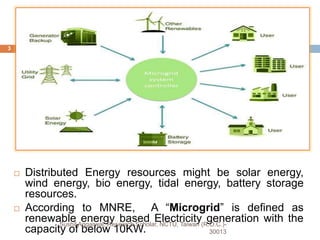
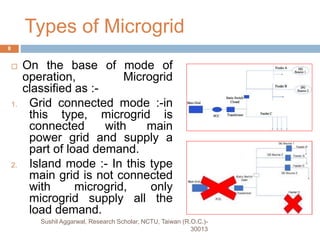
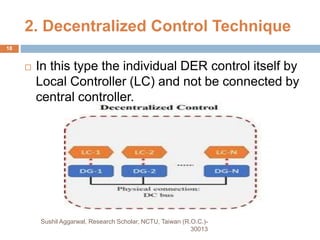
The document discusses the role and importance of microgrids in the power sector, defining microgrids as integrated systems of small power generation units and loads utilizing renewable energy sources. It outlines various components, operational modes, control structures, and trends such as the transition from traditional microgrids to 'prosumer' microgrids, where consumers also produce energy. The document emphasizes the need for microgrids to address energy demand and promote sustainability through renewable resources.