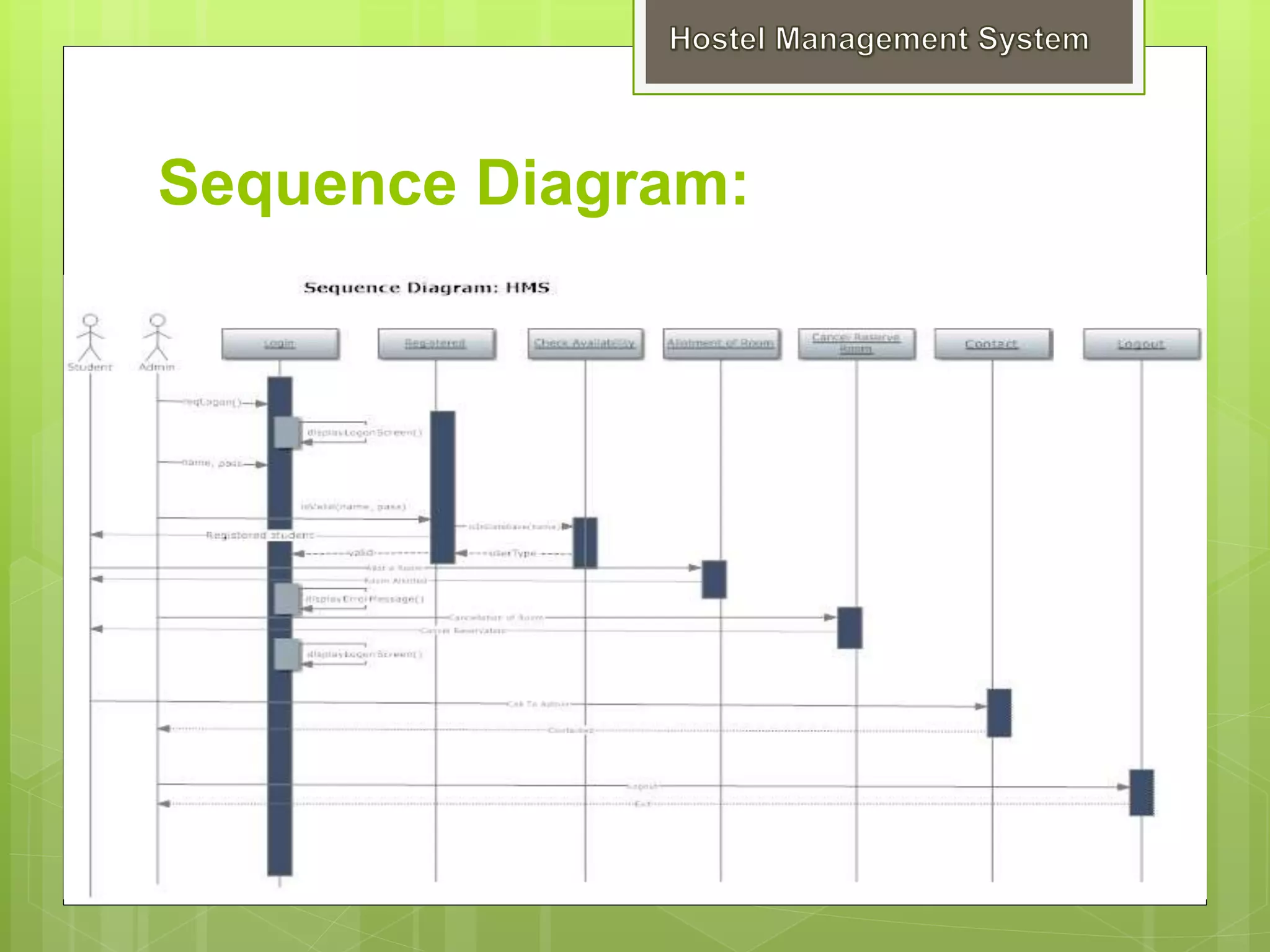
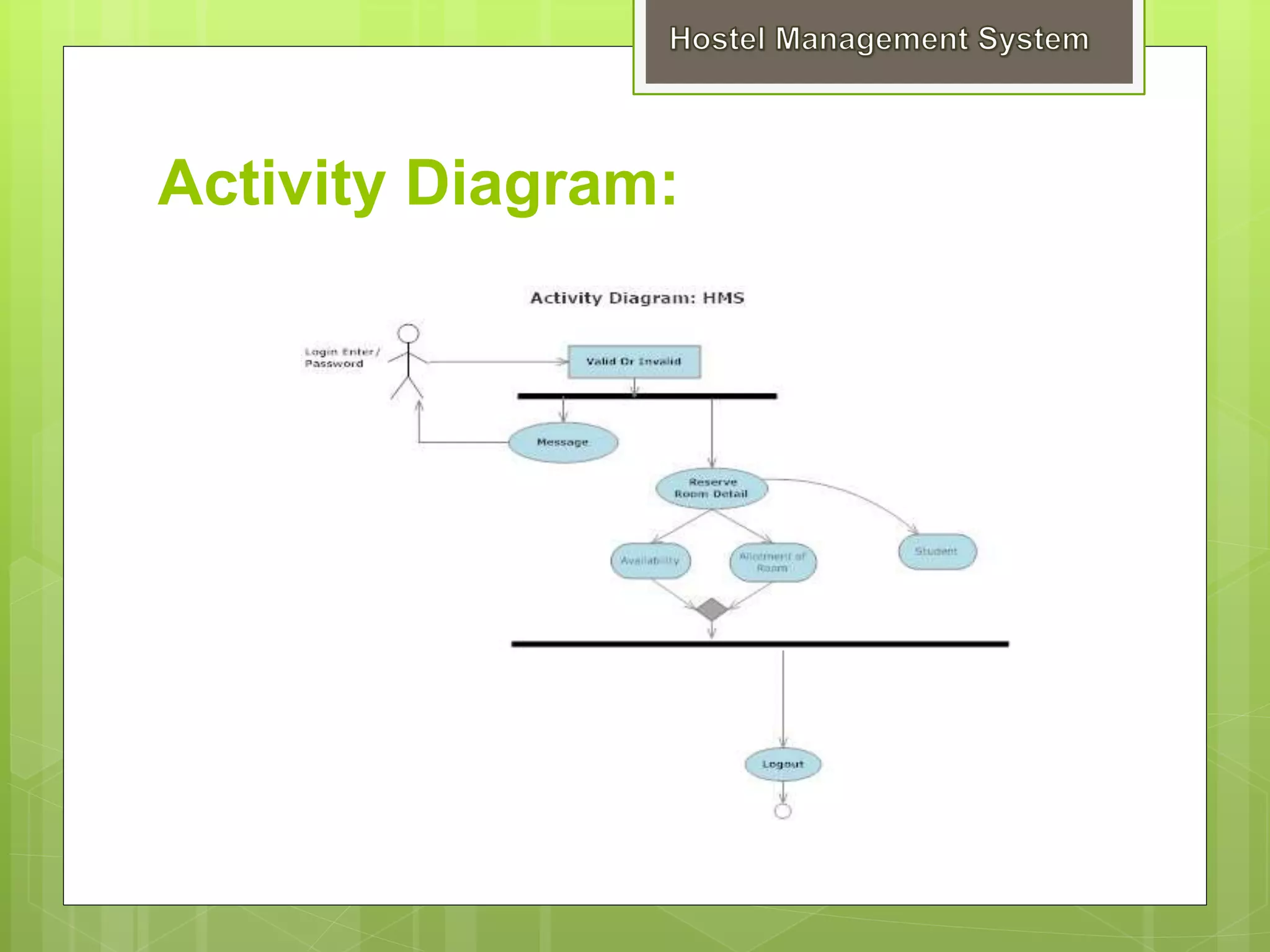
This presentation summarizes a student project on developing a Hostel Management System. It includes sections on introduction, objectives, scope, system requirements, design, and testing. The project uses a waterfall model and involves designing modules for administration, users, hostels, and registration. It outlines functional and non-functional requirements, hardware and software needs, and system architecture including context and flow diagrams. Both white-box and black-box testing strategies are proposed to validate and verify that the software meets requirements.