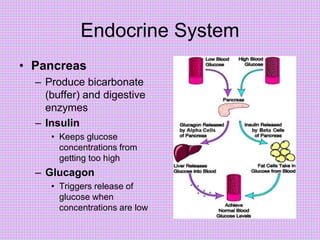
The endocrine system is comprised of glands that produce hormones which are chemicals released into the bloodstream to stimulate reactions in target organs. The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland which controls other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, lactation, and water balance. Other important glands are the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries and testes which regulate processes like calcium levels, stress response, blood sugar, and sexual development.