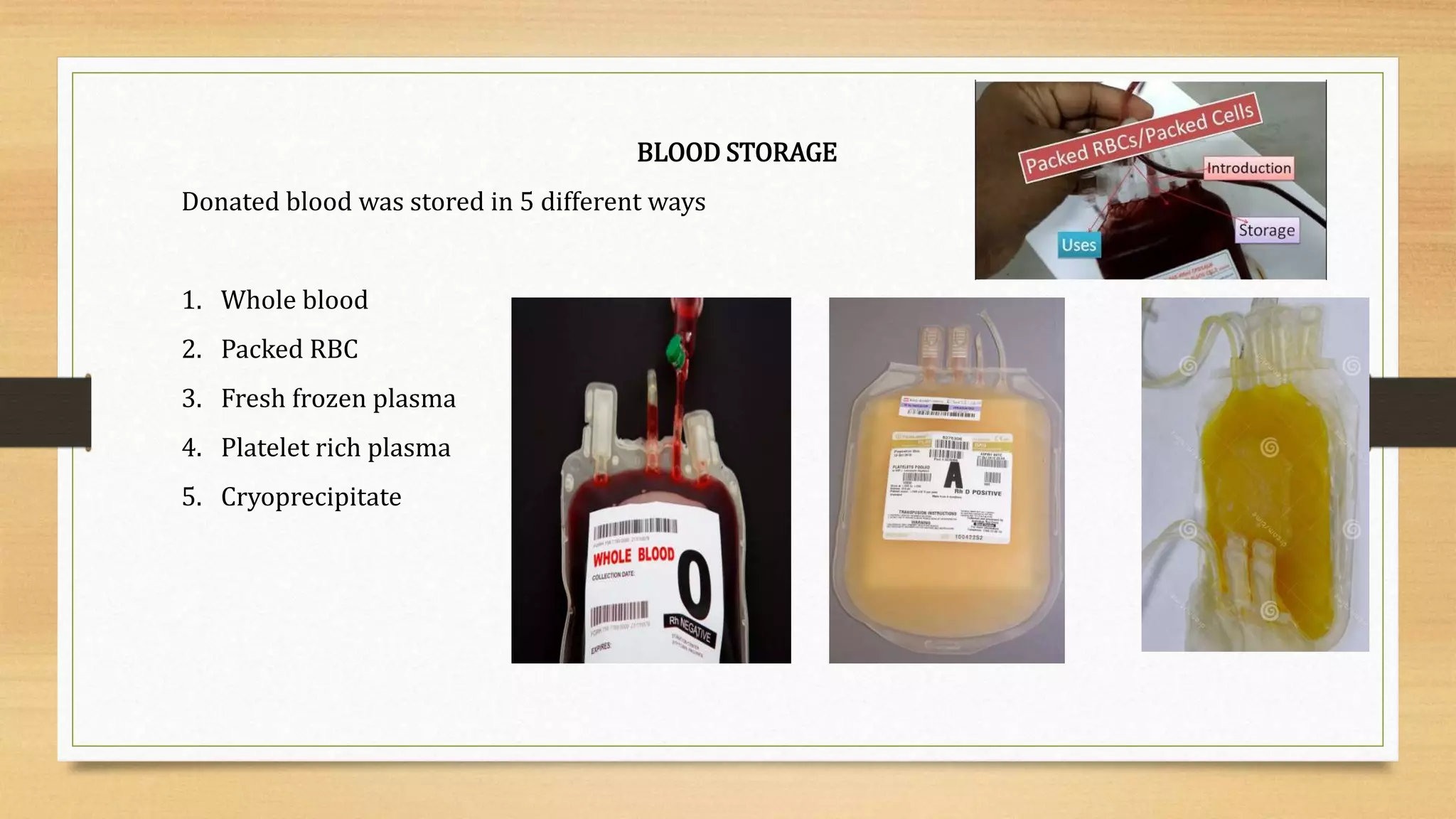
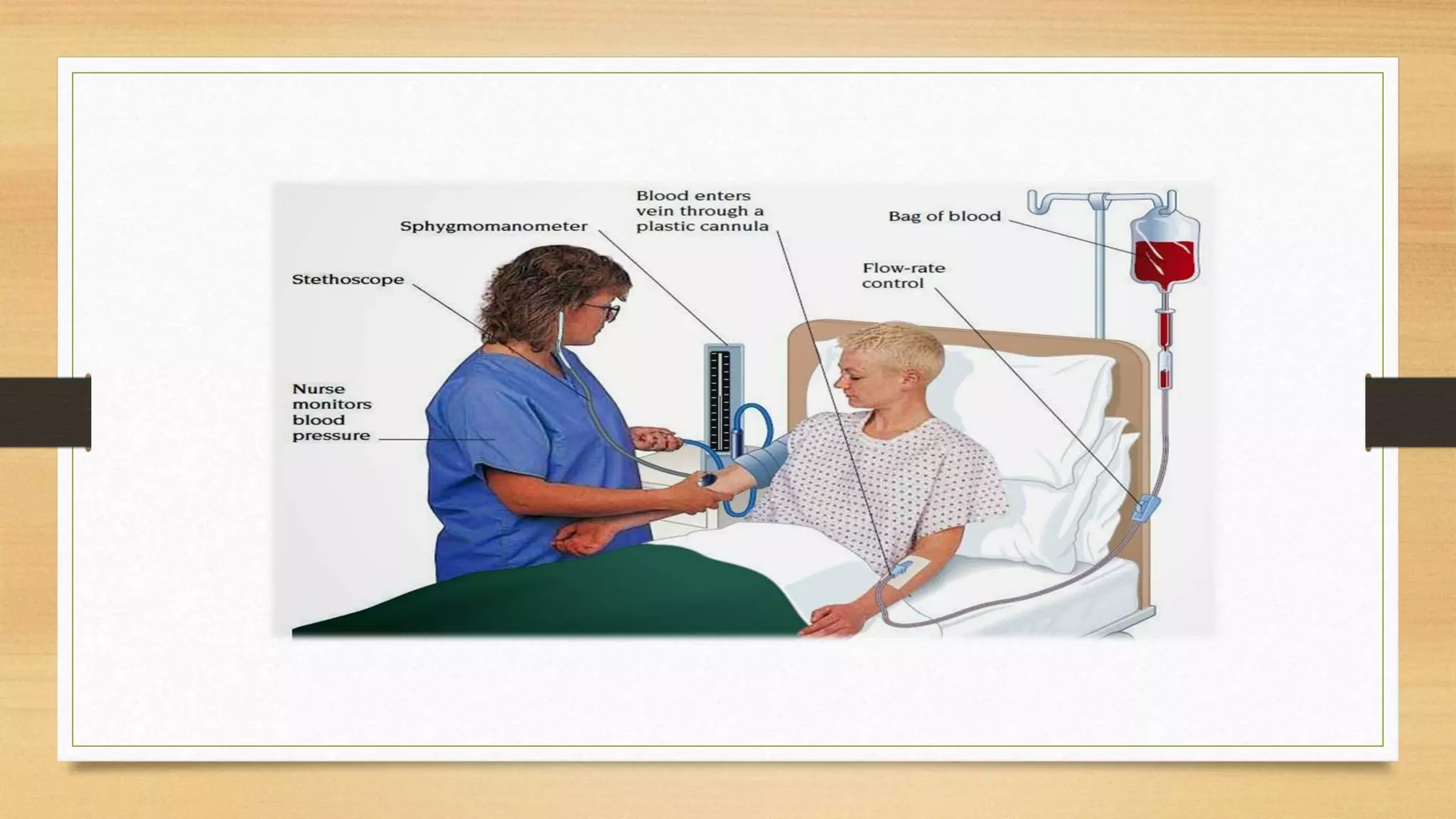
A blood bank is a center that stores and preserves donated blood for transfusions. It tests blood to reduce transfusion risks. Key functions include blood collection, processing, testing, separation, and storage. Blood has red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and white blood cells. It is grouped by the ABO and Rh blood group systems. Donor selection, counseling, collection and testing ensure safe blood. Components are stored separately as whole blood, packed red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma, platelet rich plasma or cryoprecipitate.