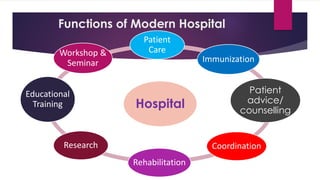
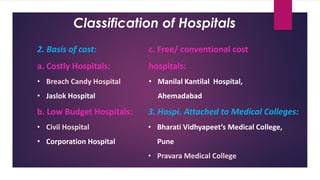
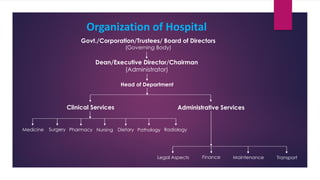
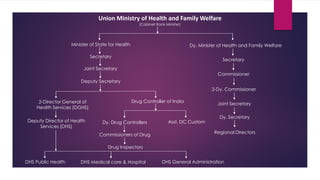
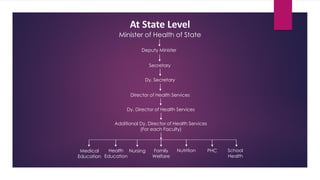
The document provides an overview of hospitals, detailing their definitions, functions, classifications, and organizational structure in the context of the health delivery system in India. It covers various types of hospitals based on clinical aspects, ownership, cost, and size, as well as the roles of medical staff and essential services like nursing, dietary management, and waste disposal. Additionally, it outlines the administrative framework governing hospitals and the involvement of both central and state governments in shaping health policies.