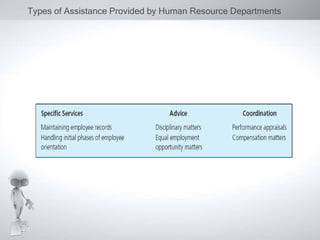
This document discusses human resource development (HRD). It begins by defining HRD as concerned with developing and implementing people strategies to ensure organizational goals are achieved. Common HRD activities are listed as training, education, and development. The document then discusses the importance of training and development for achieving strategic goals in the 21st century. It notes that HRD practices may differ between countries and cultural differences are important to consider. The document also provides context on the history and development of HRD as a field in India. It identifies factors that have contributed to the growth of HRD as a profession and types of assistance provided by human resource departments.