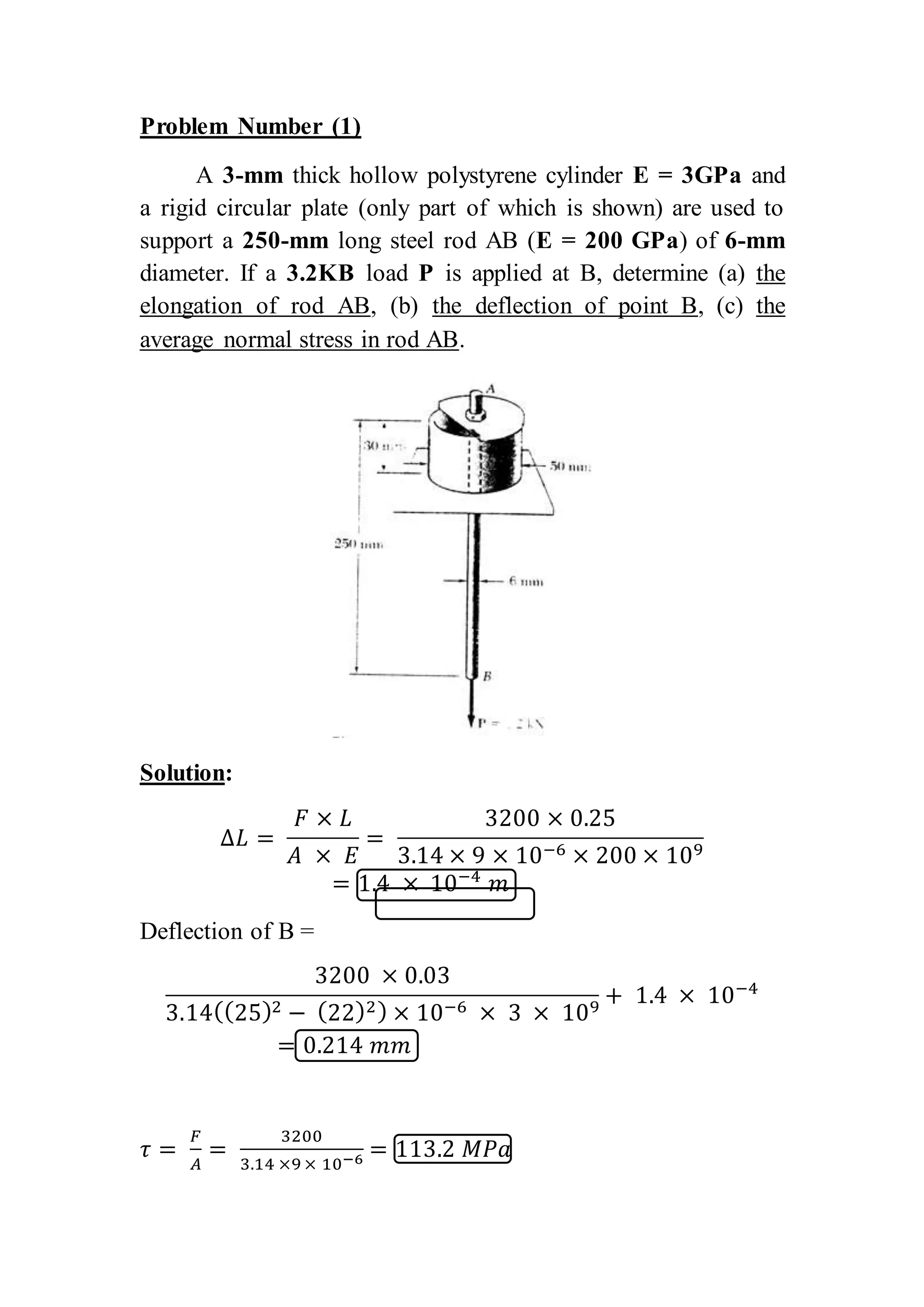
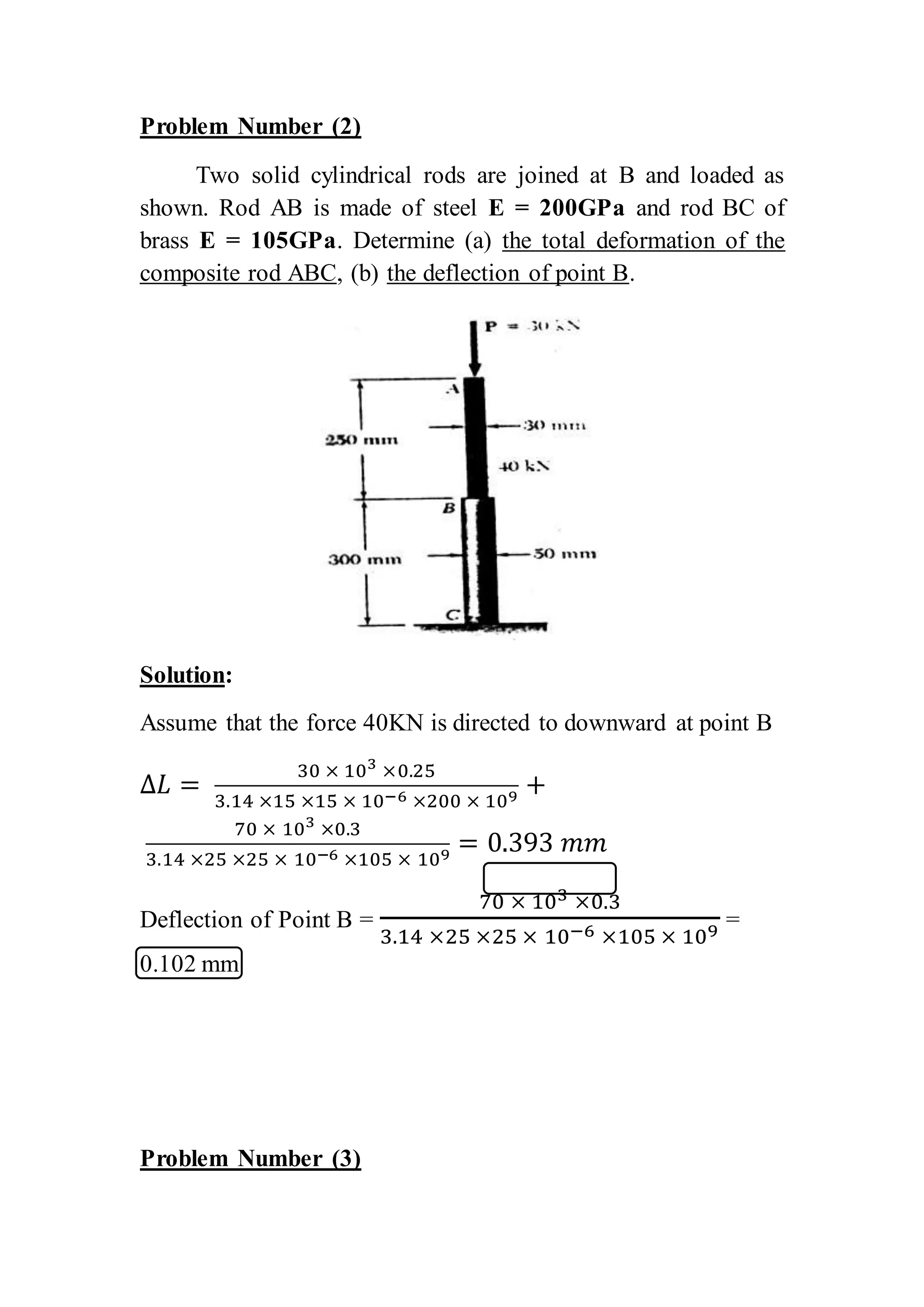
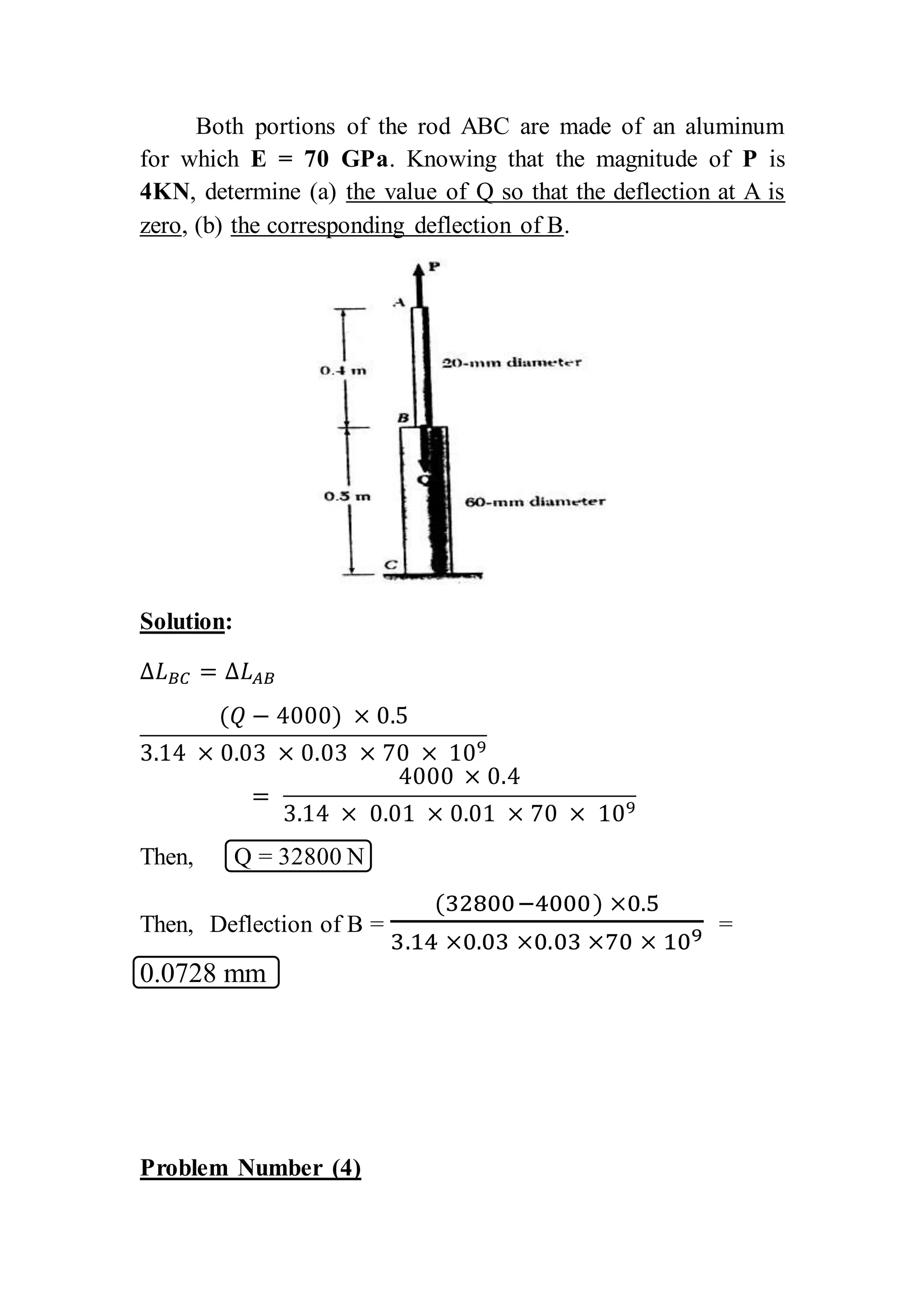
