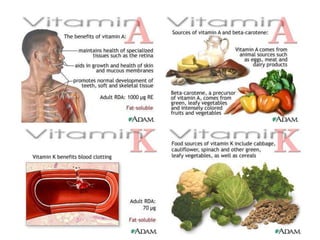
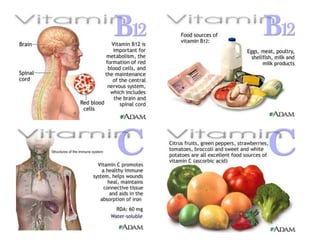
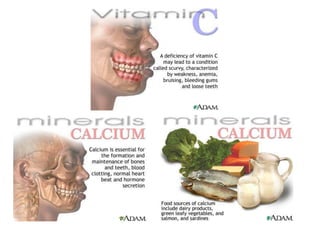
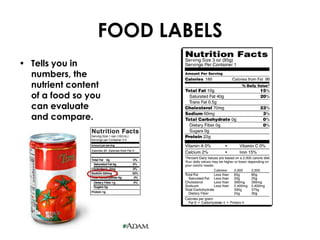
Food provides the energy and materials needed to grow and repair tissues through nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. Carbohydrates and fats are the body's primary sources of energy, providing calories, while proteins, vitamins, and minerals supply the raw materials for tissue growth and maintenance. The food guide pyramid recommends daily servings from each food group to help ensure intake of necessary nutrients. Food labels provide numeric information on nutrients to allow for evaluation and comparison of foods.