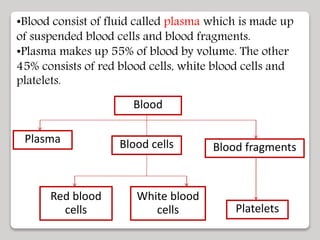
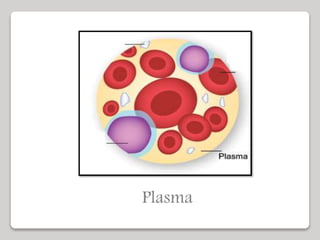
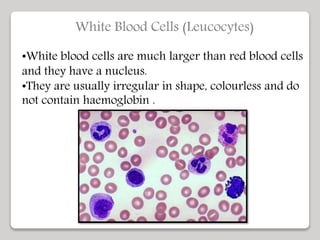
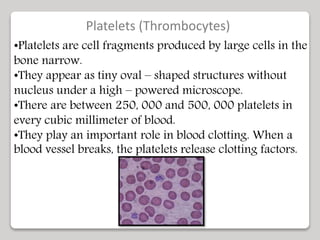
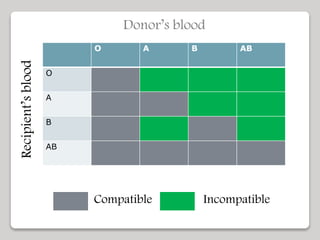
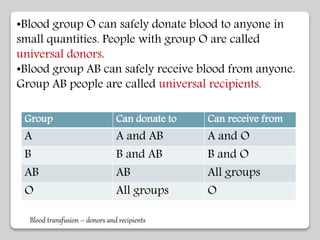
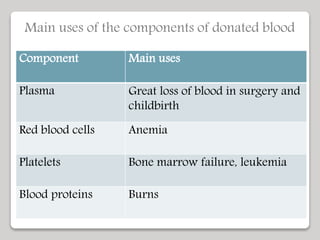
The document discusses the constituents of human blood. Blood consists of plasma and blood cells. Plasma is made up of water, proteins, nutrients, and waste products. It transports these substances between tissues. Blood also contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells help fight infection. Platelets aid in blood clotting. The document also covers blood typing and transfusion compatibility, as well as the importance of blood donations.