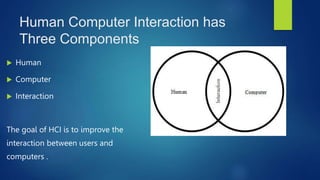
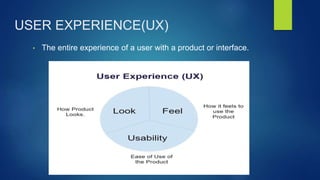
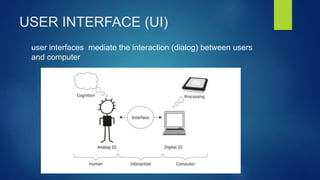
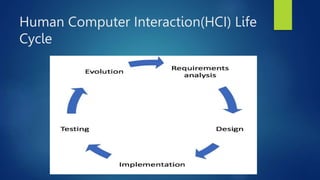
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) focuses on the design and evaluation of interactive computing systems to improve user-computer interactions. The document discusses HCI's goals, components, and lifecycle, highlighting its evolution from complex early computers to modern user-friendly interfaces and emerging technologies like AI and wearable devices. It also outlines the benefits and challenges associated with HCI, emphasizing the importance of usability and user experience.