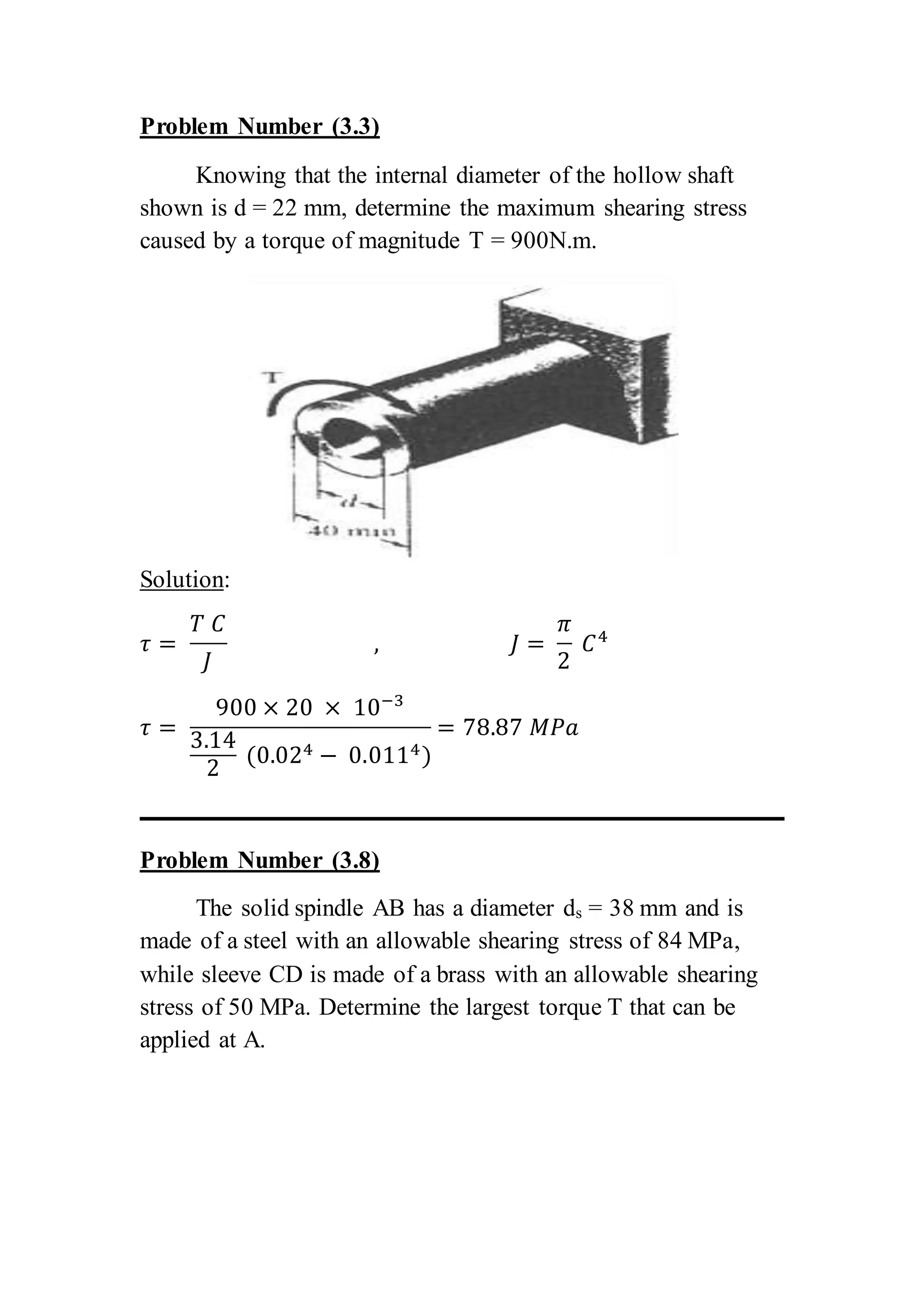
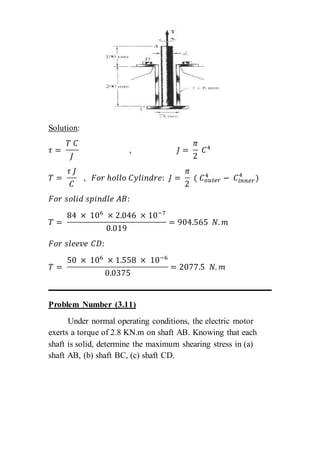
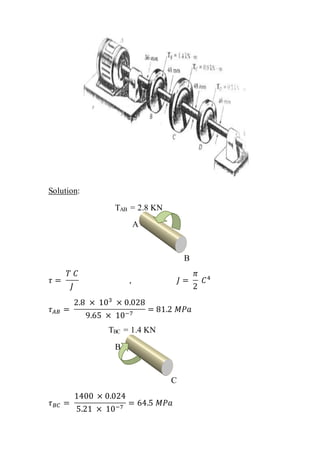
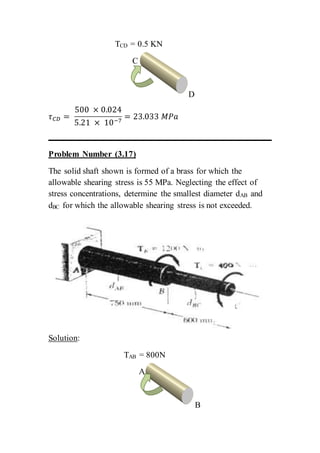
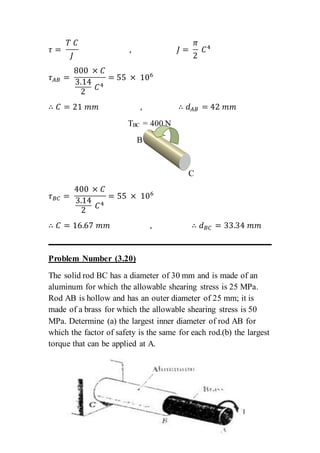
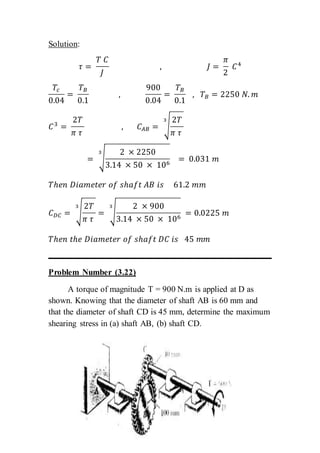
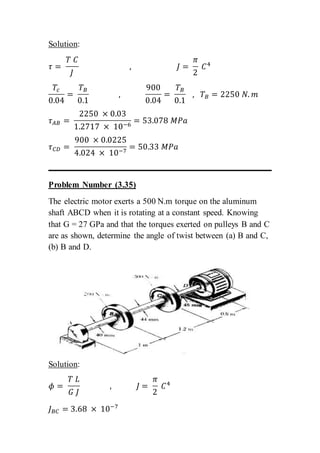
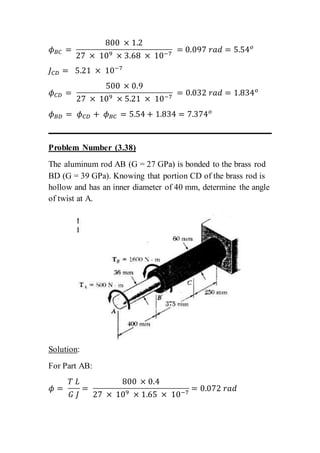
The document contains solutions to multiple problems involving determining shear stress, torque, and angle of twist in shaft and rod systems. Key details include formulas for calculating shear stress given torque and geometry, determining required diameters to not exceed allowable stress, and calculating angle of twist between sections using torque, length, shear modulus, and polar second moment of area. Examples analyze hollow and solid shafts made of materials like steel, brass, and aluminum under different torque conditions.