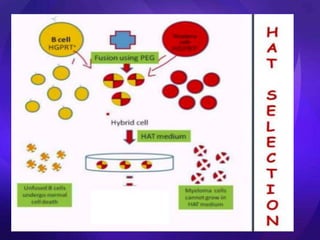
The hybridoma technique was developed in 1975 by Georges Kohler and Cesar Milstein. It involves fusing B lymphocytes that produce antibodies against a specific antigen with myeloma cells to form a hybrid cell or hybridoma. This hybridoma has the ability to produce antibodies from the B cell and can divide continuously like the myeloma cell. The hybridomas are screened and isolated to produce monoclonal antibodies of a single specificity. This hybridoma technology provides a way to produce large quantities of monoclonal antibodies.