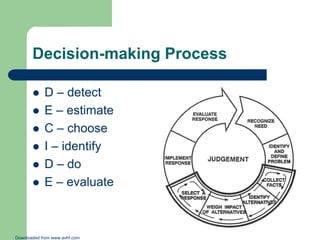
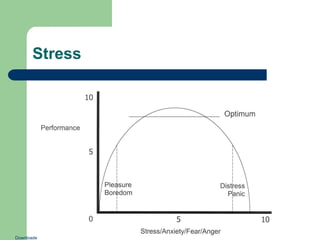
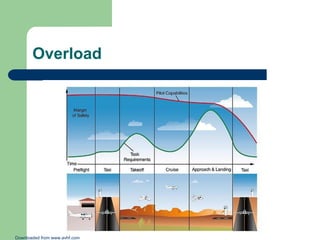
The document discusses aeronautical decision-making by outlining risk elements related to pilots, aircraft, environment, operation, and situation awareness. It elaborates on the importance of communication and judgment in improving flight safety while highlighting the series of errors that lead to accidents. Furthermore, it emphasizes maintaining situational awareness and effective workload management to prevent incidents in aviation.