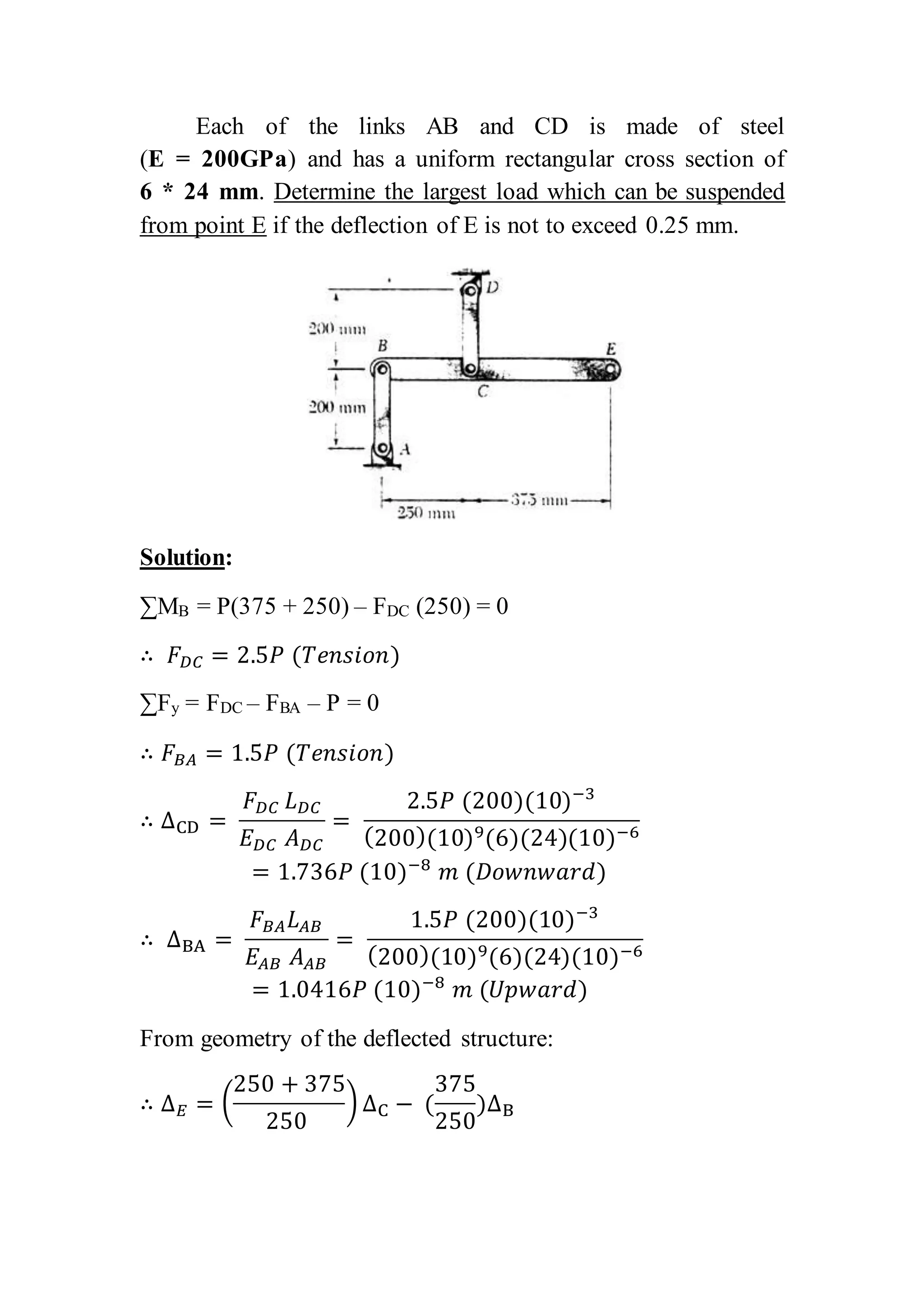
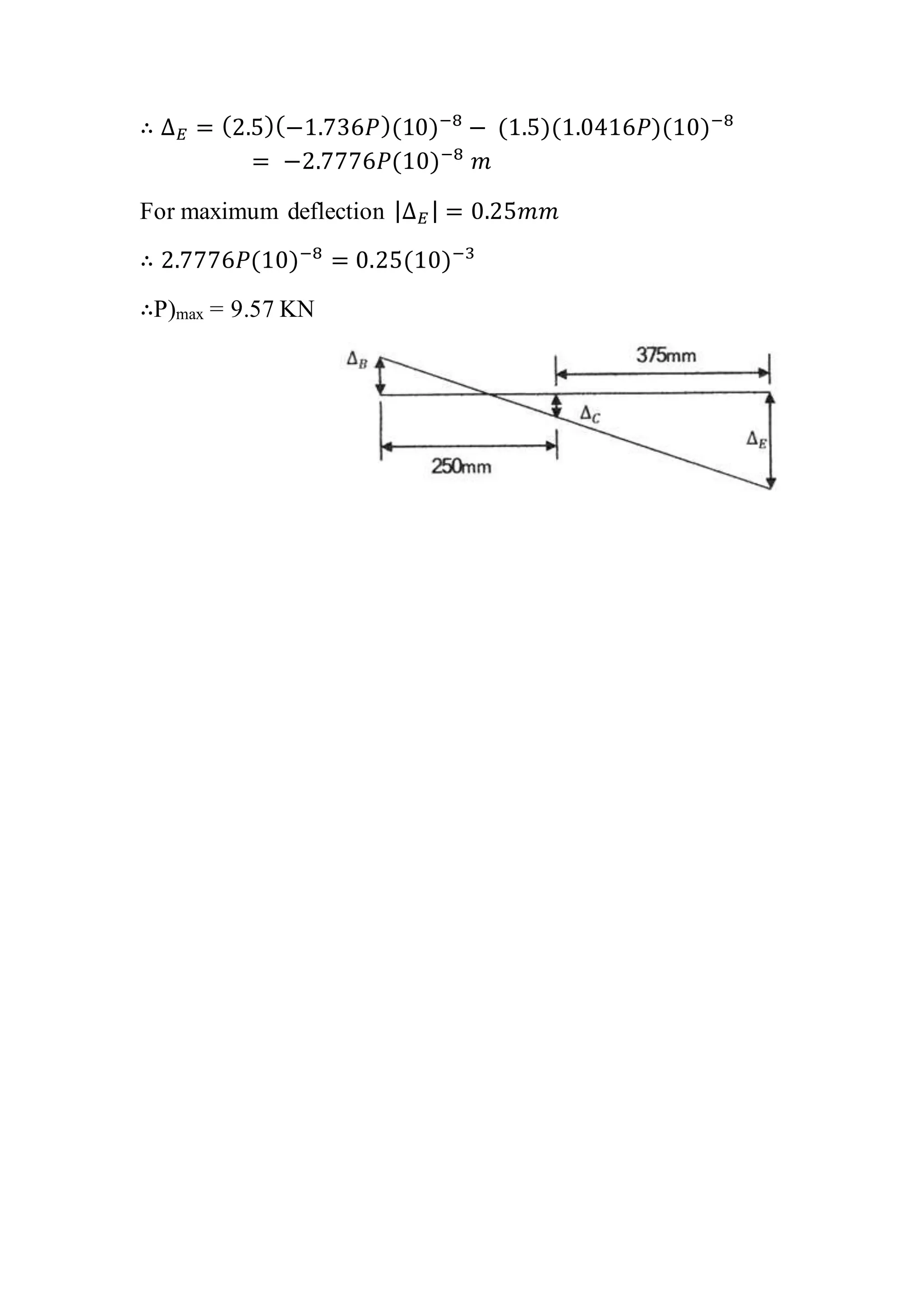
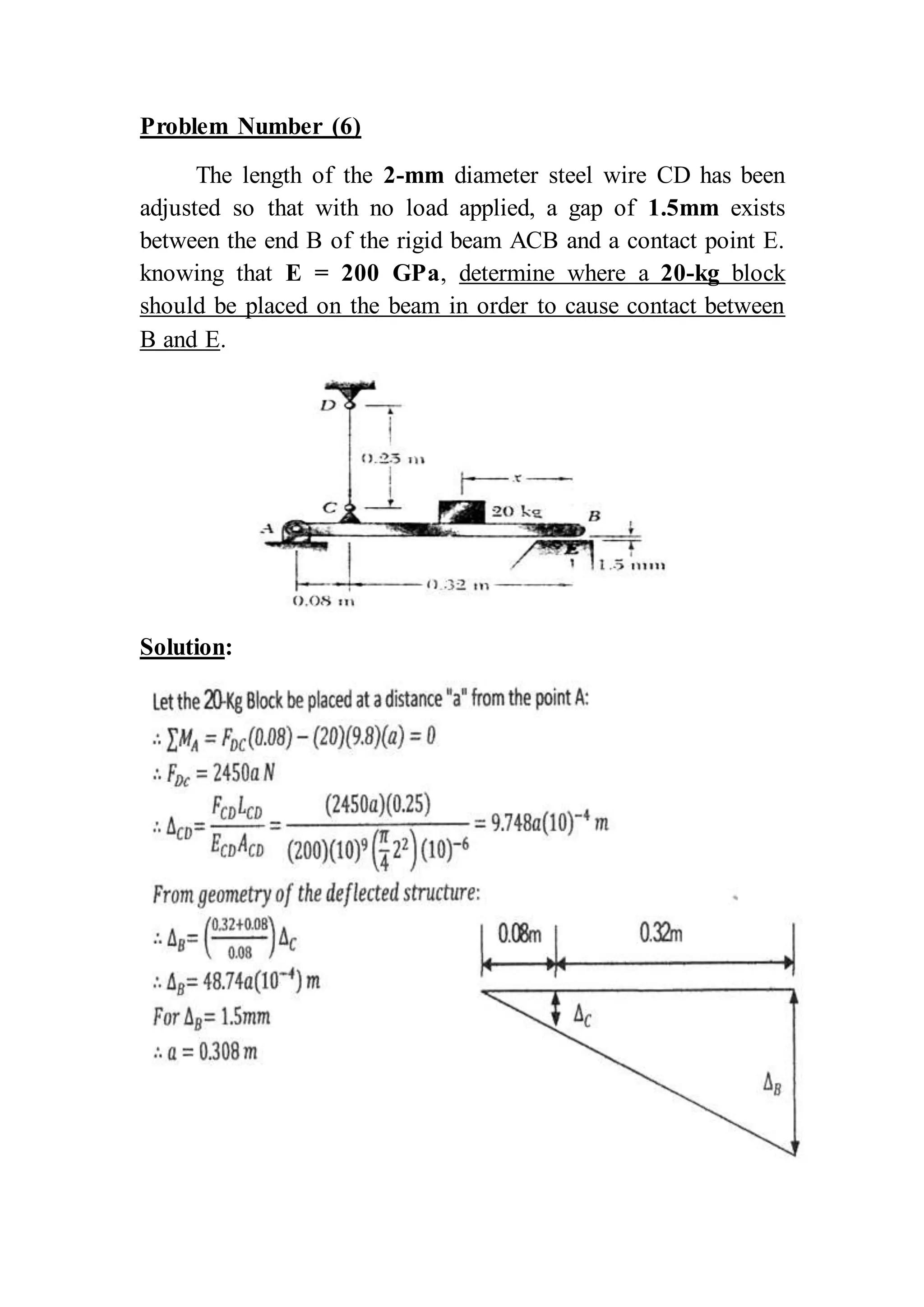
This document contains 6 problems involving calculations of stress, strain, deflection and load capacity for mechanical structures composed of rods, beams, and wires under various loading conditions. The materials involved include steel, aluminum, brass and polystyrene. Deflections, elongations, average stresses and maximum supported loads are calculated using basic mechanics of materials equations relating force, stress, strain, modulus of elasticity and structural geometry.